Predictive Energy Balancing for Agile Control of Switched-Mode Power Converters
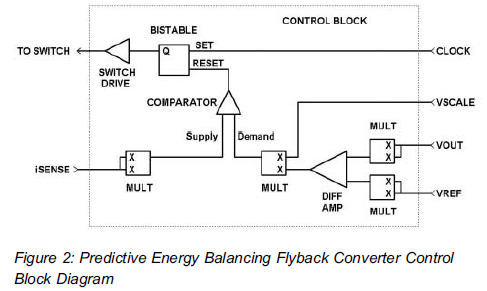
The lack of compensation facilitates the processes of development and testing. The figure of 6 billion frequently appears as the estimated number of cell phones in use globally. Published estimates indicate an average.
The discussion of compensation in electronic circuits often pertains to the adjustments made to ensure that the performance of a system meets specified requirements under varying conditions. In the context of circuit design, the absence of compensation can lead to simpler development and testing phases, as designers may not need to implement additional components or algorithms to correct for performance deviations.
The reference to 6 billion cell phones highlights the extensive scale of mobile communication technology, underscoring the importance of reliable and efficient circuit designs. With such a vast number of devices in operation, it becomes crucial for engineers to develop circuits that can operate under a wide range of conditions without the need for complex compensation mechanisms.
This scenario emphasizes the need for robust design principles that prioritize simplicity and reliability. For example, circuits may be designed with inherent stability through the selection of appropriate components, such as resistors and capacitors, which can mitigate variations in temperature and supply voltage without requiring external compensation.
Furthermore, the trend of increasing mobile device usage suggests a growing demand for efficient power management solutions within these circuits. Engineers may focus on optimizing power consumption while maintaining performance, which can be achieved through techniques such as dynamic voltage scaling or the use of low-power components.
In summary, the absence of compensation can streamline the design process, particularly in the context of the rapidly expanding mobile phone market, where efficiency, reliability, and simplicity are paramount.The absence of compensation simplifies development and testing. The number 6 billion turns up often as the number of cell phones in use worldwide. Published estimates average.. 🔗 External reference
The discussion of compensation in electronic circuits often pertains to the adjustments made to ensure that the performance of a system meets specified requirements under varying conditions. In the context of circuit design, the absence of compensation can lead to simpler development and testing phases, as designers may not need to implement additional components or algorithms to correct for performance deviations.
The reference to 6 billion cell phones highlights the extensive scale of mobile communication technology, underscoring the importance of reliable and efficient circuit designs. With such a vast number of devices in operation, it becomes crucial for engineers to develop circuits that can operate under a wide range of conditions without the need for complex compensation mechanisms.
This scenario emphasizes the need for robust design principles that prioritize simplicity and reliability. For example, circuits may be designed with inherent stability through the selection of appropriate components, such as resistors and capacitors, which can mitigate variations in temperature and supply voltage without requiring external compensation.
Furthermore, the trend of increasing mobile device usage suggests a growing demand for efficient power management solutions within these circuits. Engineers may focus on optimizing power consumption while maintaining performance, which can be achieved through techniques such as dynamic voltage scaling or the use of low-power components.
In summary, the absence of compensation can streamline the design process, particularly in the context of the rapidly expanding mobile phone market, where efficiency, reliability, and simplicity are paramount.The absence of compensation simplifies development and testing. The number 6 billion turns up often as the number of cell phones in use worldwide. Published estimates average.. 🔗 External reference