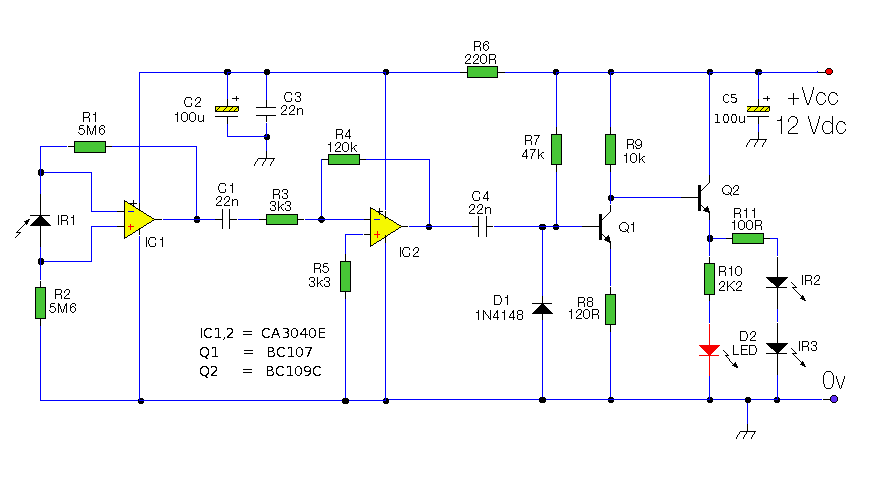
Micro-power 32.768kHz clock oscillator circuit
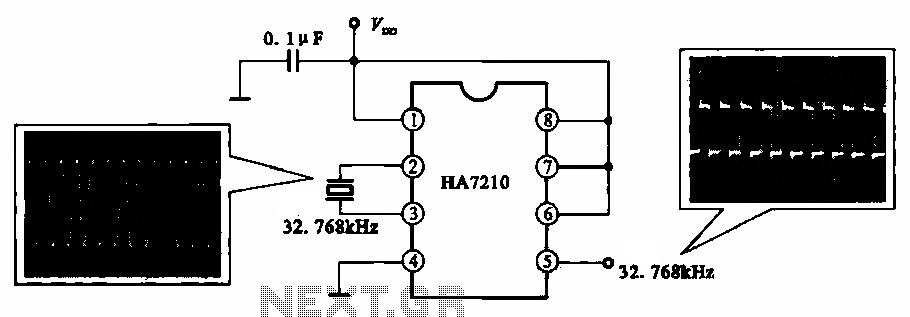
This circuit illustrates a 32.768 kHz micro-power clock oscillator, suitable for use in mobile phones, laptop computers, and home appliances. It generates a clock signal that can be utilized in various applications.
The 32.768 kHz micro-power clock oscillator circuit is designed to provide a stable and low-power clock signal, which is essential for timing applications in electronic devices. The circuit typically employs a crystal oscillator, which utilizes the mechanical resonance of a quartz crystal to produce a precise frequency.
In this configuration, the crystal is connected to an inverter or operational amplifier configured as an oscillator. The output of the oscillator is a square wave clock signal, which can be used to synchronize operations in digital circuits. The low power consumption of this oscillator makes it particularly advantageous for battery-operated devices, ensuring extended operational life.
The circuit should include output terminals that allow for the detection of the clock signal. These terminals enable interfacing with microcontrollers or other digital logic devices that require timing signals. The design may also incorporate decoupling capacitors to filter any noise and ensure stable operation of the oscillator.
Overall, the 32.768 kHz micro-power clock oscillator circuit is a critical component in modern electronic systems, providing essential timing functions while maintaining energy efficiency.Shows a 32.768 kl-b: micro-power clock oscillator circuit, and can be used in mobile phones, laptop computers and home appliances production generates a clock signal supplements. Feet should detect the output clock signal, detecting its feet , feet due oscillator signal.
The 32.768 kHz micro-power clock oscillator circuit is designed to provide a stable and low-power clock signal, which is essential for timing applications in electronic devices. The circuit typically employs a crystal oscillator, which utilizes the mechanical resonance of a quartz crystal to produce a precise frequency.
In this configuration, the crystal is connected to an inverter or operational amplifier configured as an oscillator. The output of the oscillator is a square wave clock signal, which can be used to synchronize operations in digital circuits. The low power consumption of this oscillator makes it particularly advantageous for battery-operated devices, ensuring extended operational life.
The circuit should include output terminals that allow for the detection of the clock signal. These terminals enable interfacing with microcontrollers or other digital logic devices that require timing signals. The design may also incorporate decoupling capacitors to filter any noise and ensure stable operation of the oscillator.
Overall, the 32.768 kHz micro-power clock oscillator circuit is a critical component in modern electronic systems, providing essential timing functions while maintaining energy efficiency.Shows a 32.768 kl-b: micro-power clock oscillator circuit, and can be used in mobile phones, laptop computers and home appliances production generates a clock signal supplements. Feet should detect the output clock signal, detecting its feet , feet due oscillator signal.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713