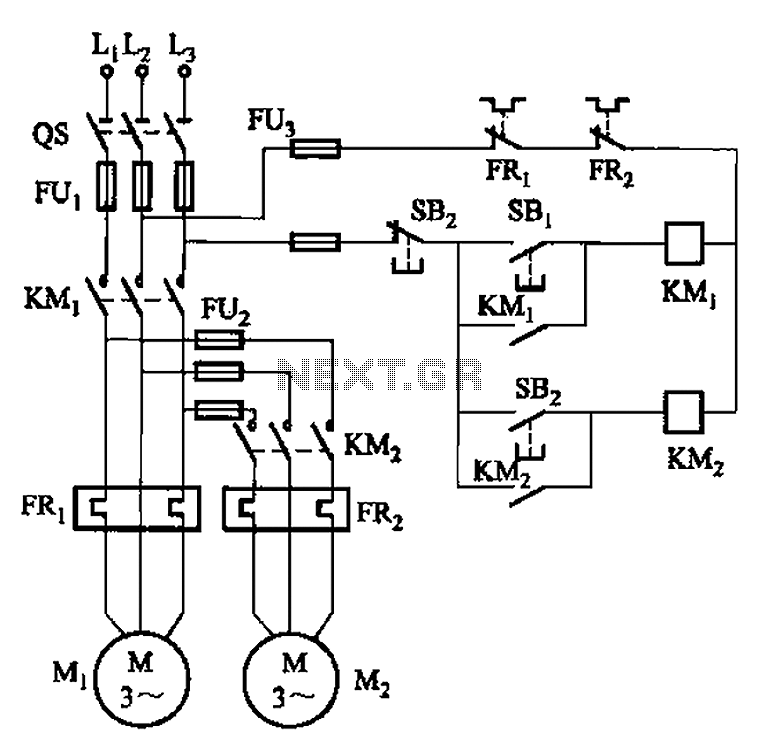
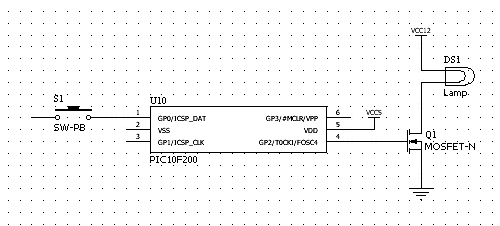
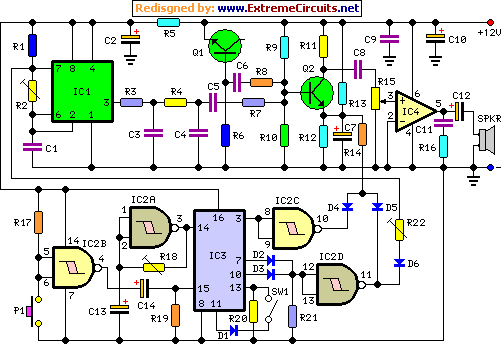
Nine one-way operation of the dynamic braking circuit
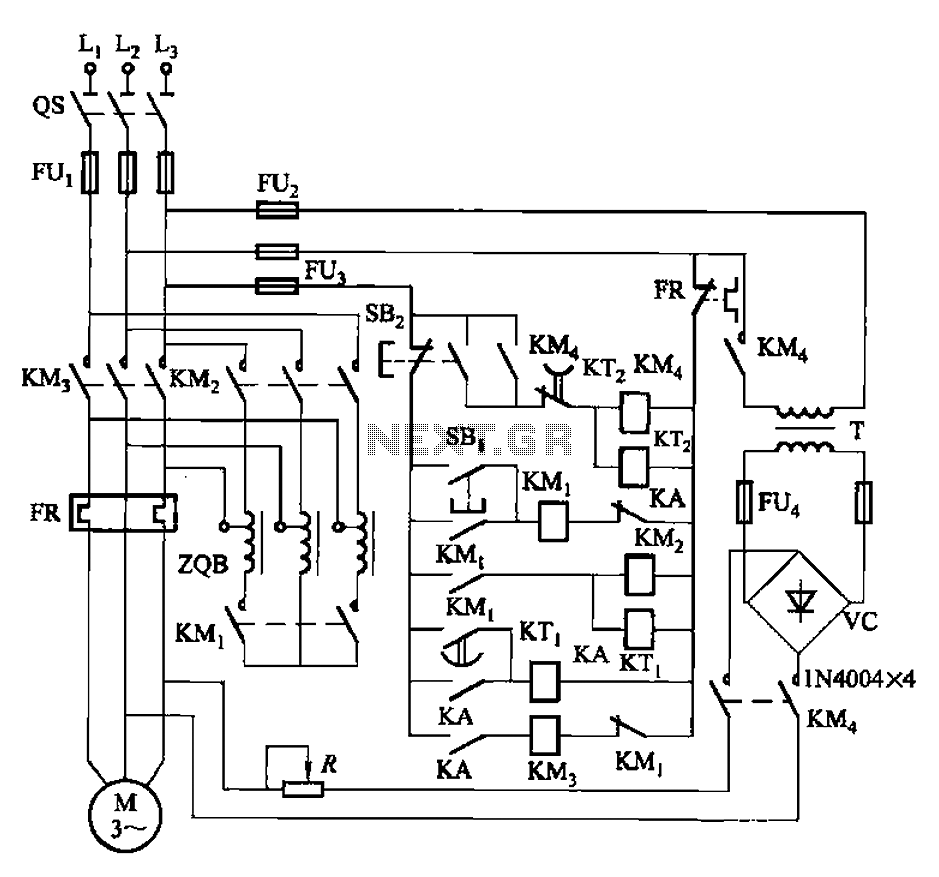
The circuit is illustrated in Figure 3-141. It includes a line autotransformer for voltage starting and dynamic braking. The circuit features a buck start button (SBi) and a stop button (SBz). The buck start-up time is controlled by the time relay KT1, while the dynamic braking duration is adjustable through the time relay KT2, which can be set between 2 to 3 seconds.
The circuit diagram in Figure 3-141 represents a control system utilizing an autotransformer for voltage regulation during motor startup and dynamic braking operations. The autotransformer serves as a variable voltage source, allowing for a smooth increase in voltage applied to the motor, thereby reducing inrush current and mechanical stress. This is particularly beneficial in applications requiring gradual acceleration.
The buck start button (SBi) initiates the startup sequence, engaging the autotransformer to provide the necessary voltage to the motor. The operation of the motor can be halted using the stop button (SBz), which interrupts the power supply.
The buck start-up time is managed by time relay KT1. This relay ensures that the voltage ramp-up is controlled over a predetermined duration, minimizing the risk of electrical and mechanical shock to the system. The specific time delay can be adjusted based on system requirements to optimize performance.
Dynamic braking is an essential feature for quickly stopping the motor and is controlled by time relay KT2. This relay offers an adjustable braking time ranging from 2 to 3 seconds, allowing for customization based on the load characteristics and operational needs. The dynamic braking function dissipates the kinetic energy of the motor, converting it to heat, which is then managed by the braking resistors in the circuit.
