Fire Alarm Using Thermistor
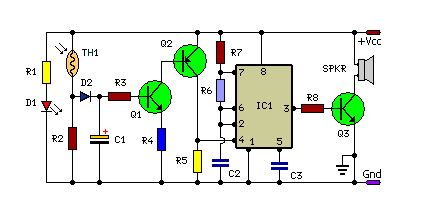
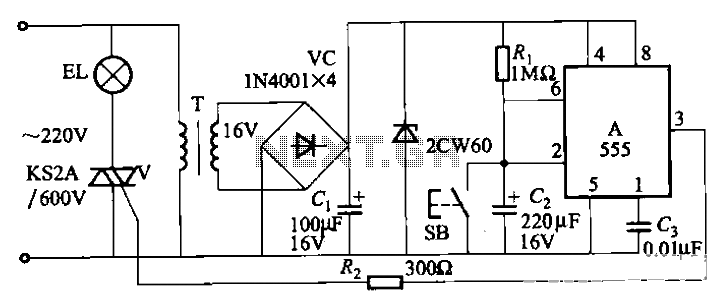
This is a small and simple unit that can be utilized for home security purposes. In this fire alarm circuit, a thermistor functions as the heat sensor. When the temperature increases...
The fire alarm circuit described utilizes a thermistor, a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes, making it an effective heat sensor for detecting fires. The circuit typically consists of a thermistor connected to a comparator or microcontroller that monitors the resistance changes. As the temperature rises due to a fire, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, resulting in a voltage change that can be detected by the comparator.
In a typical configuration, the thermistor is positioned within the environment to be monitored, often in a location where heat accumulation is likely to occur. The comparator is set to a predefined threshold voltage that corresponds to a specific temperature. When the thermistor detects a temperature above this threshold, it triggers an alarm system, which may include an audible alarm, visual indicators, or notifications to a central security system.
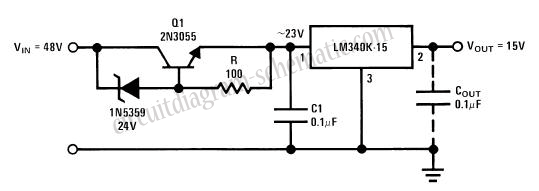
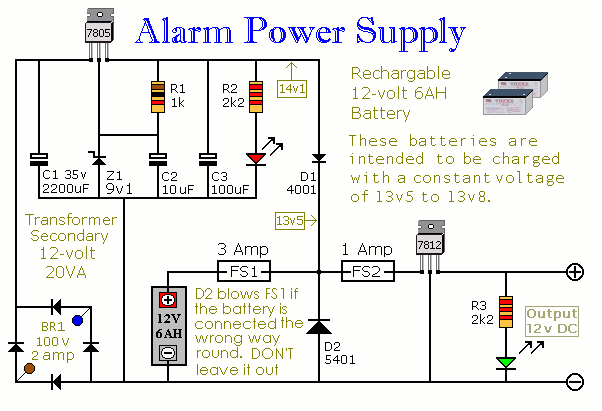
Power supply considerations are crucial for this circuit. It is common to use a low-voltage DC power source, which can be provided by batteries or a transformer. To enhance the reliability of the alarm system, additional components such as capacitors may be included to filter noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
For optimal performance, the circuit may also incorporate features such as a reset mechanism, allowing the user to silence the alarm after verification of a false alarm, and an indicator LED that provides a visual confirmation of the alarm status. The overall design should ensure minimal power consumption while maintaining sensitivity to temperature changes, making it suitable for continuous operation in a home security environment.Small and simple unit, Can be used for Home-Security purpose In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases.. 🔗 External reference
The fire alarm circuit described utilizes a thermistor, a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes, making it an effective heat sensor for detecting fires. The circuit typically consists of a thermistor connected to a comparator or microcontroller that monitors the resistance changes. As the temperature rises due to a fire, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, resulting in a voltage change that can be detected by the comparator.
In a typical configuration, the thermistor is positioned within the environment to be monitored, often in a location where heat accumulation is likely to occur. The comparator is set to a predefined threshold voltage that corresponds to a specific temperature. When the thermistor detects a temperature above this threshold, it triggers an alarm system, which may include an audible alarm, visual indicators, or notifications to a central security system.
Power supply considerations are crucial for this circuit. It is common to use a low-voltage DC power source, which can be provided by batteries or a transformer. To enhance the reliability of the alarm system, additional components such as capacitors may be included to filter noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
For optimal performance, the circuit may also incorporate features such as a reset mechanism, allowing the user to silence the alarm after verification of a false alarm, and an indicator LED that provides a visual confirmation of the alarm status. The overall design should ensure minimal power consumption while maintaining sensitivity to temperature changes, making it suitable for continuous operation in a home security environment.Small and simple unit, Can be used for Home-Security purpose In this fire alarm circuit, a Thermistor works as the heat sensor. When temperature increases.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713