Line Follower Sensor
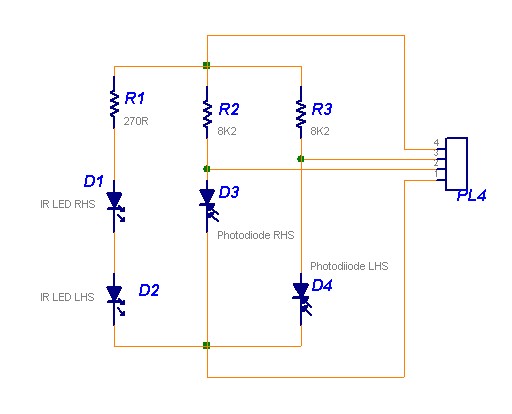
The following circuit illustrates a Line Follower Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features include a simple design, with Infrared LEDs D1 and D2 emitting infrared light.
The Line Follower Sensor Circuit is designed to detect the presence of a line, typically a black line on a white surface, allowing a robot or vehicle to follow the path. The core components of this circuit include two Infrared LEDs (D1 and D2) and phototransistors or photodiodes that act as sensors.
When the Infrared LEDs emit light, it reflects off the surface beneath them. If the surface is light-colored (like white), the light is reflected back to the phototransistors, which will not trigger the sensors. Conversely, if the surface is dark (like black), less infrared light is reflected, leading to a different response from the sensors. This contrast allows the circuit to determine the position of the line.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller or an operational amplifier to process the signals received from the phototransistors. Based on the input from the sensors, the microcontroller can adjust the motion of the motors controlling the wheels of the robot, ensuring that it stays on the designated path.
Powering the circuit can be achieved using a battery or a power supply, ensuring that the LEDs and sensors receive the necessary voltage and current for operation. The simplicity of this circuit makes it an excellent choice for educational purposes, as well as for hobbyists interested in robotics.
Overall, the Line Follower Sensor Circuit exemplifies a fundamental application of infrared technology in automation and robotics, demonstrating how basic electronic components can be used to create intelligent behavior in machines.The following circuit shows about Line Follower Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features:Simple circuit, Infra-Red LEDs D1 and D2 will emit Infra-Red .. 🔗 External reference
The Line Follower Sensor Circuit is designed to detect the presence of a line, typically a black line on a white surface, allowing a robot or vehicle to follow the path. The core components of this circuit include two Infrared LEDs (D1 and D2) and phototransistors or photodiodes that act as sensors.
When the Infrared LEDs emit light, it reflects off the surface beneath them. If the surface is light-colored (like white), the light is reflected back to the phototransistors, which will not trigger the sensors. Conversely, if the surface is dark (like black), less infrared light is reflected, leading to a different response from the sensors. This contrast allows the circuit to determine the position of the line.
The circuit typically includes a microcontroller or an operational amplifier to process the signals received from the phototransistors. Based on the input from the sensors, the microcontroller can adjust the motion of the motors controlling the wheels of the robot, ensuring that it stays on the designated path.
Powering the circuit can be achieved using a battery or a power supply, ensuring that the LEDs and sensors receive the necessary voltage and current for operation. The simplicity of this circuit makes it an excellent choice for educational purposes, as well as for hobbyists interested in robotics.
Overall, the Line Follower Sensor Circuit exemplifies a fundamental application of infrared technology in automation and robotics, demonstrating how basic electronic components can be used to create intelligent behavior in machines.The following circuit shows about Line Follower Sensor Circuit Diagram. Features:Simple circuit, Infra-Red LEDs D1 and D2 will emit Infra-Red .. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713