LED Driver Circuit with 555 Timer
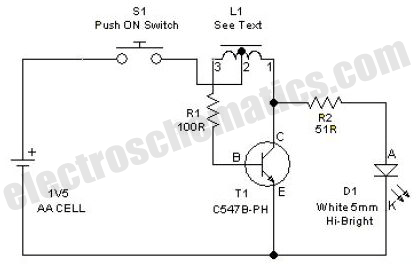
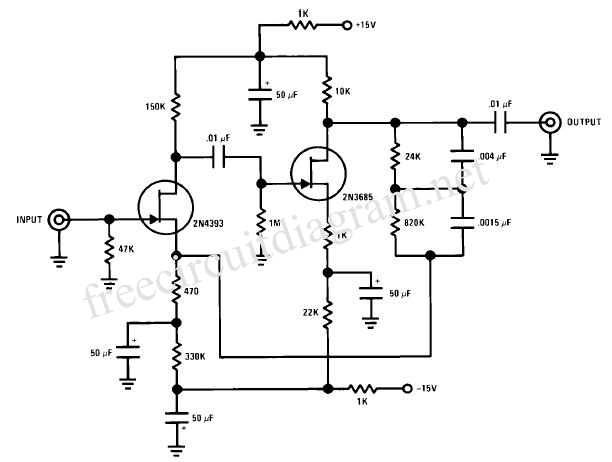
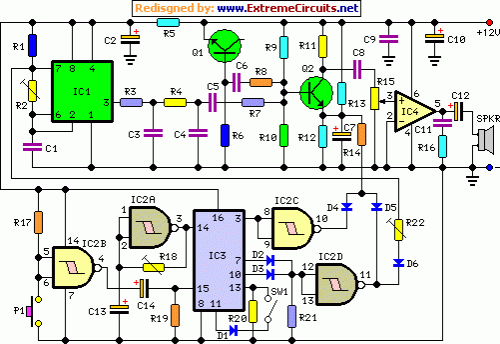
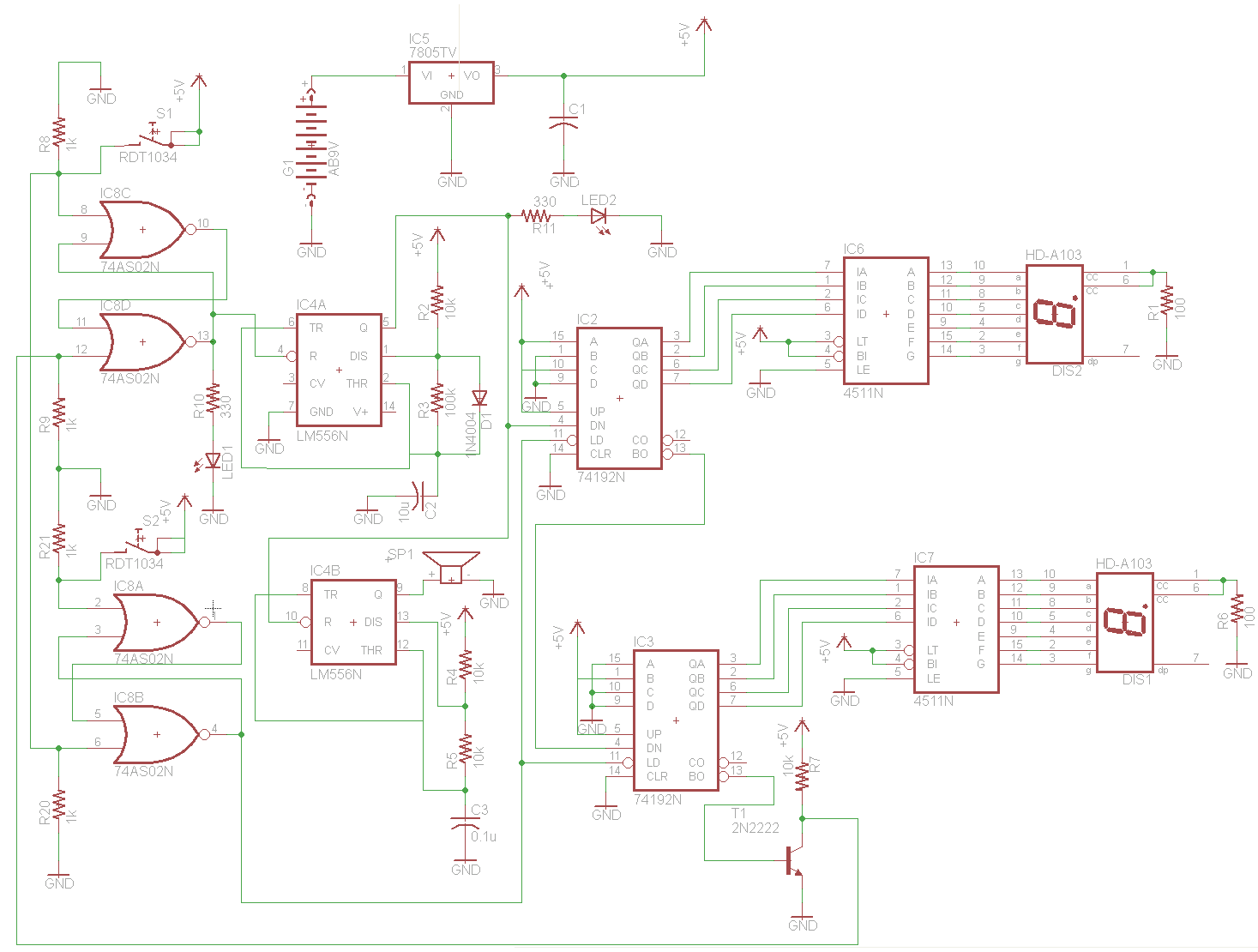
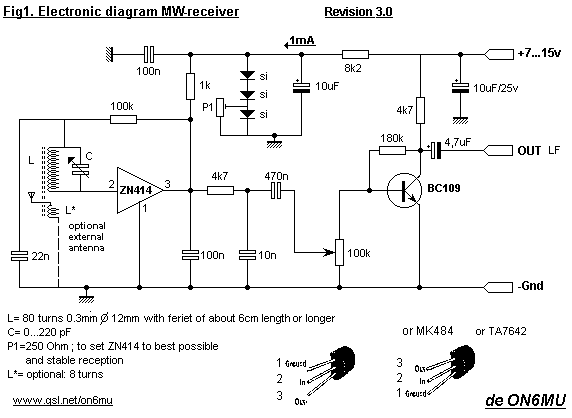
This simple LED driver circuit allows the operation of up to seven LEDs using a single NiMH (Nickel Metal Hydride) AA cell. The circuit generates voltage pulses.
The LED driver circuit is designed to efficiently power multiple LEDs while maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the components involved. The core of the circuit is typically based on a switching regulator or a simple transistor-based design that enables the control of current flowing through the LEDs.
In this configuration, a single NiMH AA cell provides the necessary voltage and current. The circuit may include a resistor to limit the current to the LEDs, ensuring that they do not exceed their rated specifications, which can lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure.
The switching regulator may consist of a transistor, such as an N-channel MOSFET, which acts as a switch that turns on and off rapidly, creating a pulse-width modulation (PWM) effect. This method allows for efficient power management, reducing heat generation and improving battery life.
An additional component, such as a capacitor, may be included in the circuit to smooth out the voltage and provide a stable power supply to the LEDs. This capacitor helps to maintain a consistent brightness level, even when the load changes or the battery voltage drops as it discharges.
The arrangement of the LEDs can be in series or parallel, depending on the desired brightness and forward voltage requirements. If arranged in series, the total forward voltage drop must be considered to ensure it does not exceed the supply voltage. Conversely, if arranged in parallel, each LED should have its own current-limiting resistor to ensure even distribution of current.
