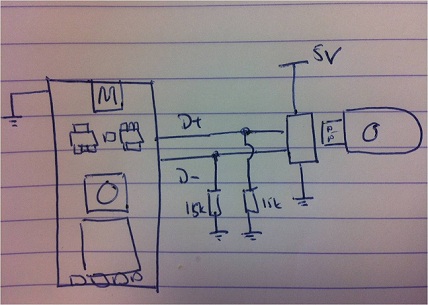
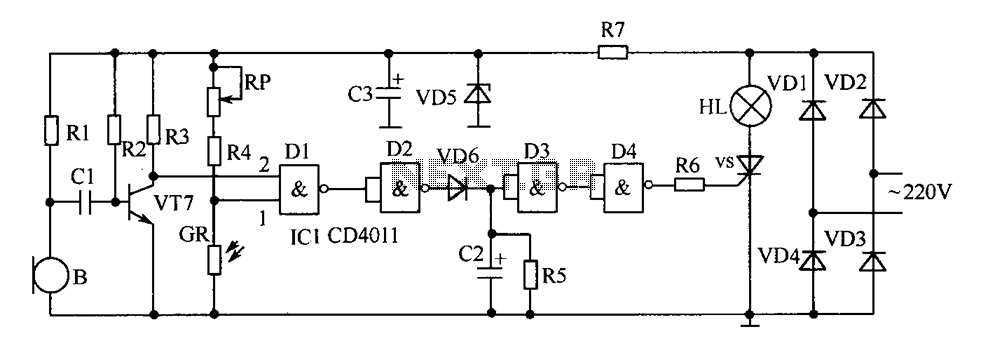
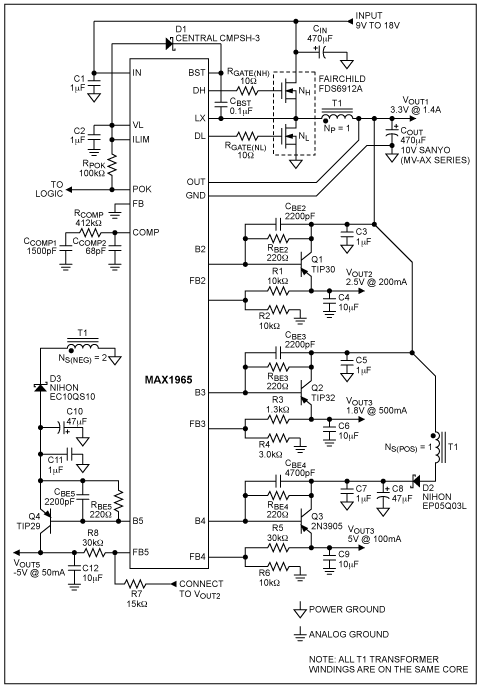
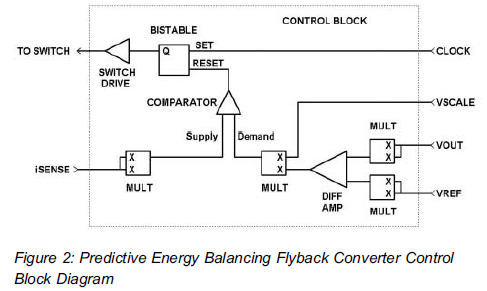
Energy losses in modem
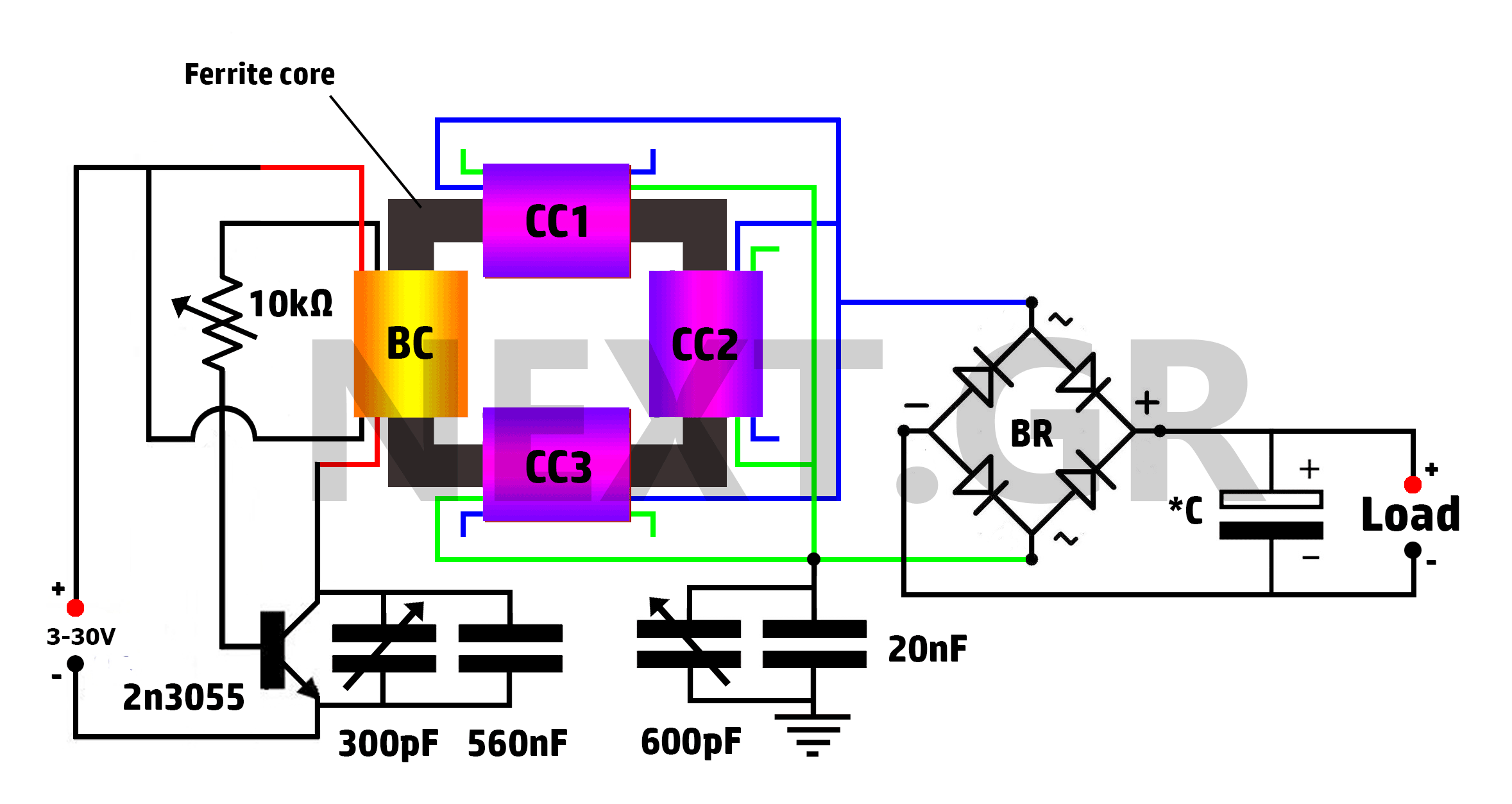
A toroidal transformer (2x12V 15VA) is utilized due to its significantly lower energy losses compared to an E-I core transformer, which was employed in the original mains adapter.
The toroidal transformer is a type of transformer that features a doughnut-shaped core made from a magnetic material, which provides several advantages over traditional E-I core transformers. The design of the toroidal transformer allows for a more efficient magnetic coupling between the primary and secondary windings, which minimizes energy losses during operation. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in applications where energy conservation is paramount.
In this specific configuration, the toroidal transformer has a dual output of 12V, making it suitable for applications requiring a dual polarity power supply. The 15VA rating indicates the maximum apparent power the transformer can handle, which is essential for ensuring that the connected load does not exceed this limit, thereby preventing overheating and potential damage to the transformer.
The winding arrangement in a toroidal transformer is tightly wound around the core, allowing for a more compact design. This compactness not only saves space but also reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to traditional transformers, making it ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Additionally, the circular geometry of the toroidal core helps to contain the magnetic field, further enhancing efficiency and reducing stray fields that could affect nearby components.
Using a toroidal transformer in place of an E-I core transformer can lead to improved performance in terms of thermal management, as the lower losses result in less heat generation. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in environments where heat dissipation is a concern, as it contributes to increased longevity and reliability of the overall circuit.
In summary, the choice of a toroidal transformer (2x12V 15VA) for this application underscores a commitment to efficiency and performance, providing a reliable power source while minimizing energy losses and thermal issues associated with traditional transformer designs.As transformer a toroidal transformer (2x12V 15VA) is used, because this gives much less energy losses then an E-I core transformer as used in the original mains adaptor (for more info, click here ). 🔗 External reference
