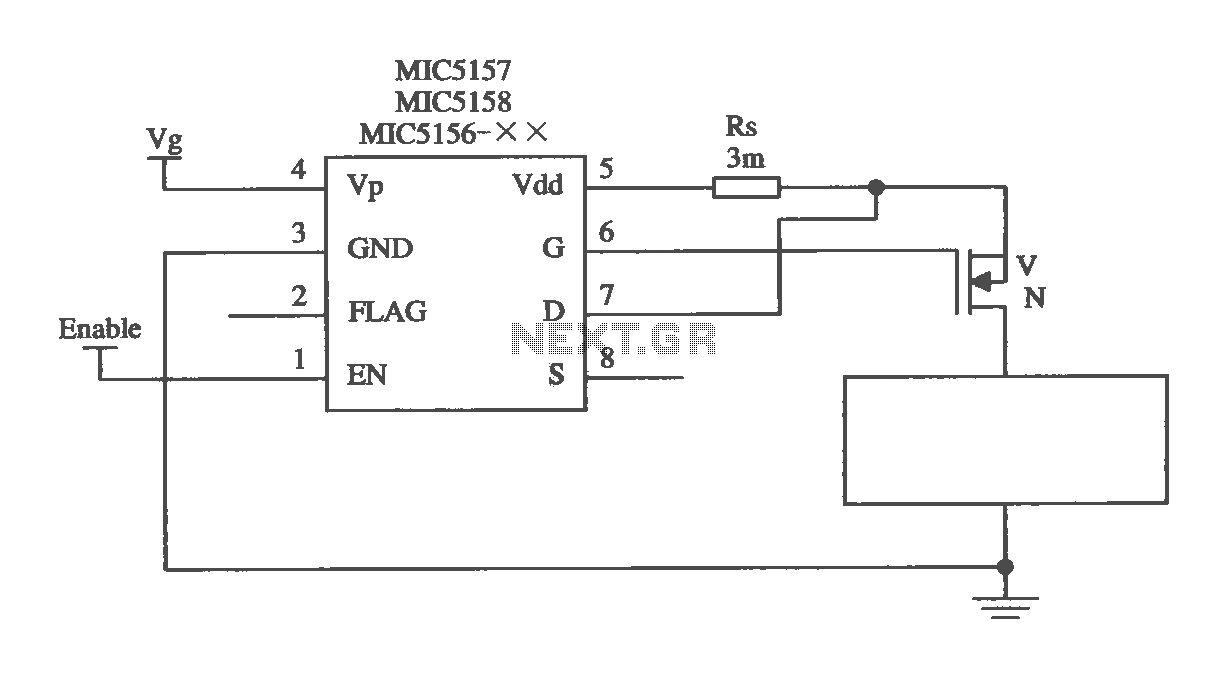
electronic toggle switch no1

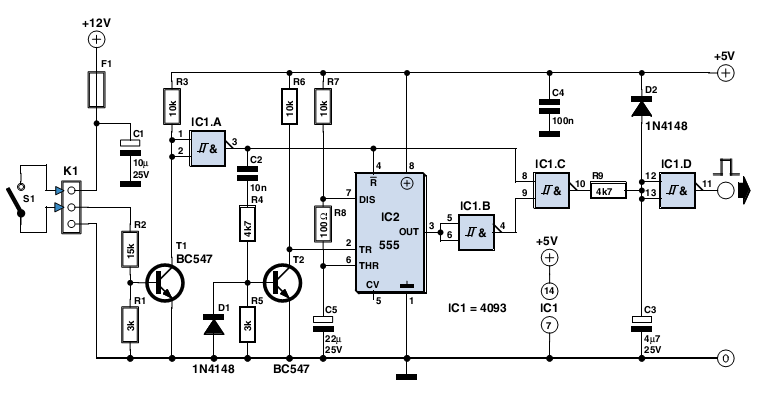
This circuit activates and deactivates a relay with the press of a button. Any momentary push-to-make switch can be utilized. Pressing the button once will activate the relay, while pressing it again will deactivate the relay. The circuit is designed using a single-pole relay, but a multi-pole relay may be employed if needed. Only one half of the CMOS 4013 IC is utilized, allowing for the construction of two independent toggle switches with a single integrated circuit. The circuit operates within a voltage range of 5 to 15 volts; therefore, selecting a relay with a coil voltage compatible with the power supply is essential. An LED is included to provide visual feedback indicating whether the relay is energized, effectively showing the switch's status. The LED and its associated resistor (R3) can be omitted if desired. Caution is advised against using the onboard relay to control mains voltage due to inadequate isolation between relay contacts and low-voltage components. For switching mains voltage, it is recommended to install a suitably rated relay in a safe location away from the board.
