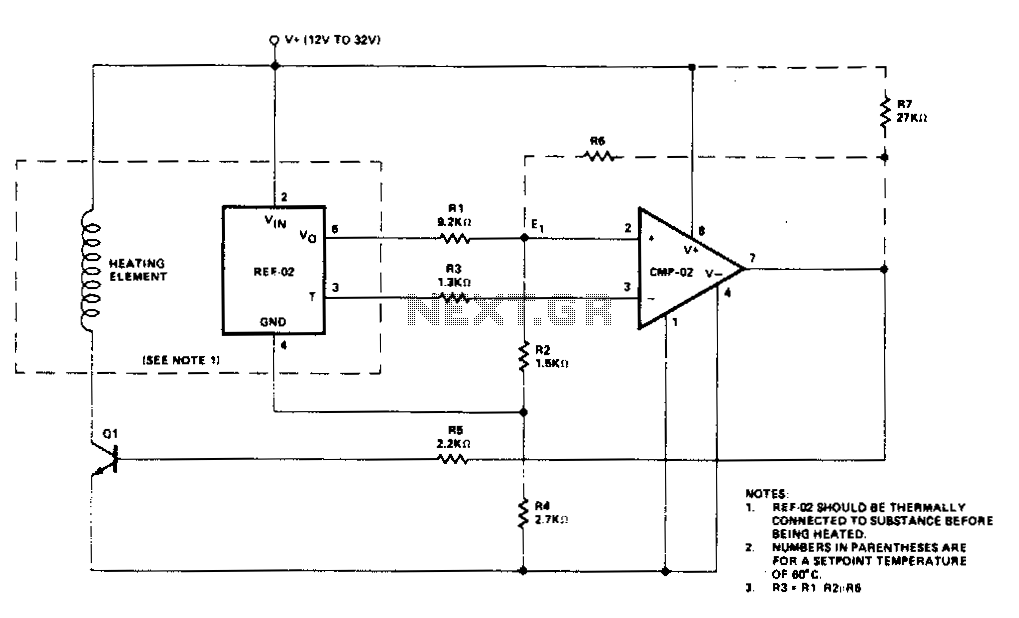
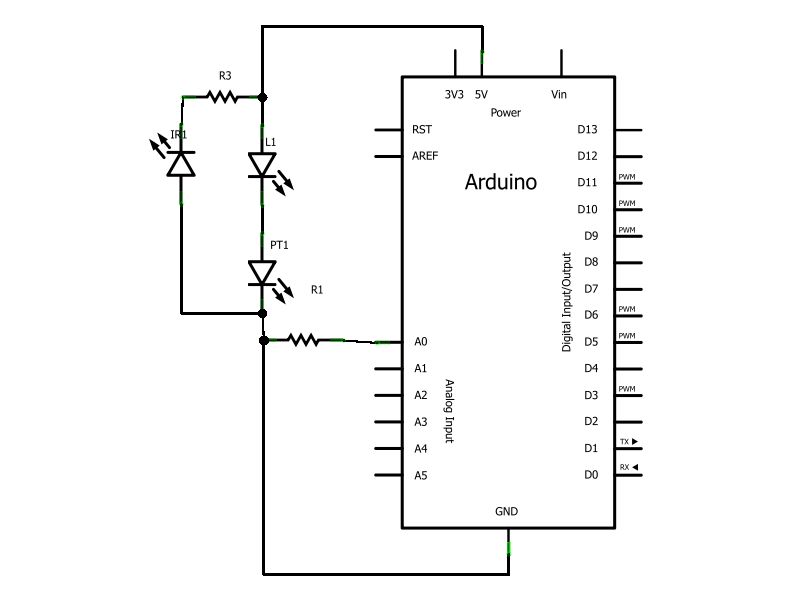
Hi-lo temperature sensor
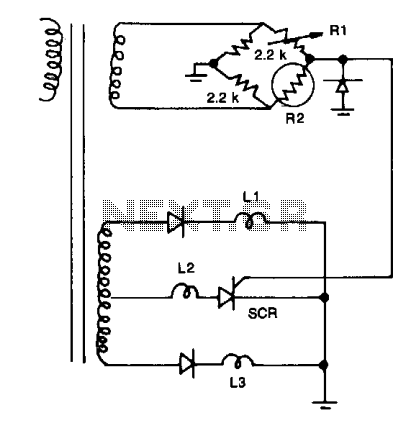
Resistors R1, R2, and the two 2.2 kΩ resistors form a bridge circuit. R2 is a thermistor, and R1 sets the temperature at which L2 lights. Lower or higher temperatures light L1 or L3 to indicate an over- or under-temperature condition.
The described circuit utilizes a bridge configuration comprising resistors R1, R2, and two additional 2.2 kΩ resistors. In this setup, R2 functions as a thermistor, which is a temperature-dependent resistor. The resistance of R2 varies with temperature, allowing it to serve as a sensing element in the circuit. R1 is configured to establish a reference temperature threshold, which dictates when indicator LED L2 will illuminate.
The bridge circuit operates on the principle of balancing the resistances. When the temperature sensed by the thermistor R2 deviates from the set point defined by R1, the balance of the bridge is disturbed. This imbalance results in a voltage change at the output of the bridge circuit, triggering the appropriate response from the indicator LEDs. Specifically, if the temperature exceeds the designated threshold, LED L1 will light up, signaling an over-temperature condition. Conversely, if the temperature falls below the threshold, LED L3 will illuminate, indicating an under-temperature condition.
The use of a thermistor in this application is critical due to its sensitivity to temperature changes, allowing for precise monitoring and indication of temperature variations. The two 2.2 kΩ resistors are likely employed to complete the bridge and ensure that the circuit remains stable across a range of operating conditions. The overall design is effective for applications requiring temperature monitoring and alerting, providing visual cues for temperature management.Resistors Rl, R2, and the two 2.2 k resistors form a bridge circuit. R2 is a thermistor, and Rl sets the temperature at which L2 lights. Lower or higher temperatures light LI or L3 to indicate an over- or under-temperature condition. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a bridge configuration comprising resistors R1, R2, and two additional 2.2 kΩ resistors. In this setup, R2 functions as a thermistor, which is a temperature-dependent resistor. The resistance of R2 varies with temperature, allowing it to serve as a sensing element in the circuit. R1 is configured to establish a reference temperature threshold, which dictates when indicator LED L2 will illuminate.
The bridge circuit operates on the principle of balancing the resistances. When the temperature sensed by the thermistor R2 deviates from the set point defined by R1, the balance of the bridge is disturbed. This imbalance results in a voltage change at the output of the bridge circuit, triggering the appropriate response from the indicator LEDs. Specifically, if the temperature exceeds the designated threshold, LED L1 will light up, signaling an over-temperature condition. Conversely, if the temperature falls below the threshold, LED L3 will illuminate, indicating an under-temperature condition.
The use of a thermistor in this application is critical due to its sensitivity to temperature changes, allowing for precise monitoring and indication of temperature variations. The two 2.2 kΩ resistors are likely employed to complete the bridge and ensure that the circuit remains stable across a range of operating conditions. The overall design is effective for applications requiring temperature monitoring and alerting, providing visual cues for temperature management.Resistors Rl, R2, and the two 2.2 k resistors form a bridge circuit. R2 is a thermistor, and Rl sets the temperature at which L2 lights. Lower or higher temperatures light LI or L3 to indicate an over- or under-temperature condition. 🔗 External reference