Overall, this LED driver circuit exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve efficient and effective illumination solutions using minimal power resources.This simple LED driver circuit allows us to drive up to seven LEDs by using a single NiMH (Nickel Metal Hydride) AA cell. The circuit produces voltage puls.. 🔗 External reference
The LED driver circuit is designed to efficiently power multiple LEDs while maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the components involved. The core of the circuit is typically based on a switching regulator or a simple transistor-based design that enables the control of current flowing through the LEDs.
In this configuration, a single NiMH AA cell provides the necessary voltage and current. The circuit may include a resistor to limit the current to the LEDs, ensuring that they do not exceed their rated specifications, which can lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure.
The switching regulator may consist of a transistor, such as an N-channel MOSFET, which acts as a switch that turns on and off rapidly, creating a pulse-width modulation (PWM) effect. This method allows for efficient power management, reducing heat generation and improving battery life.
An additional component, such as a capacitor, may be included in the circuit to smooth out the voltage and provide a stable power supply to the LEDs. This capacitor helps to maintain a consistent brightness level, even when the load changes or the battery voltage drops as it discharges.
The arrangement of the LEDs can be in series or parallel, depending on the desired brightness and forward voltage requirements. If arranged in series, the total forward voltage drop must be considered to ensure it does not exceed the supply voltage. Conversely, if arranged in parallel, each LED should have its own current-limiting resistor to ensure even distribution of current.
Overall, this LED driver circuit exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic components to achieve efficient and effective illumination solutions using minimal power resources.This simple LED driver circuit allows us to drive up to seven LEDs by using a single NiMH (Nickel Metal Hydride) AA cell. The circuit produces voltage puls.. 🔗 External reference