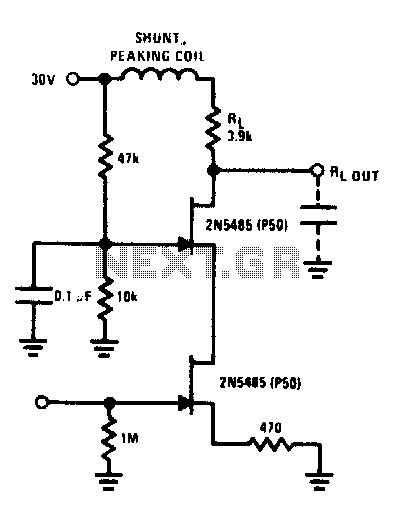
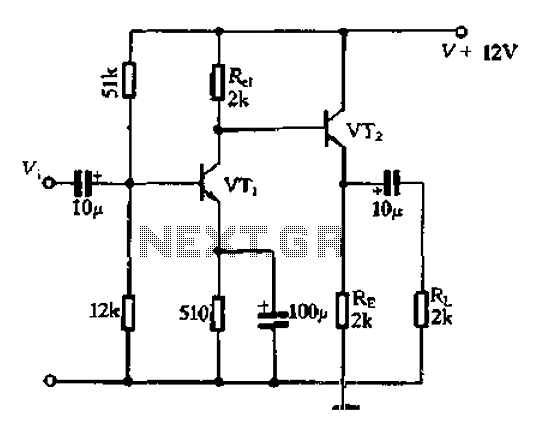
JFET-Bipolar Cascode
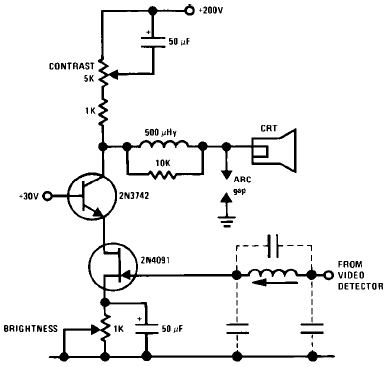
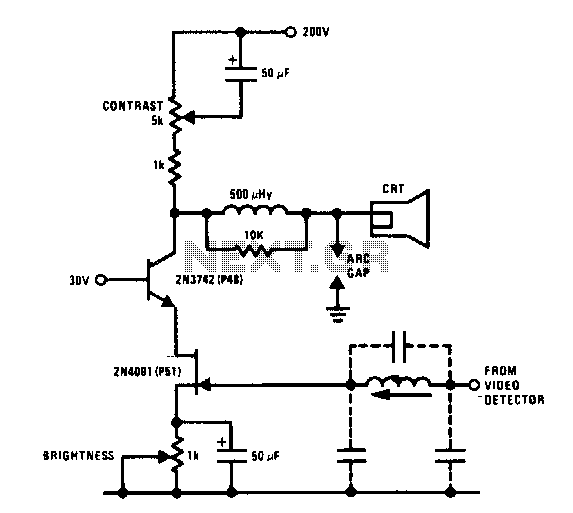
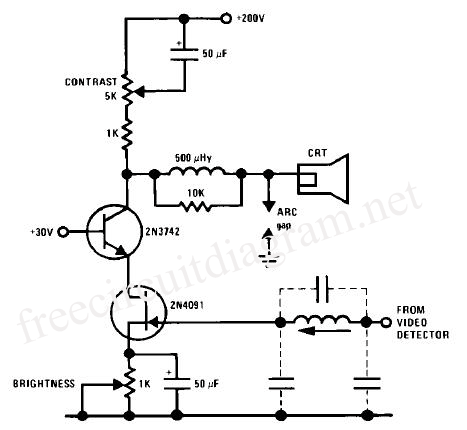
The schematic illustrates the JFET-Bipolar Cascode Circuit Diagram, designed to deliver full video output for the CRT cathode drive. The circuit achieves a gain of approximately 90. It consists of a two-stage amplifier that includes a transconductance amplifier followed by a current buffer. This cascode configuration effectively mitigates Miller capacitance issues associated with the 2N4091 JFET, enabling direct drive from the video detector. Additionally, an m-derived filter utilizing stray capacitance and a variable inductor is incorporated to prevent amplification of the 4.5 MHz sound frequency by the video amplifier.
