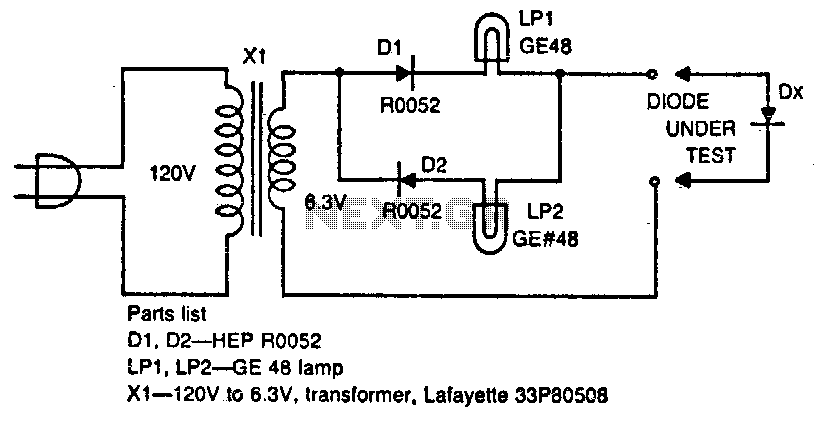
LASER DIODE SOURCE
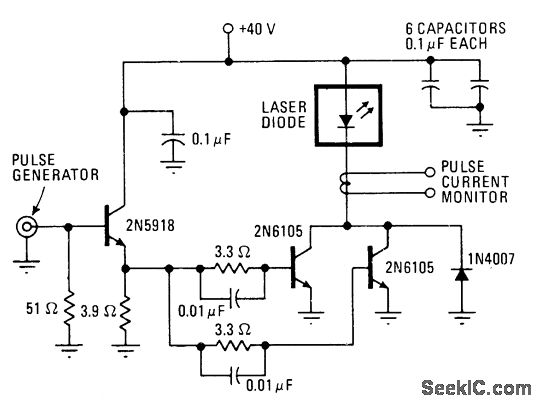
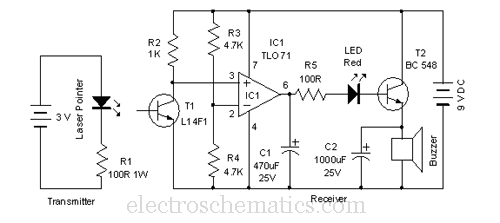
A transistor switching circuit for the RCA SG2007 laser diode is capable of generating pulses as short as 10 ns at repetition rates exceeding 100 kHz. This circuit is utilized in optical communication systems where a fiber bundle or single fiber is directly connected to the laser pellet.
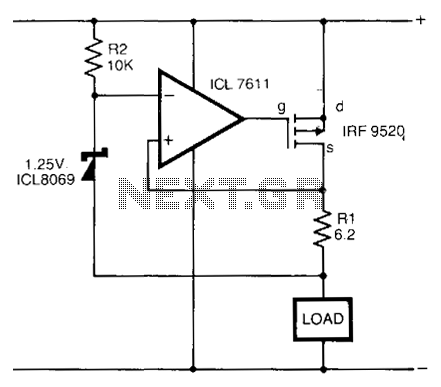
The transistor switching circuit employs a configuration designed to efficiently drive the RCA SG2007 laser diode, which is known for its high-speed performance and reliability in communication applications. The circuit typically consists of a biasing network, a switching transistor, and the laser diode itself. The switching transistor is responsible for rapidly turning the laser diode on and off, generating the required pulse width and frequency.
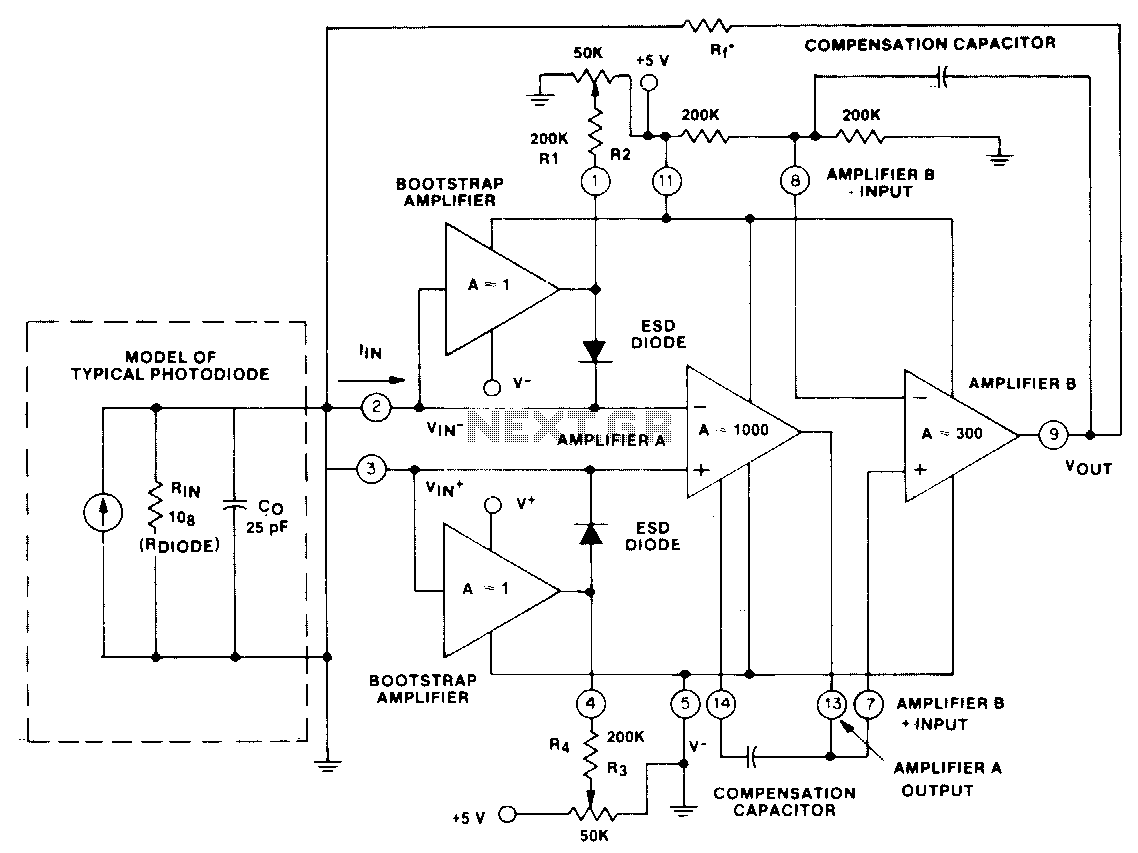
When activated, the transistor allows current to flow through the laser diode, causing it to emit light. The rapid switching capability of the transistor enables the generation of very short pulses, essential for high-speed data transmission in optical communication systems. The circuit is designed to minimize power loss and maintain signal integrity, ensuring that the laser diode operates efficiently even at high repetition rates.
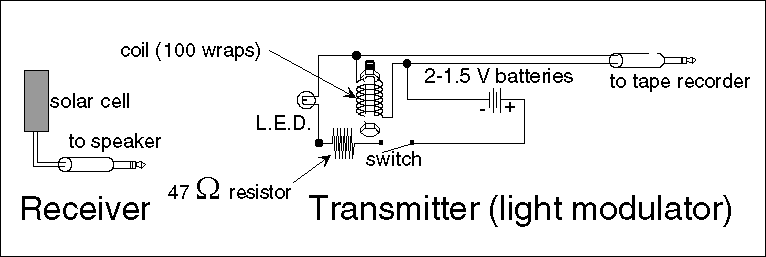
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into larger communication systems, where it interfaces with other components such as modulators and receivers. The ability to achieve pulse widths of 10 ns makes this setup particularly suitable for advanced communication protocols that require high data rates and low latency. The direct connection of the fiber bundle or single fiber to the laser pellet further enhances the performance by reducing signal degradation and improving coupling efficiency.
Overall, the transistor switching circuit for the RCA SG2007 laser diode represents a critical component in modern optical communication systems, facilitating high-speed data transmission with minimal signal loss.With transistor switching circuit shown for RCA SG2007 laser diode, pulses as short as 10 ns are possible at repetition rates above 100 kHz. Used in optical communication system in which fiber bundle or singlefiber is attached directly to laser pellet.
