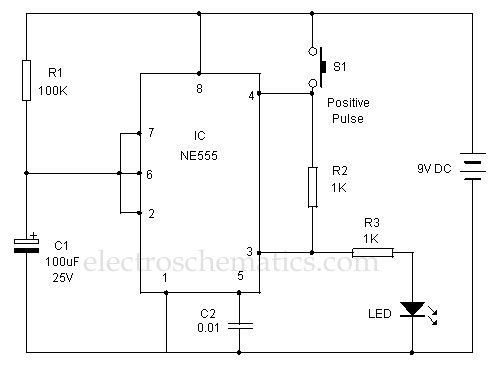
Dual Relay Driver Board Circuit Schematic

This relay driver enhances the input impedance using a standard BC547 NPN transistor (or its equivalent). It is a widely used driver capable of operating various relays, including reed relays. Transistors Q1 and Q2 function as a simple common-emitter amplifier, significantly increasing the effective sensitivity of the 12-volt relay coil by approximately 100 times. In other terms, the current gain for this circuit is 100. This configuration effectively reduces the relay's sensitivity to a few volts. Resistors R3 and R4 limit the input current to Q1 and Q2, ensuring safe operation. Diodes D3 and D4 serve as EMF dampers, filtering out any sparking that occurs when the relay is activated.
The relay driver circuit utilizes a BC547 NPN transistor, which acts as a key component in controlling the relay's operation. The common-emitter configuration of transistors Q1 and Q2 allows for significant amplification of the input signal, which is crucial for driving the relay coil effectively. The 100-fold increase in current gain means that a small input current can activate the relay, making the circuit highly efficient.
Resistors R3 and R4 play an essential role in protecting the transistors from excessive current, which could lead to damage or malfunction. By limiting the input current, these resistors ensure that the transistors operate within their safe limits, enhancing the reliability of the circuit.
Diodes D3 and D4 are critical for managing inductive kickback generated when the relay coil is de-energized. This kickback can produce high-voltage spikes that may damage the transistors or other components in the circuit. The diodes effectively clamp these voltage spikes, allowing for smoother operation and preventing potential damage.
Overall, this relay driver circuit design is a robust solution for controlling various types of relays, providing both efficiency and protection for the components involved. The careful selection of components and their configuration ensures a reliable performance in various applications where relay control is required.This relay driver boosts the input impedance with a regular BC547 NPN transistor (or equivalent). Very common driver. It can drive a variety of relays, including a reed-relay. Transistor Q1and Q2 are a simple common-emitter amplifier that increases the effective sensitivity of the 12 volt relay coil about a 100 times, or in other words, the current gain for this circuit is 100. Using this setup reduces the relay sensitivity to a few volts. R3 and R4 restricts the input current to Q1 and Q2 to a safe limit. Diodes D3 and D4 are EMF dampers and filter off any sparking when the relay 🔗 External reference
The relay driver circuit utilizes a BC547 NPN transistor, which acts as a key component in controlling the relay's operation. The common-emitter configuration of transistors Q1 and Q2 allows for significant amplification of the input signal, which is crucial for driving the relay coil effectively. The 100-fold increase in current gain means that a small input current can activate the relay, making the circuit highly efficient.
Resistors R3 and R4 play an essential role in protecting the transistors from excessive current, which could lead to damage or malfunction. By limiting the input current, these resistors ensure that the transistors operate within their safe limits, enhancing the reliability of the circuit.
Diodes D3 and D4 are critical for managing inductive kickback generated when the relay coil is de-energized. This kickback can produce high-voltage spikes that may damage the transistors or other components in the circuit. The diodes effectively clamp these voltage spikes, allowing for smoother operation and preventing potential damage.
Overall, this relay driver circuit design is a robust solution for controlling various types of relays, providing both efficiency and protection for the components involved. The careful selection of components and their configuration ensures a reliable performance in various applications where relay control is required.This relay driver boosts the input impedance with a regular BC547 NPN transistor (or equivalent). Very common driver. It can drive a variety of relays, including a reed-relay. Transistor Q1and Q2 are a simple common-emitter amplifier that increases the effective sensitivity of the 12 volt relay coil about a 100 times, or in other words, the current gain for this circuit is 100. Using this setup reduces the relay sensitivity to a few volts. R3 and R4 restricts the input current to Q1 and Q2 to a safe limit. Diodes D3 and D4 are EMF dampers and filter off any sparking when the relay 🔗 External reference