The toroidal transformer is a type of transformer that features a doughnut-shaped core made from a magnetic material, which provides several advantages over traditional E-I core transformers. The design of the toroidal transformer allows for a more efficient magnetic coupling between the primary and secondary windings, which minimizes energy losses during operation. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in applications where energy conservation is paramount.
In this specific configuration, the toroidal transformer has a dual output of 12V, making it suitable for applications requiring a dual polarity power supply. The 15VA rating indicates the maximum apparent power the transformer can handle, which is essential for ensuring that the connected load does not exceed this limit, thereby preventing overheating and potential damage to the transformer.
The winding arrangement in a toroidal transformer is tightly wound around the core, allowing for a more compact design. This compactness not only saves space but also reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to traditional transformers, making it ideal for sensitive electronic applications. Additionally, the circular geometry of the toroidal core helps to contain the magnetic field, further enhancing efficiency and reducing stray fields that could affect nearby components.
Using a toroidal transformer in place of an E-I core transformer can lead to improved performance in terms of thermal management, as the lower losses result in less heat generation. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in environments where heat dissipation is a concern, as it contributes to increased longevity and reliability of the overall circuit.
In summary, the choice of a toroidal transformer (2x12V 15VA) for this application underscores a commitment to efficiency and performance, providing a reliable power source while minimizing energy losses and thermal issues associated with traditional transformer designs.As transformer a toroidal transformer (2x12V 15VA) is used, because this gives much less energy losses then an E-I core transformer as used in the original mains adaptor (for more info, click here ). 🔗 External reference