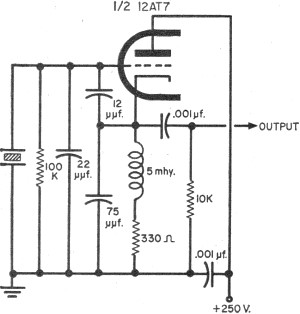
Ignition Coil Buzz Box circuit
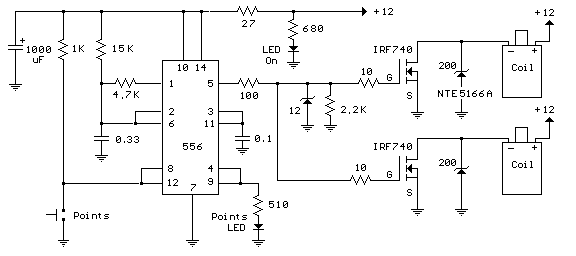
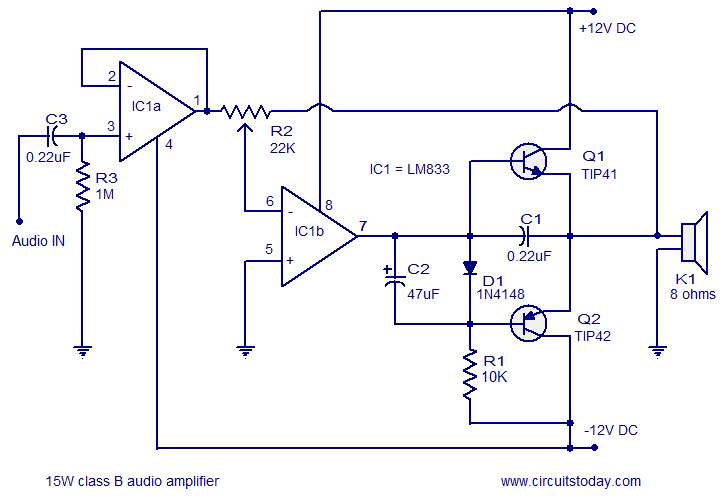
This circuit creates a buzz coil using a standard automotive ignition coil. A 556 dual timer is employed to establish the frequency and duty cycle of the coil current. One timer functions as an oscillator to generate the 200 Hz rectangular waveform required to control the IRF740 MOSFET, while the second timer switches the oscillator on and off as the breaker points open and close (closed = on). The outcome is a consistent stream of sparks from the ignition coil, spaced approximately 5 milliseconds apart while the breaker points are closed.
The buzz coil circuit utilizes a standard automotive ignition coil, which is designed to transform low voltage from the vehicle's battery into a high-voltage spark necessary for igniting fuel in an engine. The core component of this circuit is the 556 dual timer, which consists of two independent timers that can be configured in various modes, including astable and monostable operations.
In this application, one of the timers is configured in astable mode to generate a continuous 200 Hz rectangular waveform. This waveform serves as the control signal for the gate of the IRF740 MOSFET, a power MOSFET capable of handling high voltages and currents. The IRF740 acts as a switch, allowing the current from the ignition coil to be rapidly turned on and off in synchronization with the generated waveform.
The second timer is configured to operate in monostable mode, where it responds to the state changes of the breaker points. When the breaker points close, the timer triggers the oscillator, allowing the MOSFET to conduct and energize the ignition coil. Conversely, when the breaker points open, the timer deactivates the oscillator, cutting off the current flow to the coil. This switching action results in the production of a series of high-voltage sparks emitted from the ignition coil, with a consistent interval of approximately 5 milliseconds between each spark while the breaker points remain closed.
The design of this circuit is particularly effective for applications requiring a high-frequency spark generation, such as in ignition systems or for creating a buzz coil effect in various electronic projects. Proper attention should be paid to the component ratings, ensuring they can handle the voltages and currents involved, particularly the MOSFET and the ignition coil, to prevent damage during operation. Additionally, adequate heat dissipation measures should be implemented for the MOSFET to maintain reliable performance during extended use.Here`s a circuit to create a buzzcoil using a standard automotive ignition coil. A 556 dual timer is used to establish the frequency and duty cycle of the coil current. One of the timers is used as an oscillator to generate the 200 Hz rectangular waveform needed to control the (IRF740 MOSFET) while the second timer switches the oscillator on and off as the breaker points open and close (closed = on). The result is a steady stream of sparks from the ignition coil spaced about 5 milliseconds apart while the breaker points are closed..
🔗 External reference
The buzz coil circuit utilizes a standard automotive ignition coil, which is designed to transform low voltage from the vehicle's battery into a high-voltage spark necessary for igniting fuel in an engine. The core component of this circuit is the 556 dual timer, which consists of two independent timers that can be configured in various modes, including astable and monostable operations.
In this application, one of the timers is configured in astable mode to generate a continuous 200 Hz rectangular waveform. This waveform serves as the control signal for the gate of the IRF740 MOSFET, a power MOSFET capable of handling high voltages and currents. The IRF740 acts as a switch, allowing the current from the ignition coil to be rapidly turned on and off in synchronization with the generated waveform.
The second timer is configured to operate in monostable mode, where it responds to the state changes of the breaker points. When the breaker points close, the timer triggers the oscillator, allowing the MOSFET to conduct and energize the ignition coil. Conversely, when the breaker points open, the timer deactivates the oscillator, cutting off the current flow to the coil. This switching action results in the production of a series of high-voltage sparks emitted from the ignition coil, with a consistent interval of approximately 5 milliseconds between each spark while the breaker points remain closed.
The design of this circuit is particularly effective for applications requiring a high-frequency spark generation, such as in ignition systems or for creating a buzz coil effect in various electronic projects. Proper attention should be paid to the component ratings, ensuring they can handle the voltages and currents involved, particularly the MOSFET and the ignition coil, to prevent damage during operation. Additionally, adequate heat dissipation measures should be implemented for the MOSFET to maintain reliable performance during extended use.Here`s a circuit to create a buzzcoil using a standard automotive ignition coil. A 556 dual timer is used to establish the frequency and duty cycle of the coil current. One of the timers is used as an oscillator to generate the 200 Hz rectangular waveform needed to control the (IRF740 MOSFET) while the second timer switches the oscillator on and off as the breaker points open and close (closed = on). The result is a steady stream of sparks from the ignition coil spaced about 5 milliseconds apart while the breaker points are closed..
🔗 External reference