One 2N2222 Transistor Code Lock
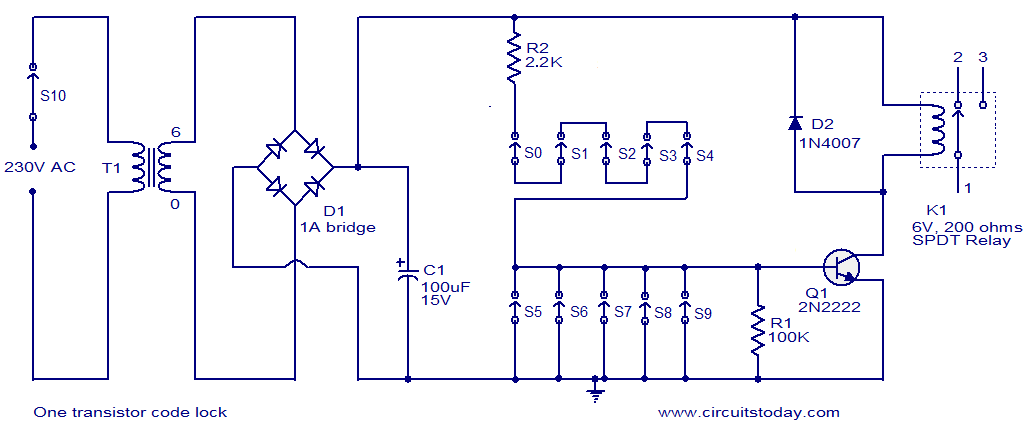
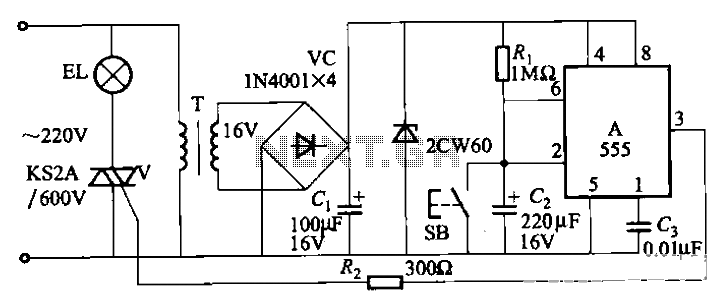
The circuit consists of a basic transistor switch with a relay connected at its collector as the load. This represents a straightforward electronic code lock circuit that employs a single transistor.
The circuit operates by utilizing a transistor as a switch to control the relay. When a specific input signal, typically a voltage from a keypad or another control mechanism, is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This action energizes the relay coil, causing the relay to switch its contacts and thereby control a connected load, such as a light or an electronic device.
In this configuration, the transistor is usually an NPN type, which is common for switching applications. The base of the transistor is connected to a resistor to limit the current flowing into it, ensuring that the transistor operates within safe parameters. The relay, which acts as the load, is designed to handle higher currents than the transistor can manage directly, allowing for the control of larger devices.
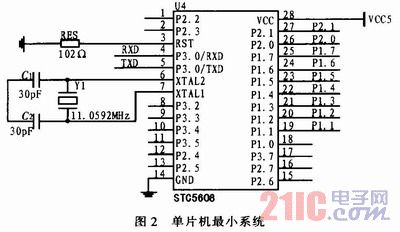
The code lock functionality can be implemented by integrating a keypad or a series of switches that provide the necessary input signal to the transistor. A microcontroller can also be employed to decode the input and provide additional features, such as timed access or multiple user codes.
Overall, this simple transistor switch circuit with a relay provides an effective means of controlling electrical devices based on specific input conditions, making it a versatile solution for various electronic locking applications.The circuit is nothing but a simple transistor switch with a relay at its collector as load. The simplest electronic code lock circuit uses one .. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a transistor as a switch to control the relay. When a specific input signal, typically a voltage from a keypad or another control mechanism, is applied to the base of the transistor, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter. This action energizes the relay coil, causing the relay to switch its contacts and thereby control a connected load, such as a light or an electronic device.
In this configuration, the transistor is usually an NPN type, which is common for switching applications. The base of the transistor is connected to a resistor to limit the current flowing into it, ensuring that the transistor operates within safe parameters. The relay, which acts as the load, is designed to handle higher currents than the transistor can manage directly, allowing for the control of larger devices.
The code lock functionality can be implemented by integrating a keypad or a series of switches that provide the necessary input signal to the transistor. A microcontroller can also be employed to decode the input and provide additional features, such as timed access or multiple user codes.
Overall, this simple transistor switch circuit with a relay provides an effective means of controlling electrical devices based on specific input conditions, making it a versatile solution for various electronic locking applications.The circuit is nothing but a simple transistor switch with a relay at its collector as load. The simplest electronic code lock circuit uses one .. 🔗 External reference