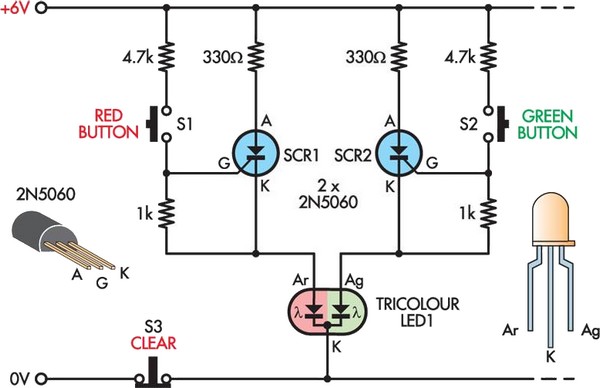
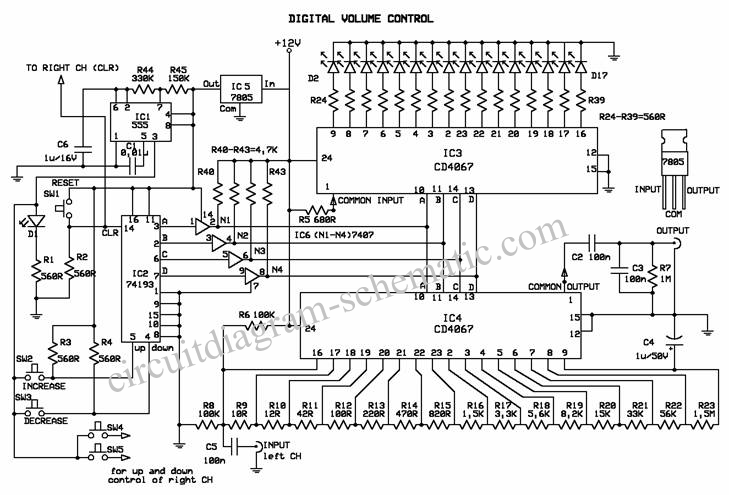
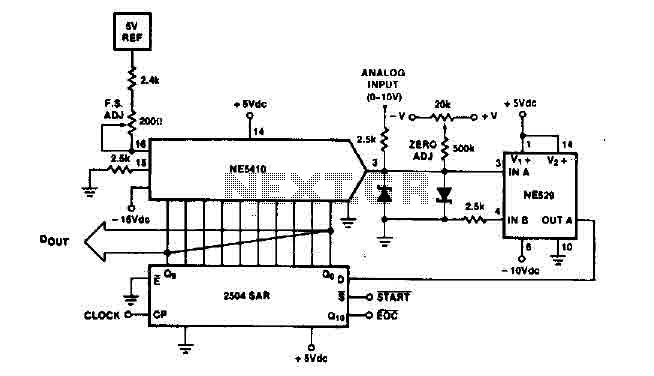
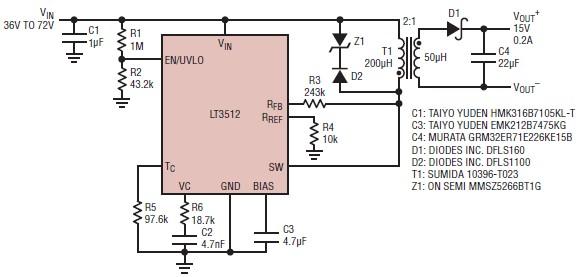
LED VU meter circuit by transistor
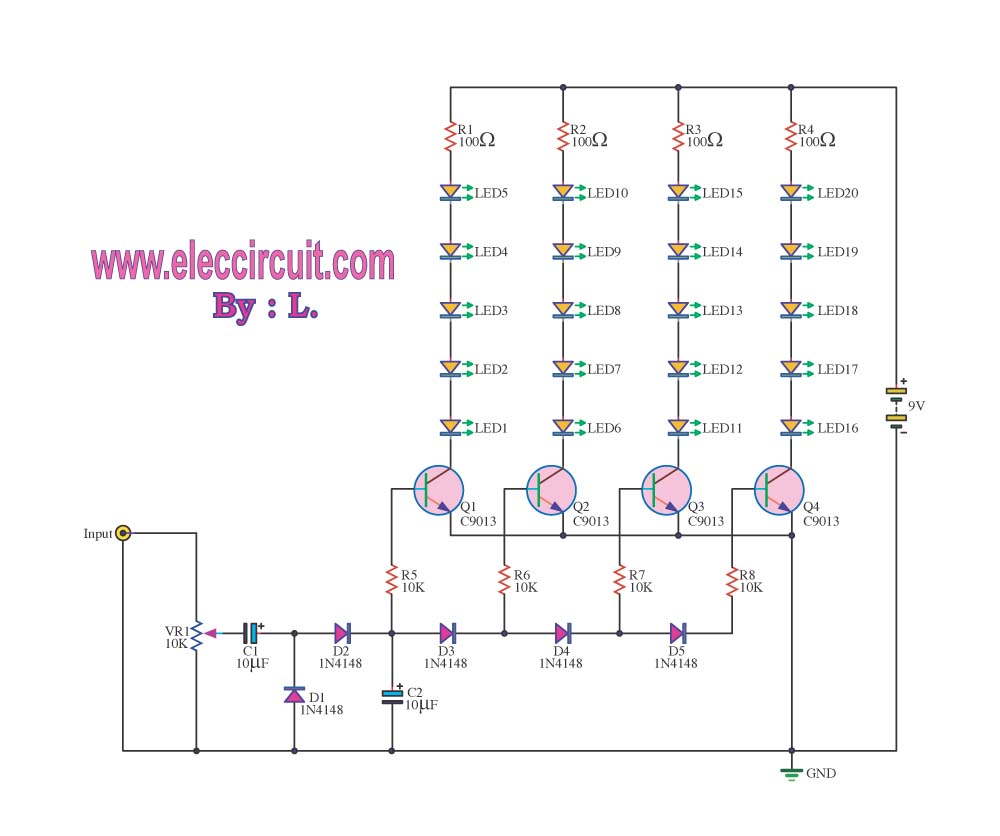
The VU meter operates in conjunction with the integrated amplifier circuit. The audio signal is processed by the audio amplifier circuit, which drives the VU meter to display the audio level.
The VU meter circuit is designed to visually represent the amplitude of an audio signal, providing a useful tool for audio engineers and sound technicians. This circuit typically consists of an analog meter, a rectifier, and a smoothing capacitor.
The integrated amplifier circuit receives the audio input signal, which is then amplified to the required level. The output from the amplifier is fed into the VU meter circuit. The rectifier converts the AC audio signal into a DC voltage, which is proportional to the audio signal's amplitude.
A smoothing capacitor is used to filter the rectified signal, ensuring that the VU meter needle responds smoothly to changes in audio levels, rather than jumping erratically. The VU meter itself is calibrated to display the audio level accurately, typically ranging from -20 dB to +3 dB, allowing for easy monitoring of audio performance.
In terms of components, the circuit may include resistors to set the sensitivity of the VU meter, a potentiometer for calibration, and possibly a transistor to drive the meter if the signal levels are low. Proper grounding and shielding are essential to minimize noise and interference, ensuring that the VU meter provides an accurate representation of the audio signal levels.
