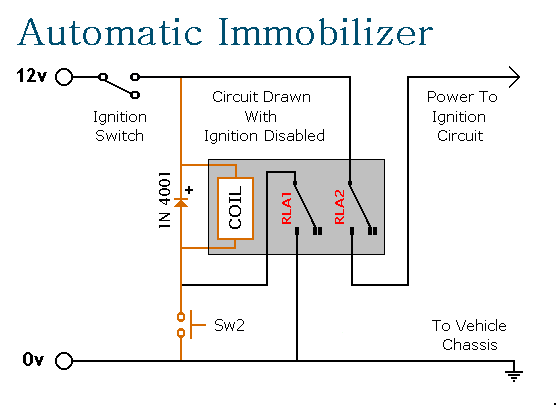
design cdba 018 m cmos
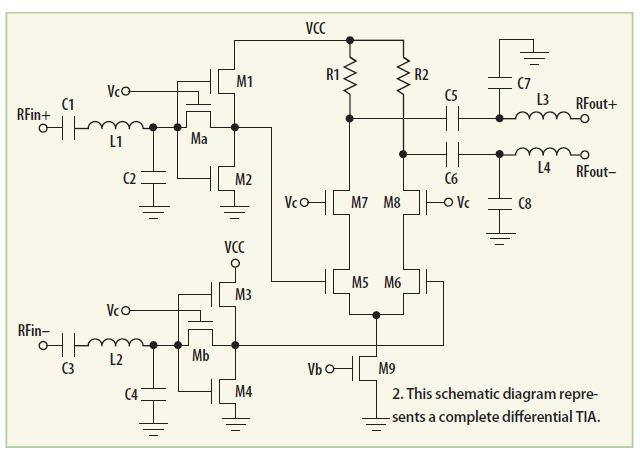
The design of a current difference buffer amplifier (CDBA) circuit for fabrication in a commercial CMOS semiconductor process allows for the versatile application of this component across various uses.
The current difference buffer amplifier (CDBA) is a specialized analog circuit that is capable of providing high input impedance while delivering a low output impedance. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications requiring signal buffering and amplification without significant loading effects on the preceding stages of a circuit. The CDBA operates by taking the difference between two input currents and producing an output voltage that is proportional to this difference.
In a typical implementation, the CDBA consists of multiple transistors configured in a differential pair arrangement, which enhances its performance in terms of linearity and bandwidth. The use of a commercial CMOS process for fabrication allows for the integration of the CDBA with other analog and digital circuitry on a single chip, promoting compact design and reduced manufacturing costs.
The versatility of the CDBA extends to various fields, including instrumentation, sensor interfacing, and communication systems. It can be utilized in applications such as current-to-voltage conversion, signal conditioning, and active filtering. The ability to operate with low power consumption while maintaining high performance makes the CDBA an attractive choice for modern electronic systems.
Furthermore, the design considerations for a CDBA include biasing techniques to ensure optimal operation across a range of input currents, temperature stability, and noise performance. The layout of the circuit must also be carefully managed to minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances, which can adversely affect the performance of high-speed applications.
Overall, the CDBA represents a crucial building block in the development of advanced electronic systems, enabling efficient signal processing and enhancing the functionality of various applications.By designing a current difference buffer amplifier (CDBA) circuit for fabrication in a commercial CMOS semiconductor process, the versatility of this component can be applied in a variety of applications.. 🔗 External reference
The current difference buffer amplifier (CDBA) is a specialized analog circuit that is capable of providing high input impedance while delivering a low output impedance. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications requiring signal buffering and amplification without significant loading effects on the preceding stages of a circuit. The CDBA operates by taking the difference between two input currents and producing an output voltage that is proportional to this difference.
In a typical implementation, the CDBA consists of multiple transistors configured in a differential pair arrangement, which enhances its performance in terms of linearity and bandwidth. The use of a commercial CMOS process for fabrication allows for the integration of the CDBA with other analog and digital circuitry on a single chip, promoting compact design and reduced manufacturing costs.
The versatility of the CDBA extends to various fields, including instrumentation, sensor interfacing, and communication systems. It can be utilized in applications such as current-to-voltage conversion, signal conditioning, and active filtering. The ability to operate with low power consumption while maintaining high performance makes the CDBA an attractive choice for modern electronic systems.
Furthermore, the design considerations for a CDBA include biasing techniques to ensure optimal operation across a range of input currents, temperature stability, and noise performance. The layout of the circuit must also be carefully managed to minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances, which can adversely affect the performance of high-speed applications.
Overall, the CDBA represents a crucial building block in the development of advanced electronic systems, enabling efficient signal processing and enhancing the functionality of various applications.By designing a current difference buffer amplifier (CDBA) circuit for fabrication in a commercial CMOS semiconductor process, the versatility of this component can be applied in a variety of applications.. 🔗 External reference