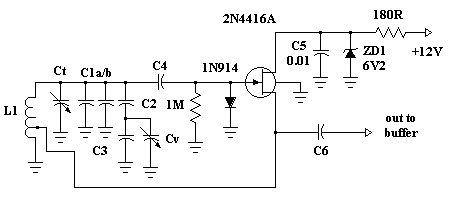
JFET Pierce Crystal Oscillator
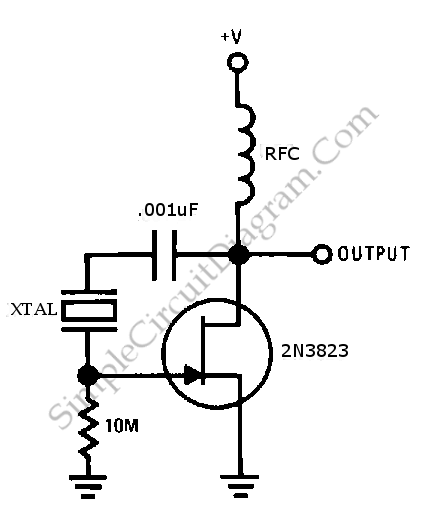
This is a simple JFET pierce crystal oscillator. A wide frequency range of crystals can be used with this circuit without requiring any modifications.
The JFET pierce crystal oscillator is a versatile circuit that utilizes a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) to achieve stable oscillation at the frequency determined by the connected crystal. The circuit typically consists of a JFET, a crystal resonator, a few passive components such as resistors and capacitors, and a power supply.
The JFET serves as an amplifier and oscillator, taking advantage of its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. The crystal resonator is connected in the feedback loop of the JFET, establishing the frequency of oscillation. The specific frequency is determined by the crystal's resonant frequency, which can cover a broad range depending on the type of crystal used.
In the circuit, the gate of the JFET is connected to the crystal, and the source is typically grounded. A resistor is placed in the drain circuit to provide the necessary biasing for the JFET to operate in the active region. Additional capacitors may be included to stabilize the oscillation and filter out unwanted noise.
One of the key advantages of this oscillator design is its ability to accommodate various crystal frequencies without the need for circuit modifications. This flexibility makes it suitable for applications requiring different frequencies, such as in communication systems, clock generation, and signal processing.
Overall, the JFET pierce crystal oscillator is a robust and efficient circuit that provides reliable frequency generation across a wide range of applications. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a popular choice among electronics engineers for various oscillator needs.This is a simple JFET pierce crystal oscillator. We can use a wide frequency range of crystal using this circuit without circuit modification. Here is the.. 🔗 External reference
The JFET pierce crystal oscillator is a versatile circuit that utilizes a Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) to achieve stable oscillation at the frequency determined by the connected crystal. The circuit typically consists of a JFET, a crystal resonator, a few passive components such as resistors and capacitors, and a power supply.
The JFET serves as an amplifier and oscillator, taking advantage of its high input impedance and low noise characteristics. The crystal resonator is connected in the feedback loop of the JFET, establishing the frequency of oscillation. The specific frequency is determined by the crystal's resonant frequency, which can cover a broad range depending on the type of crystal used.
In the circuit, the gate of the JFET is connected to the crystal, and the source is typically grounded. A resistor is placed in the drain circuit to provide the necessary biasing for the JFET to operate in the active region. Additional capacitors may be included to stabilize the oscillation and filter out unwanted noise.
One of the key advantages of this oscillator design is its ability to accommodate various crystal frequencies without the need for circuit modifications. This flexibility makes it suitable for applications requiring different frequencies, such as in communication systems, clock generation, and signal processing.
Overall, the JFET pierce crystal oscillator is a robust and efficient circuit that provides reliable frequency generation across a wide range of applications. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a popular choice among electronics engineers for various oscillator needs.This is a simple JFET pierce crystal oscillator. We can use a wide frequency range of crystal using this circuit without circuit modification. Here is the.. 🔗 External reference