In summary, this circuit design effectively integrates an autotransformer for controlled voltage application during startup and employs time relays to manage both the startup and braking processes, ensuring efficient and safe operation of the motor system. Circuit shown in Figure 3-141. The line autotransformer voltage starting, dynamic braking. Figure, SBi buck start button, SBz the stop button. Buck start-up time by the time re lay KT] control. Dynamic braking time is determined by the time relay KT2 (2 ~ 3s adjustable).
The circuit diagram in Figure 3-141 represents a control system utilizing an autotransformer for voltage regulation during motor startup and dynamic braking operations. The autotransformer serves as a variable voltage source, allowing for a smooth increase in voltage applied to the motor, thereby reducing inrush current and mechanical stress. This is particularly beneficial in applications requiring gradual acceleration.
The buck start button (SBi) initiates the startup sequence, engaging the autotransformer to provide the necessary voltage to the motor. The operation of the motor can be halted using the stop button (SBz), which interrupts the power supply.
The buck start-up time is managed by time relay KT1. This relay ensures that the voltage ramp-up is controlled over a predetermined duration, minimizing the risk of electrical and mechanical shock to the system. The specific time delay can be adjusted based on system requirements to optimize performance.
Dynamic braking is an essential feature for quickly stopping the motor and is controlled by time relay KT2. This relay offers an adjustable braking time ranging from 2 to 3 seconds, allowing for customization based on the load characteristics and operational needs. The dynamic braking function dissipates the kinetic energy of the motor, converting it to heat, which is then managed by the braking resistors in the circuit.
In summary, this circuit design effectively integrates an autotransformer for controlled voltage application during startup and employs time relays to manage both the startup and braking processes, ensuring efficient and safe operation of the motor system. Circuit shown in Figure 3-141. The line autotransformer voltage starting, dynamic braking. Figure, SBi buck start button, SBz the stop button. Buck start-up time by the time re lay KT] control. Dynamic braking time is determined by the time relay KT2 (2 ~ 3s adjustable).