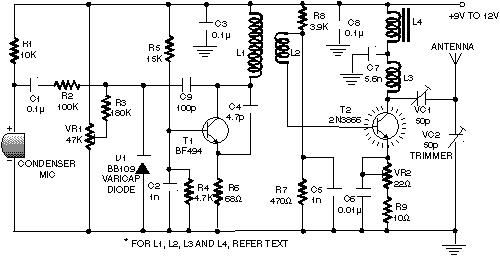
LOW POWER FM TRANSMITTER
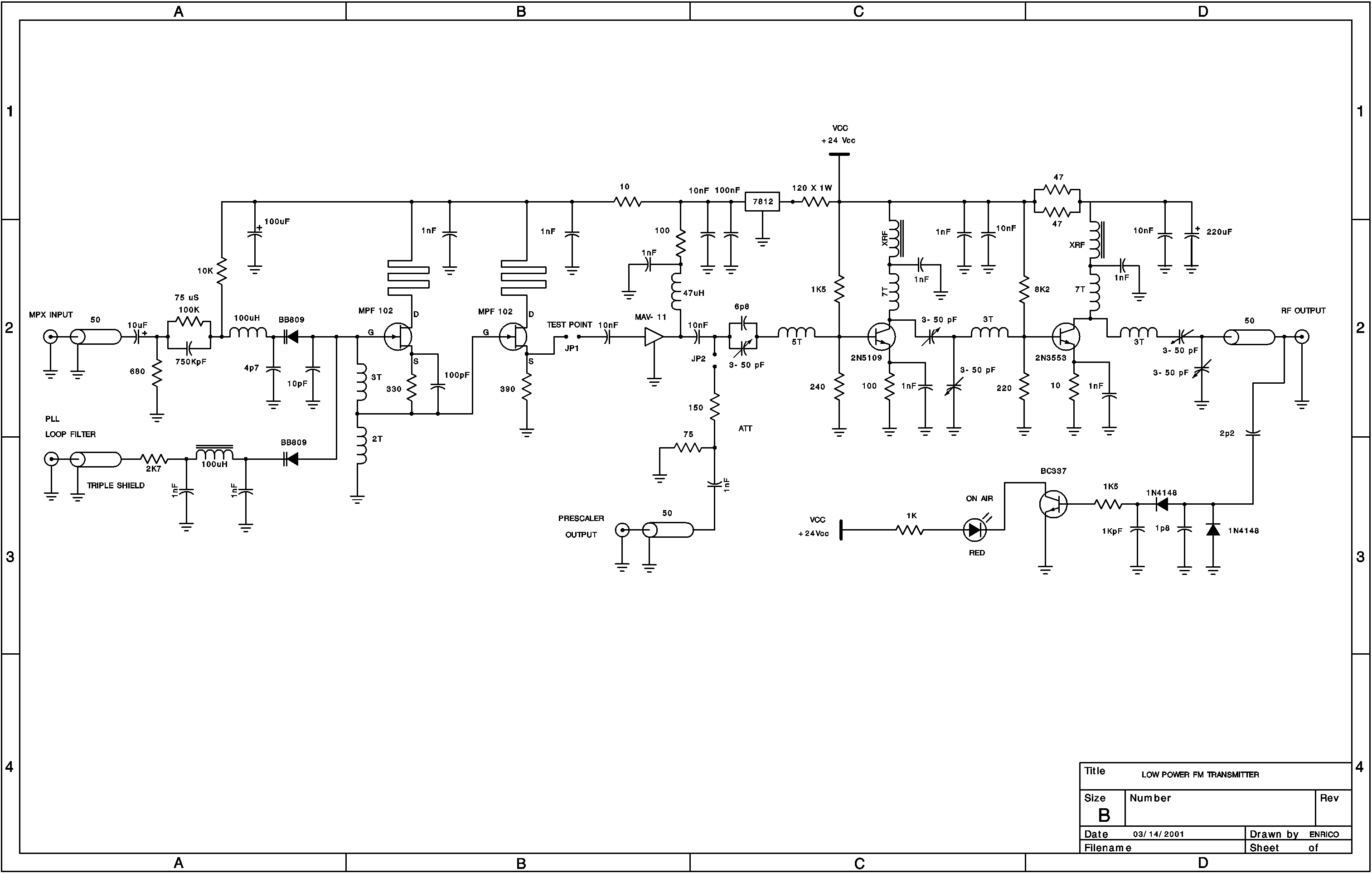
A low power FM pirate radio. The output power is approximately +35 dBm (3.16 watts) over a 50-ohm load and operates on a +24-volt power supply. The project consists of a Hartley oscillator (modulated VCO) and three stages (Class A, common emitter) of RF amplifiers. The first amplifier can utilize a MAV-11 (from MiniCircuits), which provides +12 dB of gain and a 1 dB compression point of +17.5 dBm. The driver stage employs an MWA-130 (from Motorola). For the second stage, a 2N5109 (Motorola) can be used, although a 2N3866 is also a viable option. The final stage utilizes a 2N3553. With appropriate biasing and adjustment of the trimmers for maximum output power, it is possible to achieve around 2.8 watts of EIRP using a 0 dBi antenna. An efficient radiating system is crucial, as is the use of low-loss coaxial cables for longer distances. RG-58A has a propagation velocity of 67% and an insertion loss of 21.65 dB/100m at 146 MHz. A low-pass filter is recommended at the final stage to prevent harmonic products that could interfere with MARS/CAP systems. In Brazil, many pirate radios do not utilize such filters, causing significant issues for MARS services. Various schematics are available, including a suggested low-pass Chebyshev filter and the corresponding frequency response curve. The filter exhibits low insertion loss, although not significantly expressive. The VCO can operate as a free (open loop) or synthesized (PLL) oscillator, with a jumper to switch between modes. Frequency deviation is controlled by a varactor diode that alters the intrinsic capacitance based on the audio input voltage, which should be set to ±75 kHz for FM broadcasting. Another varactor, BB809, controls the operating frequency, allowing for 200 kHz step increments in the PLL schematic circuit. The oscillator is designed to function within the FM broadcast range (88 to 108 MHz) without component modifications. As a Hartley oscillator, changing the operating frequency can be achieved by adjusting the number of turns in the inductors of the LC tank circuit. Reducing the number of turns results in higher frequencies and vice versa. Care must be taken when starting the oscillator if transitioning to higher frequencies than FM broadcast. Following the Barkhausen Criteria, feedback in a simple amplifier sustains oscillations, requiring that the loop gain (K factor) equals one. The MPF 102 oscillator transistor performs well up to 150 MHz, necessitating a high Ft transistor for higher frequency operations. Implementing a network of varactor diodes (in parallel) to control frequency deviation may be beneficial, as the BB809 has hyper-abrupt curves. An MV209 in parallel could potentially reduce distortion and enhance linearity. At the input (audio signal), a pre-emphasis network is included to ensure the modulation index at high audio frequencies (up to 1 kHz). In FM