Invisible Infrared Alarm Circuit
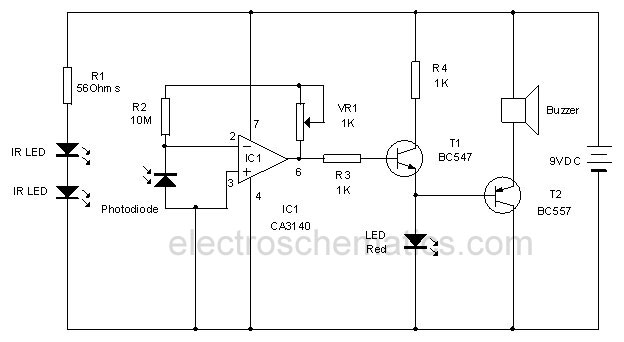
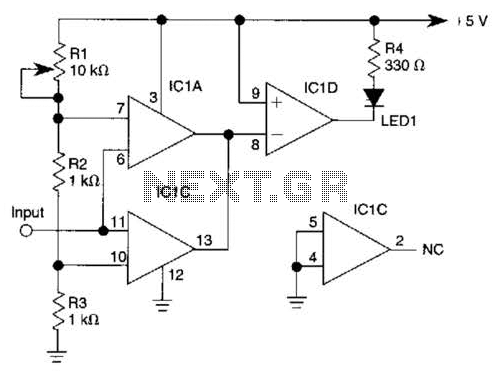
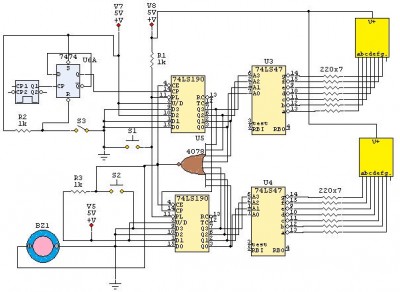
This circuit utilizes invisible infrared light to detect the movement of individuals through a doorway. A brief beep will be emitted when the infrared beam is interrupted.
The infrared movement detection circuit employs an infrared LED and a photodiode or phototransistor as its primary components. The infrared LED emits light that is not visible to the human eye, creating an invisible beam across the doorway. When a person passes through this beam, the emitted infrared light is reflected or blocked, causing a change in the light intensity detected by the photodiode or phototransistor.
The circuit is typically powered by a low-voltage DC source, such as a battery or a DC power supply. The infrared LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, while the photodiode or phototransistor is connected in a configuration that allows it to respond to the changes in light intensity.
Upon detecting the interruption of the infrared beam, the photodiode or phototransistor triggers a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit. This component processes the signal and activates a sound-generating device, such as a buzzer or speaker, producing a short beep to alert when motion is detected.
For optimal performance, the circuit may include additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, delay timers, or indicators to enhance functionality. The placement of the infrared LED and photodiode or phototransistor is crucial; they must be aligned correctly to ensure the integrity of the infrared beam across the doorway. Proper housing and positioning can also mitigate false triggers from ambient light sources.This circuit uses invisible infrared light to detect the movement of people through the door. A short beep will be generated when the infrared beam breaks 🔗 External reference
The infrared movement detection circuit employs an infrared LED and a photodiode or phototransistor as its primary components. The infrared LED emits light that is not visible to the human eye, creating an invisible beam across the doorway. When a person passes through this beam, the emitted infrared light is reflected or blocked, causing a change in the light intensity detected by the photodiode or phototransistor.
The circuit is typically powered by a low-voltage DC source, such as a battery or a DC power supply. The infrared LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, while the photodiode or phototransistor is connected in a configuration that allows it to respond to the changes in light intensity.
Upon detecting the interruption of the infrared beam, the photodiode or phototransistor triggers a microcontroller or a simple comparator circuit. This component processes the signal and activates a sound-generating device, such as a buzzer or speaker, producing a short beep to alert when motion is detected.
For optimal performance, the circuit may include additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, delay timers, or indicators to enhance functionality. The placement of the infrared LED and photodiode or phototransistor is crucial; they must be aligned correctly to ensure the integrity of the infrared beam across the doorway. Proper housing and positioning can also mitigate false triggers from ambient light sources.This circuit uses invisible infrared light to detect the movement of people through the door. A short beep will be generated when the infrared beam breaks 🔗 External reference