Overall, the integration of a VU meter with an audio amplifier circuit enhances the functionality of audio systems by providing real-time visual feedback on signal levels, facilitating better sound management and control.The V.U. meter that works with the integrated amplifier circuit.The signal will sound, the audio amplifier circuit into VU meter circuit.And will show the level.. 🔗 External reference
The VU meter circuit is designed to visually represent the amplitude of an audio signal, providing a useful tool for audio engineers and sound technicians. This circuit typically consists of an analog meter, a rectifier, and a smoothing capacitor.
The integrated amplifier circuit receives the audio input signal, which is then amplified to the required level. The output from the amplifier is fed into the VU meter circuit. The rectifier converts the AC audio signal into a DC voltage, which is proportional to the audio signal's amplitude.
A smoothing capacitor is used to filter the rectified signal, ensuring that the VU meter needle responds smoothly to changes in audio levels, rather than jumping erratically. The VU meter itself is calibrated to display the audio level accurately, typically ranging from -20 dB to +3 dB, allowing for easy monitoring of audio performance.
In terms of components, the circuit may include resistors to set the sensitivity of the VU meter, a potentiometer for calibration, and possibly a transistor to drive the meter if the signal levels are low. Proper grounding and shielding are essential to minimize noise and interference, ensuring that the VU meter provides an accurate representation of the audio signal levels.
Overall, the integration of a VU meter with an audio amplifier circuit enhances the functionality of audio systems by providing real-time visual feedback on signal levels, facilitating better sound management and control.The V.U. meter that works with the integrated amplifier circuit.The signal will sound, the audio amplifier circuit into VU meter circuit.And will show the level.. 🔗 External reference