This circuit serves as a toggle switch mechanism, where a momentary push-button switch controls the state of a relay. The relay acts as an electromechanical switch that can control higher voltage or current loads, making this design suitable for various applications, such as home automation or industrial control systems.
The circuit utilizes a single half of the CMOS 4013 dual D flip-flop IC, which is key to achieving the toggle functionality. When the button is pressed, it sends a pulse to the flip-flop, changing its output state. The output from the flip-flop is connected to the relay coil, which energizes the relay when the output is high. A second press of the button sends another pulse, reversing the output state and de-energizing the relay.
The LED indicator is connected in parallel with the relay coil, providing a visual cue that the relay is active. The LED will illuminate when the relay is energized, offering a straightforward way to confirm the relay's status without needing to measure voltages or currents directly.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to select components that match the intended operating voltage. The relay must have a coil voltage rating that corresponds to the power supply voltage, which can range from 5V to 15V, allowing flexibility in applications.
It is also important to note the safety precautions regarding the use of the relay. The onboard relay is not suitable for switching mains voltage due to the proximity of low-voltage components, which could lead to dangerous situations. For applications involving higher voltages, an external relay rated for the required voltage should be used, and it should be mounted in a safe location away from the main circuit board to ensure adequate isolation and safety.This simple circuit will energize and de-energize a relay at the push of a button. Any type of momentary action push-to-make switch can be used. Pushing the button once - will energize the relay. And pushing it a second time - will de-energize the relay. I`ve drawn the circuit with a single pole relay. But you can use a multi-pole relay if it suit s your application. Only one half of the Cmos 4013 is used. So you could construct two independent toggle switches with a single IC. The circuit will work at anything from 5 to 15-volts. All you need do is select a relay with a coil voltage that suits your supply. The LED provides a visual indication that the relay is energized. In effect - it tells you whether the switch is on or off. It`s not necessary to the operation of the circuit. If you wish you may leave out R3 and the LED. Do not use the "on-board" relay to switch mains voltage. The board`s layout does not offer sufficient isolation between the relay contacts and the low-voltage components. If you want to switch mains voltage - mount a suitably rated relay somewhere safe - Away From The Board.
🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as a toggle switch mechanism, where a momentary push-button switch controls the state of a relay. The relay acts as an electromechanical switch that can control higher voltage or current loads, making this design suitable for various applications, such as home automation or industrial control systems.
The circuit utilizes a single half of the CMOS 4013 dual D flip-flop IC, which is key to achieving the toggle functionality. When the button is pressed, it sends a pulse to the flip-flop, changing its output state. The output from the flip-flop is connected to the relay coil, which energizes the relay when the output is high. A second press of the button sends another pulse, reversing the output state and de-energizing the relay.
The LED indicator is connected in parallel with the relay coil, providing a visual cue that the relay is active. The LED will illuminate when the relay is energized, offering a straightforward way to confirm the relay's status without needing to measure voltages or currents directly.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to select components that match the intended operating voltage. The relay must have a coil voltage rating that corresponds to the power supply voltage, which can range from 5V to 15V, allowing flexibility in applications.
It is also important to note the safety precautions regarding the use of the relay. The onboard relay is not suitable for switching mains voltage due to the proximity of low-voltage components, which could lead to dangerous situations. For applications involving higher voltages, an external relay rated for the required voltage should be used, and it should be mounted in a safe location away from the main circuit board to ensure adequate isolation and safety.This simple circuit will energize and de-energize a relay at the push of a button. Any type of momentary action push-to-make switch can be used. Pushing the button once - will energize the relay. And pushing it a second time - will de-energize the relay. I`ve drawn the circuit with a single pole relay. But you can use a multi-pole relay if it suit s your application. Only one half of the Cmos 4013 is used. So you could construct two independent toggle switches with a single IC. The circuit will work at anything from 5 to 15-volts. All you need do is select a relay with a coil voltage that suits your supply. The LED provides a visual indication that the relay is energized. In effect - it tells you whether the switch is on or off. It`s not necessary to the operation of the circuit. If you wish you may leave out R3 and the LED. Do not use the "on-board" relay to switch mains voltage. The board`s layout does not offer sufficient isolation between the relay contacts and the low-voltage components. If you want to switch mains voltage - mount a suitably rated relay somewhere safe - Away From The Board.
🔗 External reference