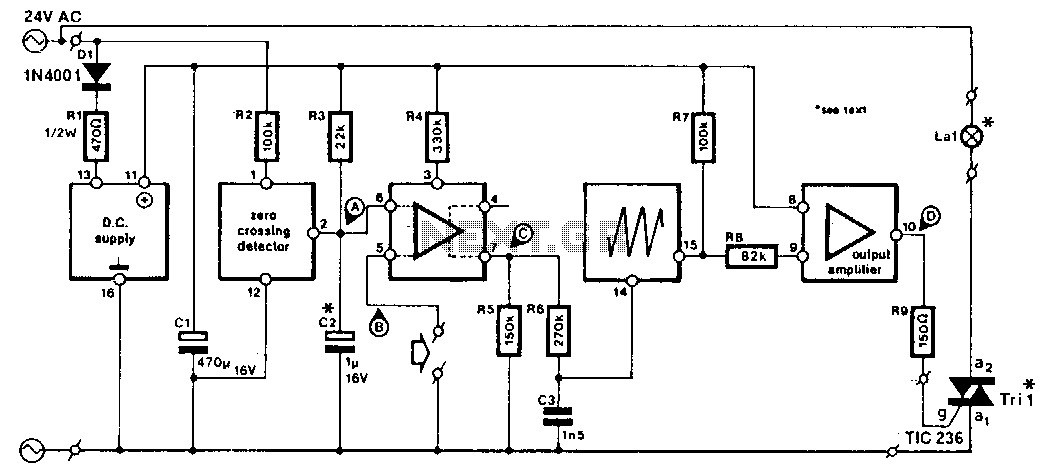
lamp dimmer
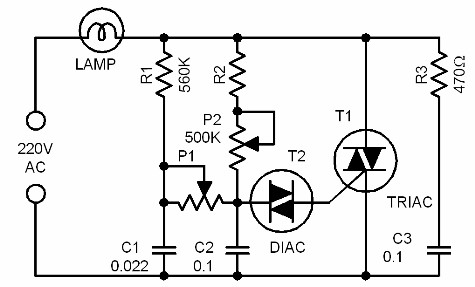
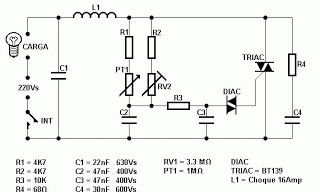
This is an advanced dimmer circuit design that allows the triac to be triggered at lower voltage levels. Typically, the triggering voltage for a triac is approximately 70V; however, this circuit enables triggering at around 35V through the incorporation of components R1, C1, and P1. It is essential to construct the circuit within a highly insulating enclosure, as it operates at 220 volts. For P2, a special potentiometer with a plastic shaft should be utilized. This circuit has various practical applications, including controlling the speed of electric drill machines, sewing machines, and electric motors in model boats.
The dimmer circuit utilizes a triac as the primary switching component, which is capable of controlling AC loads by allowing current to flow in both directions when triggered. The design aims to enhance the performance of the triac by lowering the required triggering voltage from the standard 70V to approximately 35V. This reduction is achieved through the strategic addition of resistors, capacitors, and a potentiometer, which work together to modify the triggering characteristics of the triac.
Component R1 serves as a current-limiting resistor, ensuring that the current flowing into the gate of the triac remains within safe limits. C1 acts as a timing capacitor that, in conjunction with R1, creates a delay in the triggering of the triac, allowing for a smooth dimming effect. The potentiometer P1 can be adjusted to fine-tune the phase angle at which the triac is triggered, thereby controlling the amount of power delivered to the load.
The circuit must be housed in an insulating enclosure to prevent electrical hazards, given that it operates at a high voltage of 220 volts. Safety precautions should be taken to ensure that all components are rated for the voltage and current levels present in the circuit.
Applications of this dimmer circuit include not only the control of speed in electric drills and sewing machines but also in various other devices that require adjustable speed or brightness. For example, it can be utilized in lighting systems to provide variable illumination levels or in hobbyist projects where motor speed control is necessary. The versatility of this design makes it a valuable addition to any electronics toolkit.This is not just another dimmer circuit. The improved design of this dimmer circuit enables its triac to be triggered with lower voltage values. Normally, the triggering voltage of a triac is around 70V. In some applications though, it is desirable to use a lower voltage in triggering the triac. A trick is used to achieve this effect in this circu it: the addition of the components R1, C1 and P1. Due to this, the trigger value can be pulled down to around 35V. Construct the circuit and put it in a highly insulating box. Remember, the circuit is working with 220 volts! For P2 use a special potentiometer with a plastic shaft. There are lots of practical applications for this circuit. One typical application is controlling the speed of an ordinary electric drill machine. It can also be used to control the speed of a sewing machine, or the electric motor in a model boat, etc. 🔗 External reference
The dimmer circuit utilizes a triac as the primary switching component, which is capable of controlling AC loads by allowing current to flow in both directions when triggered. The design aims to enhance the performance of the triac by lowering the required triggering voltage from the standard 70V to approximately 35V. This reduction is achieved through the strategic addition of resistors, capacitors, and a potentiometer, which work together to modify the triggering characteristics of the triac.
Component R1 serves as a current-limiting resistor, ensuring that the current flowing into the gate of the triac remains within safe limits. C1 acts as a timing capacitor that, in conjunction with R1, creates a delay in the triggering of the triac, allowing for a smooth dimming effect. The potentiometer P1 can be adjusted to fine-tune the phase angle at which the triac is triggered, thereby controlling the amount of power delivered to the load.
The circuit must be housed in an insulating enclosure to prevent electrical hazards, given that it operates at a high voltage of 220 volts. Safety precautions should be taken to ensure that all components are rated for the voltage and current levels present in the circuit.
Applications of this dimmer circuit include not only the control of speed in electric drills and sewing machines but also in various other devices that require adjustable speed or brightness. For example, it can be utilized in lighting systems to provide variable illumination levels or in hobbyist projects where motor speed control is necessary. The versatility of this design makes it a valuable addition to any electronics toolkit.This is not just another dimmer circuit. The improved design of this dimmer circuit enables its triac to be triggered with lower voltage values. Normally, the triggering voltage of a triac is around 70V. In some applications though, it is desirable to use a lower voltage in triggering the triac. A trick is used to achieve this effect in this circu it: the addition of the components R1, C1 and P1. Due to this, the trigger value can be pulled down to around 35V. Construct the circuit and put it in a highly insulating box. Remember, the circuit is working with 220 volts! For P2 use a special potentiometer with a plastic shaft. There are lots of practical applications for this circuit. One typical application is controlling the speed of an ordinary electric drill machine. It can also be used to control the speed of a sewing machine, or the electric motor in a model boat, etc. 🔗 External reference