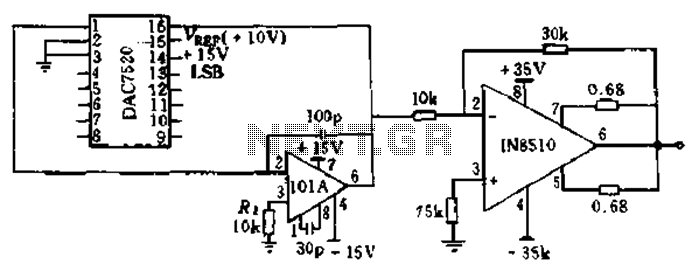
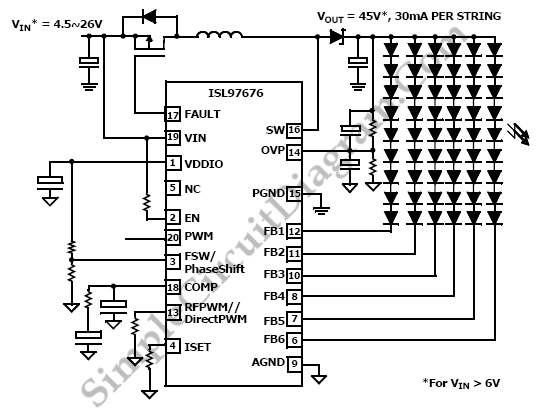
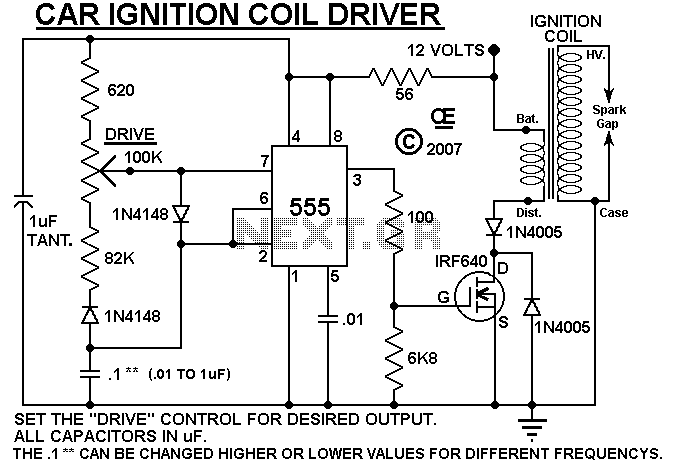
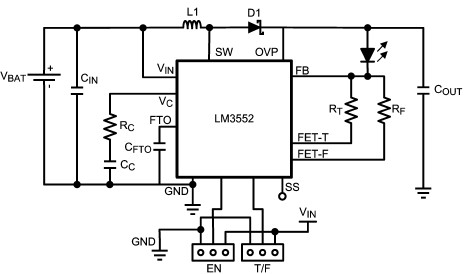
High-speed laser diode driver
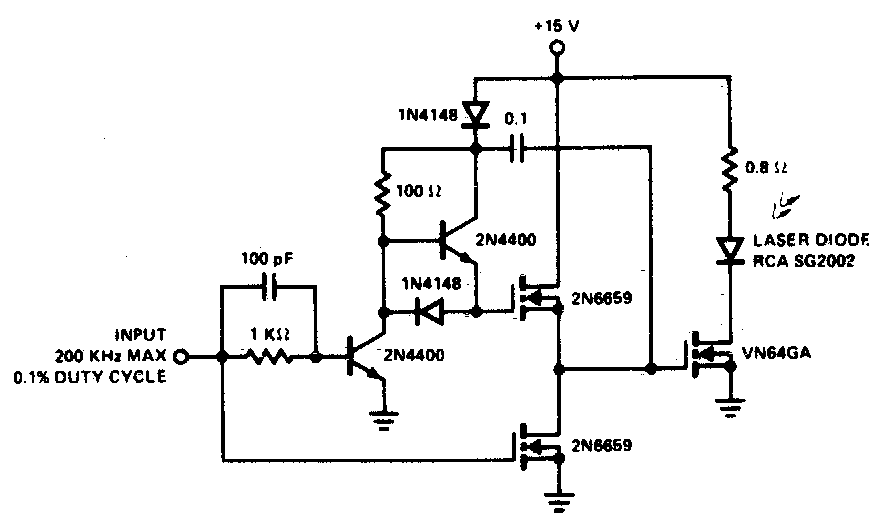
A faster driver can supply a higher peak gate current to switch the VN64GA very quickly. The circuit uses a VMOS totem pole stage to drive the high power switch.
The described circuit employs a VMOS (Vertical Metal Oxide Semiconductor) totem pole configuration, which is essential for driving high-power switches such as the VN64GA efficiently. The primary function of the faster driver is to provide a significant peak gate current, which enables rapid switching of the MOSFET. This is crucial in applications where swift on-off transitions are necessary to minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency.
In the totem pole arrangement, two VMOS transistors are configured in a complementary fashion. One transistor is responsible for pulling the gate voltage high (turning the switch on), while the other pulls it low (turning the switch off). This configuration not only allows for a quick response time but also ensures that the gate capacitance of the VN64GA is charged and discharged effectively, leading to reduced switching times.
The peak gate current supplied by the driver is a critical parameter, as it must be sufficiently high to overcome the gate charge of the VN64GA. The driver circuit typically includes a dedicated power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current levels. It may also incorporate additional components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the switching characteristics and enhance stability.
Overall, the use of a VMOS totem pole stage in conjunction with a fast driver significantly enhances the performance of high-power switching applications, ensuring rapid and efficient operation of the VN64GA MOSFET. This design approach is particularly beneficial in power electronics where efficiency and speed are paramount.A faster driver can supply higher peak gate current to switch the VN64GA very quicklyThe circuit uses a VMOS totempole stage to drive the high power switch 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a VMOS (Vertical Metal Oxide Semiconductor) totem pole configuration, which is essential for driving high-power switches such as the VN64GA efficiently. The primary function of the faster driver is to provide a significant peak gate current, which enables rapid switching of the MOSFET. This is crucial in applications where swift on-off transitions are necessary to minimize power loss and improve overall efficiency.
In the totem pole arrangement, two VMOS transistors are configured in a complementary fashion. One transistor is responsible for pulling the gate voltage high (turning the switch on), while the other pulls it low (turning the switch off). This configuration not only allows for a quick response time but also ensures that the gate capacitance of the VN64GA is charged and discharged effectively, leading to reduced switching times.
The peak gate current supplied by the driver is a critical parameter, as it must be sufficiently high to overcome the gate charge of the VN64GA. The driver circuit typically includes a dedicated power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current levels. It may also incorporate additional components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the switching characteristics and enhance stability.
Overall, the use of a VMOS totem pole stage in conjunction with a fast driver significantly enhances the performance of high-power switching applications, ensuring rapid and efficient operation of the VN64GA MOSFET. This design approach is particularly beneficial in power electronics where efficiency and speed are paramount.A faster driver can supply higher peak gate current to switch the VN64GA very quicklyThe circuit uses a VMOS totempole stage to drive the high power switch 🔗 External reference