Oscillator Simulation Example Using RINCON
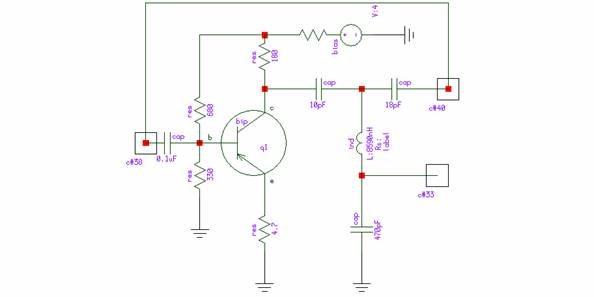
To demonstrate Rincon's capability to simulate autonomous circuits, a one-transistor oscillator utilizing a phase-inverting resonance T-shape LC circuit is considered. The schematic of this simulator is illustrated in Figure 1. The design of the simulator is detailed in reference [2]. For the simulation purpose, attention will first be given to the component models. The proposed circuit will then be subjected to a frequency sweep to determine the oscillation conditions. Subsequently, a time domain simulation will be conducted using the MHB solver. The code includes a frequency parameter in the generic interface of the entity, allowing the frequency value to be passed externally. This frequency is utilized by the voltage source, vin, which is set to an amplitude of 0.001 to ensure the signal remains small. Since Rincon does not support small signal AC simulation, large-signal simulation will be employed to compute the necessary quantities. This report illustrates how to utilize the Rincon VHDL-AMS/FD simulator for time domain simulations of oscillators, including how to simulate an open-loop cascade and set initial conditions to initiate oscillator simulations. Instructions are provided on running the simulator in various modes, including Harmonic Balance (HB) and Modulated Harmonic Balance (MHB).
The one-transistor oscillator described operates based on the principles of resonance within an LC circuit, which is characterized by its ability to oscillate at specific frequencies determined by the inductance (L) and capacitance (C) values. The phase-inverting configuration allows for the necessary feedback to sustain oscillations. The Rincon simulator facilitates the simulation of this oscillator by allowing the user to define component models accurately, which are critical for achieving realistic simulation results.
In the frequency sweep analysis, the simulator systematically varies the frequency of the input signal to identify the range over which oscillation can be sustained. This process helps to pinpoint the resonant frequency of the circuit, where the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal, leading to maximum voltage oscillations. Following this, the time domain simulation using the MHB solver provides insight into the transient behavior of the oscillator, illustrating how it responds to initial conditions and external perturbations.
The inclusion of a small amplitude for the input voltage source is crucial for ensuring that the simulation remains within the linear operating region of the transistor, allowing for accurate modeling of the oscillatory behavior without introducing significant distortion. The large-signal simulation approach compensates for the lack of small-signal AC simulation capabilities in Rincon, ensuring that the nonlinear characteristics of the transistor are adequately captured.
The report also emphasizes the versatility of the Rincon simulator, detailing how it can be operated in different modes such as HB and MHB. The HB mode is useful for steady-state analysis of periodic signals, while MHB is advantageous for analyzing modulated signals, providing a comprehensive toolkit for engineers to explore the dynamic behavior of oscillators and similar circuits. This capability is essential for the design and optimization of modern electronic systems where oscillators play a pivotal role in signal generation and processing.To demonstrate Rincon`s capability to simulate autonomous circuits, let us consider one-transistor oscillator, which uses phase-inverting resonance T-shape LC circuit. Schematic of this simulator is shown at fig. 1. Design of simulator is described in details in [2]. For purpose of simulation, let us pay attention to component models first. Then proposed circuit will be simulated in frequency sweep to look does oscillation condition are possible. After that time domain (using MHB solver) simulation will be performed. That code contains f in generic interface of entity. That means that frequency value may be passed there from outside. This frequency is used by vin voltage source. Amplitude of that source is set to 0. 001 to be sure that signal is really small. Rincon does not contain small signal AC simulation, so large-signal simulation is used to compute quantities. This report shows how to use Rincon VHDL-AMS/FD simulator to simulate oscillators in time domain - how to simulate open loop cascade, set up initial condition to start oscillator simulations.
Shown how to run simulator in different modes HB and MHB (Harmonic Balance and Modulated Harmonic Balance). 🔗 External reference
The one-transistor oscillator described operates based on the principles of resonance within an LC circuit, which is characterized by its ability to oscillate at specific frequencies determined by the inductance (L) and capacitance (C) values. The phase-inverting configuration allows for the necessary feedback to sustain oscillations. The Rincon simulator facilitates the simulation of this oscillator by allowing the user to define component models accurately, which are critical for achieving realistic simulation results.
In the frequency sweep analysis, the simulator systematically varies the frequency of the input signal to identify the range over which oscillation can be sustained. This process helps to pinpoint the resonant frequency of the circuit, where the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal, leading to maximum voltage oscillations. Following this, the time domain simulation using the MHB solver provides insight into the transient behavior of the oscillator, illustrating how it responds to initial conditions and external perturbations.
The inclusion of a small amplitude for the input voltage source is crucial for ensuring that the simulation remains within the linear operating region of the transistor, allowing for accurate modeling of the oscillatory behavior without introducing significant distortion. The large-signal simulation approach compensates for the lack of small-signal AC simulation capabilities in Rincon, ensuring that the nonlinear characteristics of the transistor are adequately captured.
The report also emphasizes the versatility of the Rincon simulator, detailing how it can be operated in different modes such as HB and MHB. The HB mode is useful for steady-state analysis of periodic signals, while MHB is advantageous for analyzing modulated signals, providing a comprehensive toolkit for engineers to explore the dynamic behavior of oscillators and similar circuits. This capability is essential for the design and optimization of modern electronic systems where oscillators play a pivotal role in signal generation and processing.To demonstrate Rincon`s capability to simulate autonomous circuits, let us consider one-transistor oscillator, which uses phase-inverting resonance T-shape LC circuit. Schematic of this simulator is shown at fig. 1. Design of simulator is described in details in [2]. For purpose of simulation, let us pay attention to component models first. Then proposed circuit will be simulated in frequency sweep to look does oscillation condition are possible. After that time domain (using MHB solver) simulation will be performed. That code contains f in generic interface of entity. That means that frequency value may be passed there from outside. This frequency is used by vin voltage source. Amplitude of that source is set to 0. 001 to be sure that signal is really small. Rincon does not contain small signal AC simulation, so large-signal simulation is used to compute quantities. This report shows how to use Rincon VHDL-AMS/FD simulator to simulate oscillators in time domain - how to simulate open loop cascade, set up initial condition to start oscillator simulations.
Shown how to run simulator in different modes HB and MHB (Harmonic Balance and Modulated Harmonic Balance). 🔗 External reference