H Bridge Qik 2s12v10 Dual Serial
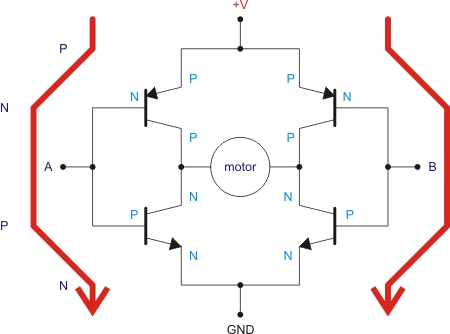
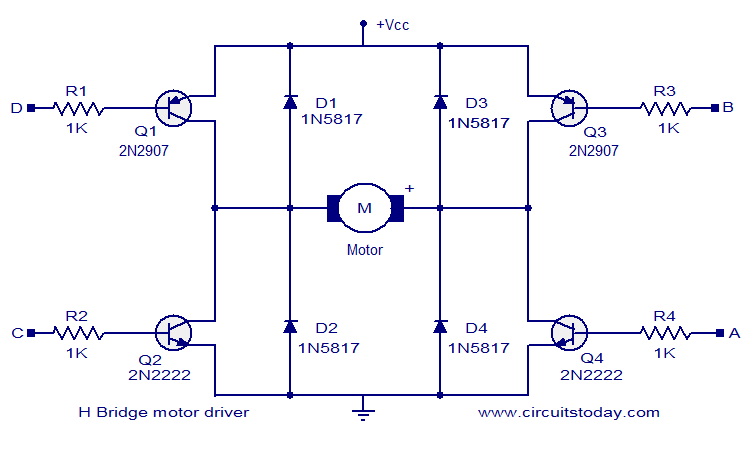
This H-bridge is currently being used for a Sumo-bot and is considered suitable for medium-sized motors, handling up to 30A peak and 13A in continuous mode. The cost is approximately $75 plus shipping. An H-bridge serves as an intermediary control phase between a microprocessor and motors, allowing the conversion of low-intensity microprocessor signals into power signals necessary for motor operation. A microprocessor typically outputs around 50 mA per pin, while robotic motors can draw between 150 mA to 5A at peak, with powerful motors potentially draining 5A during stall conditions. The basic circuit consists of four transistors, which can be either MOSFETs or BJTs. The term "H-bridge" derives from the configuration of the basic schematic diagram. The Pololu Qik 2s12v10 Dual Serial Motor Controller is managed via a Serial Port, often using PWM outputs. This type of H-bridge allows for the monitoring, control, and limitation of various parameters such as acceleration, current limits, errors, and data feedback. A single cable, including a ground connection, can control both speed and direction. All square pins are ground (GND), and it is essential to connect the power source or battery on the right side (power side) rather than the low-intensity side (left side). To set the Serial speed, jumpers 1 and 2 must be shorted, which will configure the device to operate at 9600 bps. For auto-detect mode, a calibration command "0x00" should be sent via Serial. For other speeds, refer to the user guide's baud rate table. Connecting an Arduino board is straightforward; the Tx (transmitter) from the Arduino should connect to the Rx (receiver) of the H-bridge and vice versa. Data can be received from the H-bridge, including configuration settings, diagnostics, errors, currents, and speeds.
The H-bridge circuit design is critical for applications requiring precise motor control in robotics, particularly in competitive environments like Sumo-bots. The integration of MOSFETs or BJTs in the H-bridge allows for efficient switching and control of motor direction and speed. In this configuration, the four transistors are arranged in an H-shape, enabling bidirectional control of the motor. When the appropriate transistors are activated, current flows through the motor in one direction, while activating the opposite pair reverses the current, allowing for reverse motion.
The Pololu Qik 2s12v10 controller is particularly advantageous due to its dual motor control capability, enabling the simultaneous operation of two motors. The use of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for speed control allows for fine-tuning of motor performance, which is essential in competitive robotics where precision is paramount. The ability to set limits on current draw protects the motors and the H-bridge from damage due to excessive load conditions.
The serial communication interface simplifies integration with microcontrollers such as Arduino, providing a user-friendly method for sending commands and receiving feedback. This feedback loop is crucial for monitoring the operational status of the motors, allowing for real-time adjustments based on performance metrics such as current draw and speed. The calibration command facilitates automatic detection of the optimal settings, enhancing the adaptability of the system in various operational scenarios.