radio, the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) is influenced by the modulation index employed, which decreases as modulation frequency increases for a constant frequency deviation. Pre-emphasis acts as a high-pass filter, with a cutoff frequency slightly above the maximum modulated frequency, providing a 6 dB/octave response, which can be established using a series capacitor with the audio signal. A buffer stage is inserted between the oscillator and driver to prevent oscillations and increase isolation, presenting high impedance at the gate (oscillator side) and low impedance at the source terminal. At the output of the MAV-11, a sample frequency output is available for the pre-scaler (if using PLL), and to prevent overload at high power, a resistive PI attenuator of 8 dB is added to protect the pre-scaler input. The driver stage is the MAV-11 itself, providing 12 dB of gain.A low power fm pirate radio. The output power is around +35 dBm ( 3. 16 watts) over 50 ohms load and +24 volts power supply. The project consists in a hartley oscillator ( modulated VCO), and tree stages ( Class A, common emitter) of RF amplifiers. The first one, you can use a MAV-11 (from MiniCircuits) that have +12 dB of gain and a good 1 dB compression point of +17.
5 dBm, at my project I used a MWA-130 ( from Motorola) as driver stage. At second stage I used a 2N5109 (Motorola), but you can also use a 2N3866, and at final stage a 2N3553. With proper biasing and setting up the trimmers to maximum output power you can achieve around 2. 8 watts of EIRP using a 0 dBi antenna. A good irradiant system is also important, as well the coax cable that I recommend low loss cables if you are using a long cable distances.
RG-58A haves a 67% of propagation velocity and 21. 65 dB/100m of insertion loss at 146 MHz. I also recommend you use a low pass filter at final stage to prevent harmonics products cause harmful interferences on the MARS/CAP systems. Here in Brazil, many pirate radios don`t use such filter causing many trouble at MARS service. At final you can found many schematics, and of couse a suggested low pass chebyshev filter and the respective response frequency curve.
You will experience a low insertion loss within this filter, but not so expressive. The VCO can operate as free ( open loop) or synthesized (PLL) oscillator, you just must insert a jumper to close the loop for PLL or release it to free oscillator operation. The frequency deviation is controled by varactor diode that change the instrinsic capacitance within the voltage audio input causing a frequency deviation.
Note: set it to ± 75 KHz to FM pattern broadcast operation. Another varactor BB809 control the operation frequency, 200 KHz step increments is allowed at PLL schematic circuit at final of this page, the oscillator was constructed to operate in FM broadcast (88 to 108 MHZ) without any change in components. As hartley oscillator, if you wanna change the operation frequency just change the numbers of turns in the inductors at LC tank circuit.
