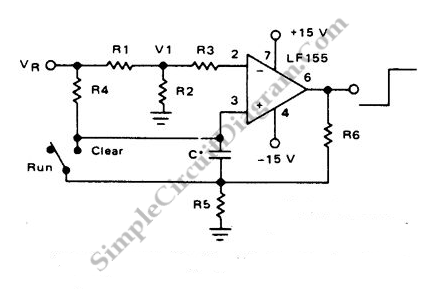
Op Amp Classic Gain and Linearity Testing
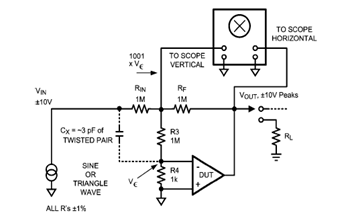
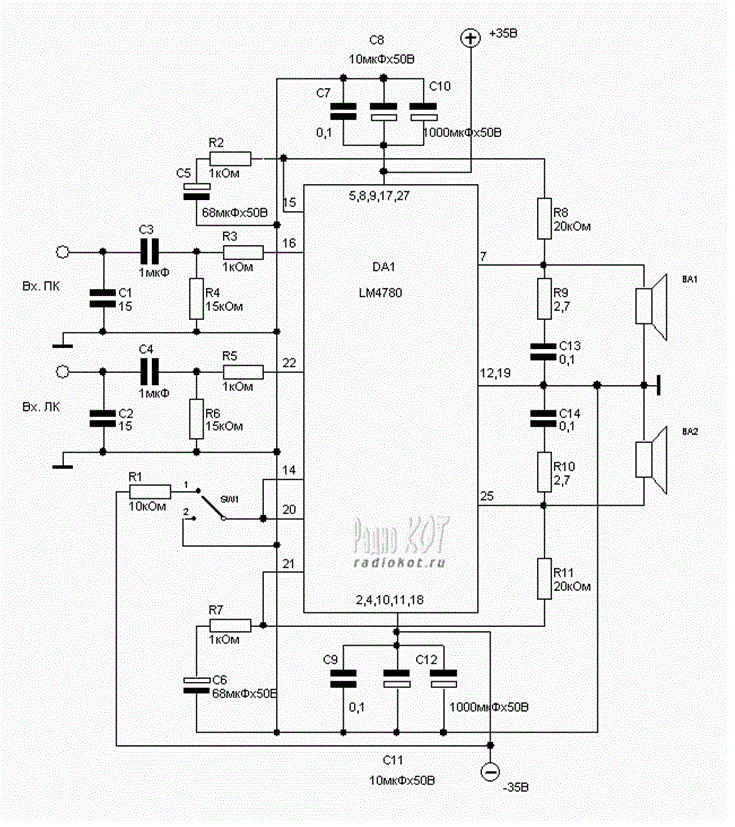
The diagram below illustrates a classic test fixture that has been utilized for an extended period to assist individuals in addressing non-linearity errors.
The classic test fixture depicted in the diagram serves as a fundamental tool in electronics testing and calibration. It is designed to evaluate and rectify non-linearity errors that may arise in various electronic components and systems. This fixture typically consists of a stable reference signal source, which generates a known input signal, and a measurement system that captures the output response of the device under test (DUT).
Key components of the test fixture may include precision resistors, operational amplifiers, and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) to ensure accurate signal conditioning and measurement. The setup often incorporates a user-friendly interface, allowing technicians to easily adjust parameters and monitor performance metrics.
The test fixture operates by applying a series of input signals of varying amplitudes and frequencies to the DUT. The output is then measured and compared against the expected linear response. Any deviations from the expected output indicate non-linearity, which can be further analyzed to identify the root cause and implement corrective measures.
In addition, the fixture may include calibration routines and software integration, enabling automated testing and data logging for performance analysis over time. This capability is essential for maintaining the reliability and accuracy of electronic components in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems.
Overall, the classic test fixture plays a crucial role in ensuring the precision and reliability of electronic devices by systematically addressing non-linearity errors, thereby enhancing overall product quality and performance.Diagram below shows you with a classic test fixture that has been used for long periods in order to give anyone for resolving the non-linearity errors for. 🔗 External reference
The classic test fixture depicted in the diagram serves as a fundamental tool in electronics testing and calibration. It is designed to evaluate and rectify non-linearity errors that may arise in various electronic components and systems. This fixture typically consists of a stable reference signal source, which generates a known input signal, and a measurement system that captures the output response of the device under test (DUT).
Key components of the test fixture may include precision resistors, operational amplifiers, and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) to ensure accurate signal conditioning and measurement. The setup often incorporates a user-friendly interface, allowing technicians to easily adjust parameters and monitor performance metrics.
The test fixture operates by applying a series of input signals of varying amplitudes and frequencies to the DUT. The output is then measured and compared against the expected linear response. Any deviations from the expected output indicate non-linearity, which can be further analyzed to identify the root cause and implement corrective measures.
In addition, the fixture may include calibration routines and software integration, enabling automated testing and data logging for performance analysis over time. This capability is essential for maintaining the reliability and accuracy of electronic components in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems.
Overall, the classic test fixture plays a crucial role in ensuring the precision and reliability of electronic devices by systematically addressing non-linearity errors, thereby enhancing overall product quality and performance.Diagram below shows you with a classic test fixture that has been used for long periods in order to give anyone for resolving the non-linearity errors for. 🔗 External reference