
Fuzz-box
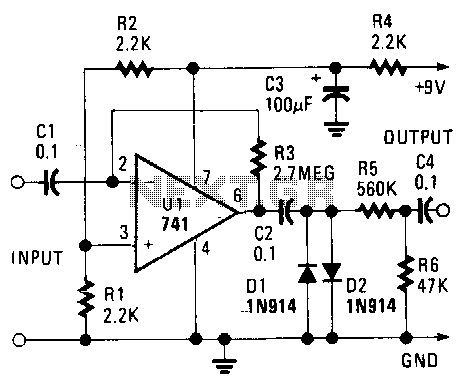
The maximum gain of the 741 operational amplifier, which is typically 20,000, can be increased to nearly 3 million dB, resulting in output distortion. This distortion produces a fuzz sound. Additionally, the signal level is reduced by clipping through the use of two diodes.
The 741 operational amplifier is a widely used device in analog electronics, known for its versatility and ease of use. When configured for high gain applications, the 741 can achieve a maximum gain of approximately 20,000. However, in certain configurations, this gain can be manipulated to reach levels close to 3 million dB, leading to significant distortion in the output signal. This distortion is a key characteristic that can be exploited in audio applications to produce a "fuzz" effect, commonly desired in electric guitar circuits.
To achieve this fuzz sound, the circuit typically incorporates two diodes that are placed in a feedback loop or in parallel with the output. The role of these diodes is to clip the output waveform, effectively limiting the amplitude of the signal. When the signal exceeds a certain threshold, the diodes become forward-biased and conduct, thereby "clipping" the peaks of the waveform. This clipping action introduces harmonic distortion, which contributes to the rich, saturated sound associated with fuzz effects.
In practical applications, the arrangement of the 741 op-amp and the clipping diodes can be adjusted to tailor the characteristics of the fuzz sound. The choice of diode type, as well as their placement within the circuit, can influence the tonal quality and response of the effect. For example, silicon diodes may produce a sharper clipping effect compared to germanium diodes, which tend to yield a warmer sound.
Overall, the combination of the 741 operational amplifier's high gain and the intentional distortion introduced by diode clipping makes this configuration a popular choice for achieving unique audio effects in various electronic music applications.The 741"s maximum gain of 20,000 is pushed to nearly 3 million dB, and therefore distorts the output. That distortion provides the fuzz sound. The level is dropped by clipping the two diodes. 🔗 External reference
The 741 operational amplifier is a widely used device in analog electronics, known for its versatility and ease of use. When configured for high gain applications, the 741 can achieve a maximum gain of approximately 20,000. However, in certain configurations, this gain can be manipulated to reach levels close to 3 million dB, leading to significant distortion in the output signal. This distortion is a key characteristic that can be exploited in audio applications to produce a "fuzz" effect, commonly desired in electric guitar circuits.
To achieve this fuzz sound, the circuit typically incorporates two diodes that are placed in a feedback loop or in parallel with the output. The role of these diodes is to clip the output waveform, effectively limiting the amplitude of the signal. When the signal exceeds a certain threshold, the diodes become forward-biased and conduct, thereby "clipping" the peaks of the waveform. This clipping action introduces harmonic distortion, which contributes to the rich, saturated sound associated with fuzz effects.
In practical applications, the arrangement of the 741 op-amp and the clipping diodes can be adjusted to tailor the characteristics of the fuzz sound. The choice of diode type, as well as their placement within the circuit, can influence the tonal quality and response of the effect. For example, silicon diodes may produce a sharper clipping effect compared to germanium diodes, which tend to yield a warmer sound.
Overall, the combination of the 741 operational amplifier's high gain and the intentional distortion introduced by diode clipping makes this configuration a popular choice for achieving unique audio effects in various electronic music applications.The 741"s maximum gain of 20,000 is pushed to nearly 3 million dB, and therefore distorts the output. That distortion provides the fuzz sound. The level is dropped by clipping the two diodes. 🔗 External reference
