LM139 One Shot Multivibrator/Timer
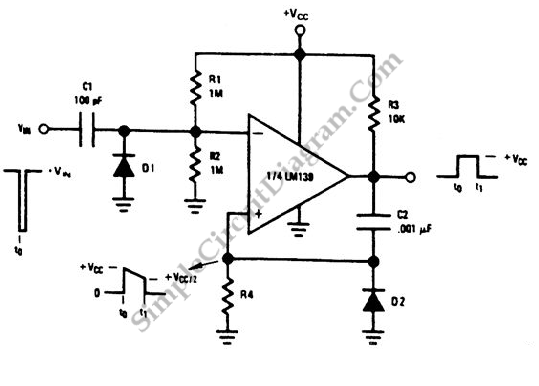
A one-shot multivibrator circuit, commonly referred to as a monostable multivibrator or timer, is designed to generate a pulse strobe of fixed duration in response to an input trigger.
The one-shot multivibrator is a fundamental circuit used in various electronic applications for pulse generation. It operates in a single stable state and transitions to a temporary state when triggered. The primary components of a typical one-shot multivibrator include a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a logic gate or a flip-flop configuration.
When a trigger signal is applied to the circuit, it causes the output to switch from its stable low state to a high state for a predetermined period, defined by the RC time constant, which is the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values used in the timing network. The output then returns to its stable low state after the time period elapses, regardless of the duration of the input trigger.
In practical applications, one-shot multivibrators are utilized in timer circuits, pulse-width modulation, and as delay elements in digital systems. The design can be implemented using discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers, or it can be integrated into microcontroller-based systems where software can dictate the timing parameters.
The reliability and precision of the pulse generated by a one-shot multivibrator make it a valuable component in synchronous systems, where timing is critical for the coordinated operation of various electronic devices.One shot multivibrator circuit is also known as monostable multivibrator or timer. The function of such circuit is simply produce a pulse strobe with a fixed.. 🔗 External reference
The one-shot multivibrator is a fundamental circuit used in various electronic applications for pulse generation. It operates in a single stable state and transitions to a temporary state when triggered. The primary components of a typical one-shot multivibrator include a timing resistor, a timing capacitor, and a logic gate or a flip-flop configuration.
When a trigger signal is applied to the circuit, it causes the output to switch from its stable low state to a high state for a predetermined period, defined by the RC time constant, which is the product of the resistance (R) and capacitance (C) values used in the timing network. The output then returns to its stable low state after the time period elapses, regardless of the duration of the input trigger.
In practical applications, one-shot multivibrators are utilized in timer circuits, pulse-width modulation, and as delay elements in digital systems. The design can be implemented using discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers, or it can be integrated into microcontroller-based systems where software can dictate the timing parameters.
The reliability and precision of the pulse generated by a one-shot multivibrator make it a valuable component in synchronous systems, where timing is critical for the coordinated operation of various electronic devices.One shot multivibrator circuit is also known as monostable multivibrator or timer. The function of such circuit is simply produce a pulse strobe with a fixed.. 🔗 External reference
%2B2%2BCH%2Bby%2BIC%2B%2BNE5532%2Bor%2BLF353.jpg)