The JFET-Bipolar Cascode Circuit is an advanced electronic configuration that combines the benefits of both JFET and bipolar transistor technologies to achieve high gain and improved bandwidth performance. In this design, the transconductance amplifier serves as the first stage, where the input signal is processed to produce a current that is proportional to the voltage input. The subsequent current buffer stage ensures that the output current can drive the load without significant signal degradation.
The cascode arrangement is particularly advantageous in this application as it minimizes the effects of parasitic capacitances, specifically the Miller capacitance, which can limit the frequency response of amplifiers. By placing the JFET in a cascode configuration with a bipolar transistor, the circuit maintains a high input impedance while providing a low output impedance, which is critical for driving the CRT effectively.
Furthermore, the incorporation of an m-derived filter is a strategic choice to suppress unwanted frequencies. Stray capacitance in the circuit is utilized in conjunction with a variable inductor to create a filter that selectively attenuates the 4.5 MHz sound frequency. This filtering action is essential in ensuring that the video amplifier focuses solely on the desired video signals, thereby enhancing the overall performance and clarity of the output.
In summary, the JFET-Bipolar Cascode Circuit Diagram represents a sophisticated design that effectively combines multiple electronic principles to deliver high-quality video output while addressing potential frequency interference issues. The careful selection of components and configuration allows for robust performance suitable for CRT applications.The following schematic shows the JFET- Bipolar Cascode Circuit Diagram. The JFET- Bipolar cascode circuit will provide full video output for the CRT cathode drive. Gain is about 90. The cascode is a two-stage amplifier composed of a transconductance amplifier followed by a current buffer. The cascode configuration eliminates Miller capacitance p roblems with the 2N4091 JFET, thus allowing direct drive from the video detector. An m derived filter using stray capacitance and a variable inductor prevents 4. 5 MHz sound frequency from being amplified by the video amplifier. 🔗 External reference
The JFET-Bipolar Cascode Circuit is an advanced electronic configuration that combines the benefits of both JFET and bipolar transistor technologies to achieve high gain and improved bandwidth performance. In this design, the transconductance amplifier serves as the first stage, where the input signal is processed to produce a current that is proportional to the voltage input. The subsequent current buffer stage ensures that the output current can drive the load without significant signal degradation.
The cascode arrangement is particularly advantageous in this application as it minimizes the effects of parasitic capacitances, specifically the Miller capacitance, which can limit the frequency response of amplifiers. By placing the JFET in a cascode configuration with a bipolar transistor, the circuit maintains a high input impedance while providing a low output impedance, which is critical for driving the CRT effectively.
Furthermore, the incorporation of an m-derived filter is a strategic choice to suppress unwanted frequencies. Stray capacitance in the circuit is utilized in conjunction with a variable inductor to create a filter that selectively attenuates the 4.5 MHz sound frequency. This filtering action is essential in ensuring that the video amplifier focuses solely on the desired video signals, thereby enhancing the overall performance and clarity of the output.
In summary, the JFET-Bipolar Cascode Circuit Diagram represents a sophisticated design that effectively combines multiple electronic principles to deliver high-quality video output while addressing potential frequency interference issues. The careful selection of components and configuration allows for robust performance suitable for CRT applications.The following schematic shows the JFET- Bipolar Cascode Circuit Diagram. The JFET- Bipolar cascode circuit will provide full video output for the CRT cathode drive. Gain is about 90. The cascode is a two-stage amplifier composed of a transconductance amplifier followed by a current buffer. The cascode configuration eliminates Miller capacitance p roblems with the 2N4091 JFET, thus allowing direct drive from the video detector. An m derived filter using stray capacitance and a variable inductor prevents 4. 5 MHz sound frequency from being amplified by the video amplifier. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713