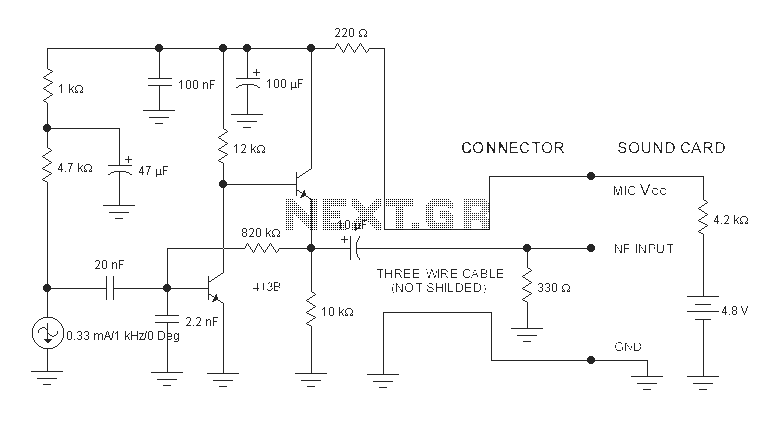
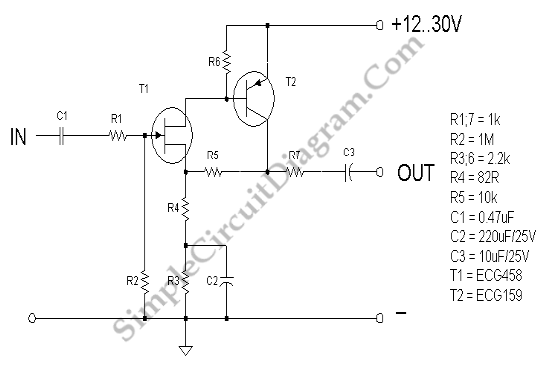
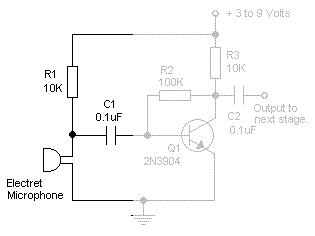
Microphone Preamp
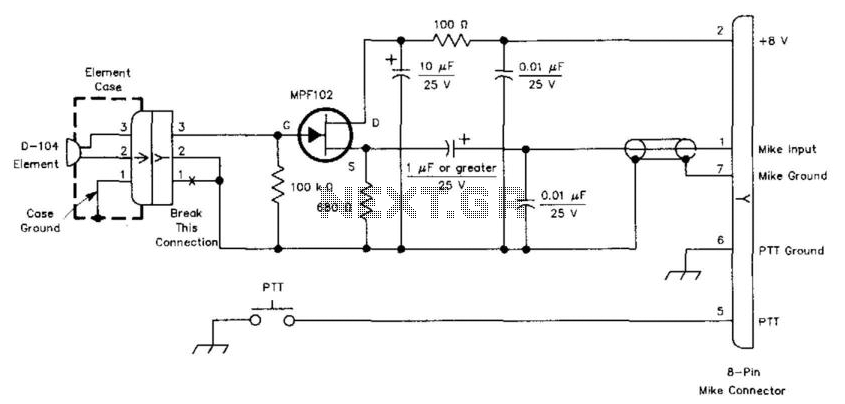
This circuit is designed to interface a high-impedance microphone with a radio transceiver that requires a low-impedance microphone. The power supply can be provided either by a battery or sourced from the transceiver itself.
This circuit typically employs a preamplifier configuration to convert the high-impedance microphone signal into a low-impedance output suitable for the radio transceiver. The preamplifier may consist of a transistor or operational amplifier (op-amp) to achieve the necessary gain and impedance transformation.
The microphone input is connected to the non-inverting input of the op-amp, while the output is connected to the transceiver's input. Biasing resistors may be utilized to ensure proper operation of the op-amp, and capacitors can be included for AC coupling to block any DC offset.
The choice of power supply, whether from a battery or the transceiver, should be considered carefully to ensure compatibility and to prevent any potential damage to the components. Power decoupling capacitors may also be added to the circuit to filter out noise from the power supply, thus enhancing the audio quality.
In summary, this circuit serves as an essential interface between a high-impedance microphone and a radio transceiver, effectively adapting the signal levels and impedances for optimal performance in audio transmission applications. This circuit is used to interface a high-impedance microphone to a radio transceiver that requires a low-impedance microp hone. The supply voltage can be either a battery or taken from the transceiver the circuit is used with.
This circuit typically employs a preamplifier configuration to convert the high-impedance microphone signal into a low-impedance output suitable for the radio transceiver. The preamplifier may consist of a transistor or operational amplifier (op-amp) to achieve the necessary gain and impedance transformation.
The microphone input is connected to the non-inverting input of the op-amp, while the output is connected to the transceiver's input. Biasing resistors may be utilized to ensure proper operation of the op-amp, and capacitors can be included for AC coupling to block any DC offset.
The choice of power supply, whether from a battery or the transceiver, should be considered carefully to ensure compatibility and to prevent any potential damage to the components. Power decoupling capacitors may also be added to the circuit to filter out noise from the power supply, thus enhancing the audio quality.
In summary, this circuit serves as an essential interface between a high-impedance microphone and a radio transceiver, effectively adapting the signal levels and impedances for optimal performance in audio transmission applications. This circuit is used to interface a high-impedance microphone to a radio transceiver that requires a low-impedance microp hone. The supply voltage can be either a battery or taken from the transceiver the circuit is used with.