Overall, the H-bridge circuit, particularly when implemented with controllers like the Pololu Qik 2s12v10, represents a robust solution for driving motors in robotic applications, balancing performance, control, and safety.This H-bridge i`m using now for my Sumo-bot ( This H-bridge )I think is fairly good for medium size motors ( untill 30A peak and 13 A continuous mode). The price is arround $75 plus sending. We start talking about what is a "H-bridge". One H-bridge is a intermediate control phase between microprocessor and motors. With this element you can co nvert the low intensity microprocessor signals into power signal to feed and manage the motors. One microprocessor can only take out arround 50 mA in each out-pin and one robotic motor can consume form 150 mA to 2 or 5 peak Ampers. In this case, our powerful motors could drain 5A in stall. The basic circuit is make up with four transistors, MOSFET or BJT. The name of "h-Bridge come from the shape of the basic schematic diagram. See the picture below. Thispololu Qik 2s12v10 Dual Serial Motor Controller is controlled by a Serial Port. Usually this kind of electronic boards are managed by PWM outputs. With this type of H-Bridge we can check, control and limite more variables like acceleration, current limitation, erros and data feedback.
With one single cable ( with also ground conection of course) we can also control speed and direction. All the square pins are ground (GND) and you can not feed the board from the low intensity side (left, battery output).
You must connect the source or battery on the right side. ( power side) To setup the Serial speed, you must short the 1 and 2 jumpers (like shown below), and we will work with 9600 bps. If we want use auto-detect mode, we shold send a calibration command "0x00" via Serial. For other speed you can read user guide `s baud rate table. Connecting Arduino board is quite easy, just connect Tx (transmiter) from Arduino to Rx (receptor) from H-Bridge and vice versa.
We can recive data from the H-bridge like configurations, diagnosis, erros, currents, speeds. 🔗 External reference
The H-bridge circuit design is critical for applications requiring precise motor control in robotics, particularly in competitive environments like Sumo-bots. The integration of MOSFETs or BJTs in the H-bridge allows for efficient switching and control of motor direction and speed. In this configuration, the four transistors are arranged in an H-shape, enabling bidirectional control of the motor. When the appropriate transistors are activated, current flows through the motor in one direction, while activating the opposite pair reverses the current, allowing for reverse motion.
The Pololu Qik 2s12v10 controller is particularly advantageous due to its dual motor control capability, enabling the simultaneous operation of two motors. The use of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for speed control allows for fine-tuning of motor performance, which is essential in competitive robotics where precision is paramount. The ability to set limits on current draw protects the motors and the H-bridge from damage due to excessive load conditions.
The serial communication interface simplifies integration with microcontrollers such as Arduino, providing a user-friendly method for sending commands and receiving feedback. This feedback loop is crucial for monitoring the operational status of the motors, allowing for real-time adjustments based on performance metrics such as current draw and speed. The calibration command facilitates automatic detection of the optimal settings, enhancing the adaptability of the system in various operational scenarios.
Overall, the H-bridge circuit, particularly when implemented with controllers like the Pololu Qik 2s12v10, represents a robust solution for driving motors in robotic applications, balancing performance, control, and safety.This H-bridge i`m using now for my Sumo-bot ( This H-bridge )I think is fairly good for medium size motors ( untill 30A peak and 13 A continuous mode). The price is arround $75 plus sending. We start talking about what is a "H-bridge". One H-bridge is a intermediate control phase between microprocessor and motors. With this element you can co nvert the low intensity microprocessor signals into power signal to feed and manage the motors. One microprocessor can only take out arround 50 mA in each out-pin and one robotic motor can consume form 150 mA to 2 or 5 peak Ampers. In this case, our powerful motors could drain 5A in stall. The basic circuit is make up with four transistors, MOSFET or BJT. The name of "h-Bridge come from the shape of the basic schematic diagram. See the picture below. Thispololu Qik 2s12v10 Dual Serial Motor Controller is controlled by a Serial Port. Usually this kind of electronic boards are managed by PWM outputs. With this type of H-Bridge we can check, control and limite more variables like acceleration, current limitation, erros and data feedback.
With one single cable ( with also ground conection of course) we can also control speed and direction. All the square pins are ground (GND) and you can not feed the board from the low intensity side (left, battery output).
You must connect the source or battery on the right side. ( power side) To setup the Serial speed, you must short the 1 and 2 jumpers (like shown below), and we will work with 9600 bps. If we want use auto-detect mode, we shold send a calibration command "0x00" via Serial. For other speed you can read user guide `s baud rate table. Connecting Arduino board is quite easy, just connect Tx (transmiter) from Arduino to Rx (receptor) from H-Bridge and vice versa.
We can recive data from the H-bridge like configurations, diagnosis, erros, currents, speeds. 🔗 External reference