-J. T. O`Brien, Laser Diodes Provide High Power for High-Speed Cornmunieations Systems, Electroni cs, Aug. 5, 1976, p 94-96. 🔗 External reference
The transistor switching circuit employs a configuration designed to efficiently drive the RCA SG2007 laser diode, which is known for its high-speed performance and reliability in communication applications. The circuit typically consists of a biasing network, a switching transistor, and the laser diode itself. The switching transistor is responsible for rapidly turning the laser diode on and off, generating the required pulse width and frequency.
When activated, the transistor allows current to flow through the laser diode, causing it to emit light. The rapid switching capability of the transistor enables the generation of very short pulses, essential for high-speed data transmission in optical communication systems. The circuit is designed to minimize power loss and maintain signal integrity, ensuring that the laser diode operates efficiently even at high repetition rates.
In practical applications, this circuit can be integrated into larger communication systems, where it interfaces with other components such as modulators and receivers. The ability to achieve pulse widths of 10 ns makes this setup particularly suitable for advanced communication protocols that require high data rates and low latency. The direct connection of the fiber bundle or single fiber to the laser pellet further enhances the performance by reducing signal degradation and improving coupling efficiency.
Overall, the transistor switching circuit for the RCA SG2007 laser diode represents a critical component in modern optical communication systems, facilitating high-speed data transmission with minimal signal loss.With transistor switching circuit shown for RCA SG2007 laser diode, pulses as short as 10 ns are possible at repetition rates above 100 kHz. Used in optical communication system in which fiber bundle or singlefiber is attached directly to laser pellet.
-J. T. O`Brien, Laser Diodes Provide High Power for High-Speed Cornmunieations Systems, Electroni cs, Aug. 5, 1976, p 94-96. 🔗 External reference