As you know, decreasing the numbers of turns, you get upper frequencies, and vice-versa. Pay attention to start up the oscillator if you wanna change it to operate in high frequency than FM braodcast. Following the Barkhausen Criteria, we have a feedback in a simple amplifier and also sustain the oscillations, so the K fator( Loop gain) must be equal to one.
The MPF 102 oscillator transistor operates quite good until 150 MHz, a high Ft transistor will be required to high frequency operation. If you could use a network of varactors diode ( paralel association) to control the frequency deviation would be interesting because the BB809 have hyper abrupt curves.
Maybe MV209 in paralel produces less distortion and also ensure more linearity. At input ( audio signal), I did a pre-emphasis network to garantee that modulation index at high audio frequencies ( up 1KHz). At FM radio, the relation S/N depends of modulation index employed. The index decrease as modulation frequency increases, to a constant frequency deviation. Pre-emphasis is a high pass filter, that the cutoff frequency is slight upper of a maximum modulated frequency.
The filter must provide 6dB/octave, that can be stablished by a series capacitor with the patch audio signal. Between the oscillator and driver, a buffer stage was inserted to prevent oscillations and increase isolation, high impedance at gate ( oscillator side) and low impedance at source terminal.
At MAV-11 output there are a sample frequency output to the pre-scaler ( if using PLL), and under the conditions of a high power, I added a resistive PI attenuator of 8 dB, it prevents not overload the pre-scaler input. The driver stage is the own MAV-11 with 12 dB of gain, I choose the 🔗 External reference
5 dBm, at my project I used a MWA-130 ( from Motorola) as driver stage. At second stage I used a 2N5109 (Motorola), but you can also use a 2N3866, and at final stage a 2N3553. With proper biasing and setting up the trimmers to maximum output power you can achieve around 2. 8 watts of EIRP using a 0 dBi antenna. A good irradiant system is also important, as well the coax cable that I recommend low loss cables if you are using a long cable distances.
RG-58A haves a 67% of propagation velocity and 21. 65 dB/100m of insertion loss at 146 MHz. I also recommend you use a low pass filter at final stage to prevent harmonics products cause harmful interferences on the MARS/CAP systems. Here in Brazil, many pirate radios don`t use such filter causing many trouble at MARS service. At final you can found many schematics, and of couse a suggested low pass chebyshev filter and the respective response frequency curve.
You will experience a low insertion loss within this filter, but not so expressive. The VCO can operate as free ( open loop) or synthesized (PLL) oscillator, you just must insert a jumper to close the loop for PLL or release it to free oscillator operation. The frequency deviation is controled by varactor diode that change the instrinsic capacitance within the voltage audio input causing a frequency deviation.
Note: set it to ± 75 KHz to FM pattern broadcast operation. Another varactor BB809 control the operation frequency, 200 KHz step increments is allowed at PLL schematic circuit at final of this page, the oscillator was constructed to operate in FM broadcast (88 to 108 MHZ) without any change in components. As hartley oscillator, if you wanna change the operation frequency just change the numbers of turns in the inductors at LC tank circuit.
As you know, decreasing the numbers of turns, you get upper frequencies, and vice-versa. Pay attention to start up the oscillator if you wanna change it to operate in high frequency than FM braodcast. Following the Barkhausen Criteria, we have a feedback in a simple amplifier and also sustain the oscillations, so the K fator( Loop gain) must be equal to one.
The MPF 102 oscillator transistor operates quite good until 150 MHz, a high Ft transistor will be required to high frequency operation. If you could use a network of varactors diode ( paralel association) to control the frequency deviation would be interesting because the BB809 have hyper abrupt curves.
Maybe MV209 in paralel produces less distortion and also ensure more linearity. At input ( audio signal), I did a pre-emphasis network to garantee that modulation index at high audio frequencies ( up 1KHz). At FM radio, the relation S/N depends of modulation index employed. The index decrease as modulation frequency increases, to a constant frequency deviation. Pre-emphasis is a high pass filter, that the cutoff frequency is slight upper of a maximum modulated frequency.
The filter must provide 6dB/octave, that can be stablished by a series capacitor with the patch audio signal. Between the oscillator and driver, a buffer stage was inserted to prevent oscillations and increase isolation, high impedance at gate ( oscillator side) and low impedance at source terminal.
At MAV-11 output there are a sample frequency output to the pre-scaler ( if using PLL), and under the conditions of a high power, I added a resistive PI attenuator of 8 dB, it prevents not overload the pre-scaler input. The driver stage is the own MAV-11 with 12 dB of gain, I choose the 🔗 External reference