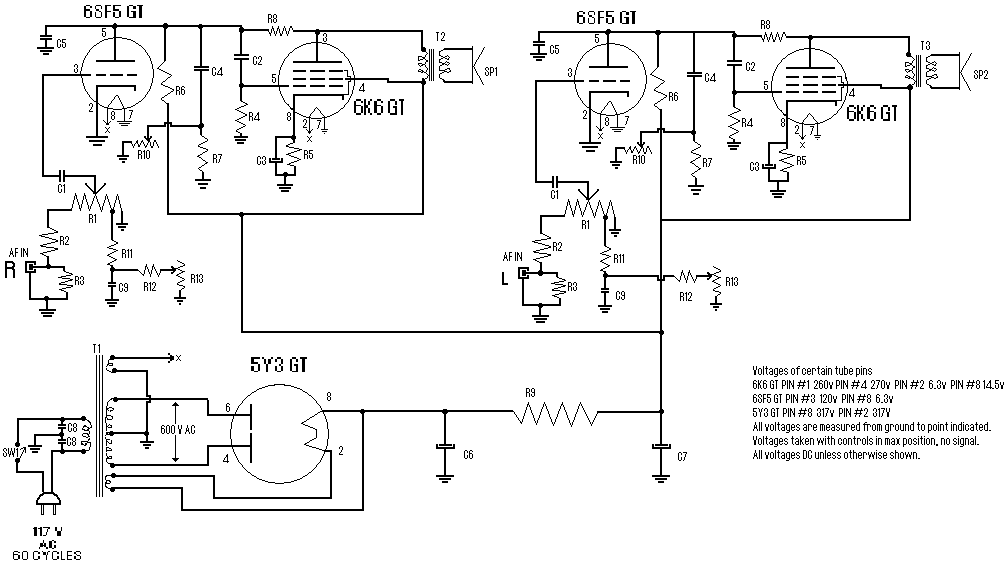
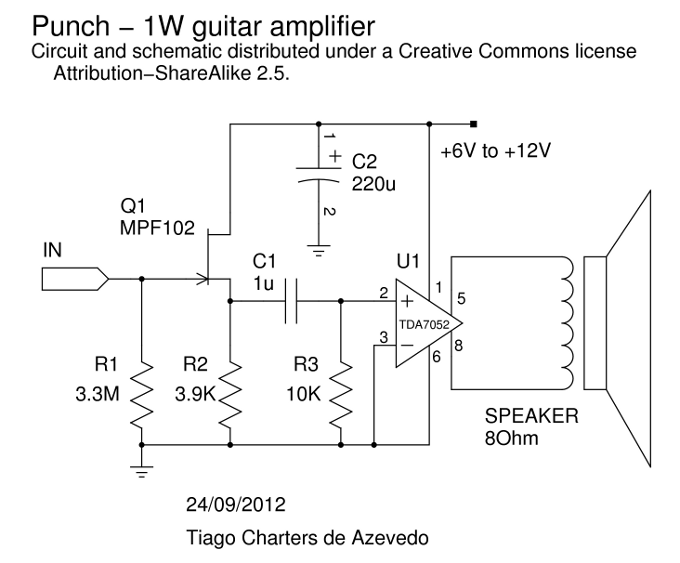
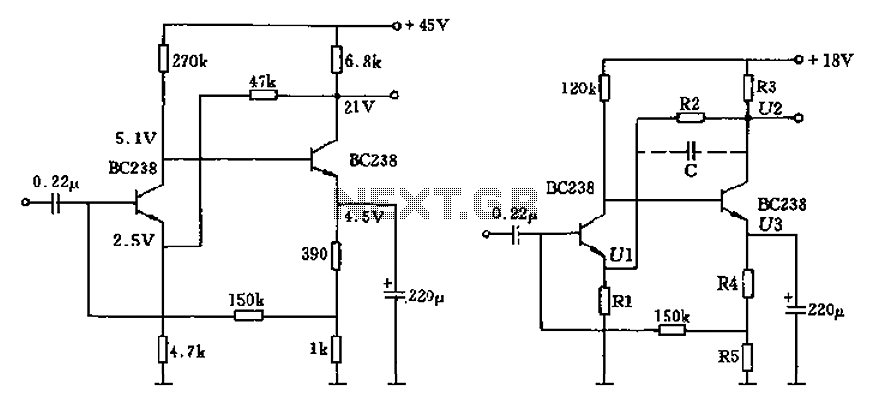
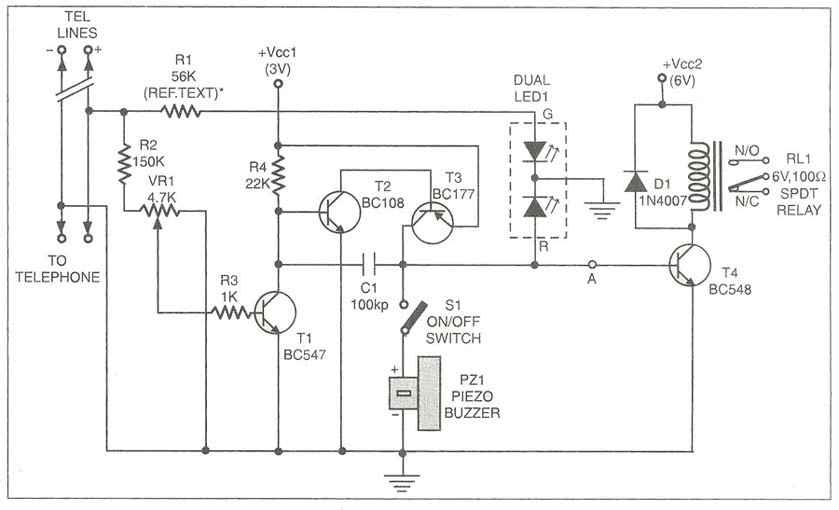
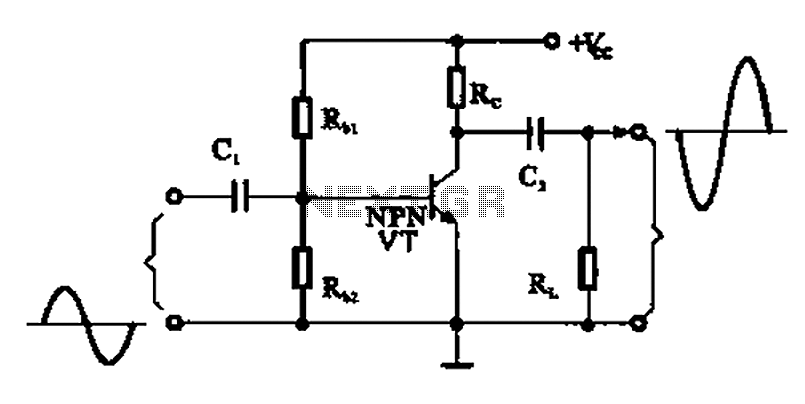
Phone Jammer linear amplifier
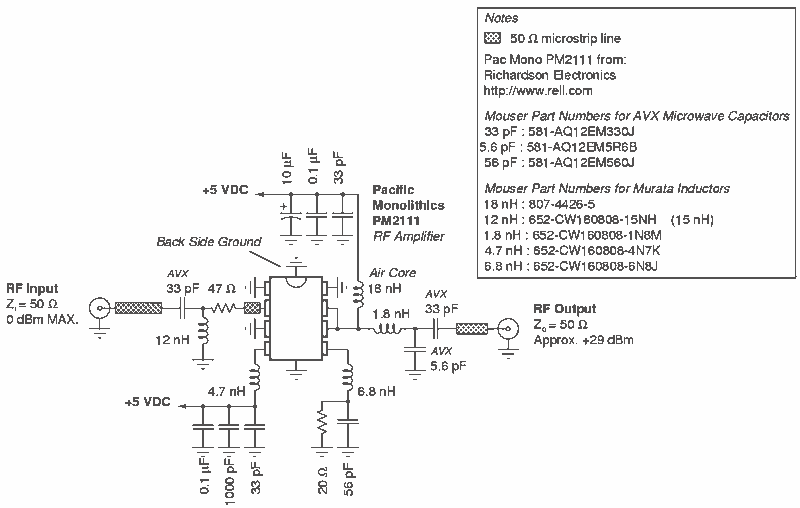
RF Power Amplifier 1 Watt. Jams Cellular Downlink Band: 800-950 MHz.
The RF power amplifier described is designed to operate within the cellular downlink frequency range of 800 to 950 MHz, delivering an output power of 1 Watt. Such amplifiers are crucial in communication systems, particularly for enhancing signal strength in various applications, including jamming scenarios.
The amplifier typically consists of several key components: a transistor, which serves as the active device for signal amplification; biasing circuits to set the operating point of the transistor; impedance matching networks to ensure efficient power transfer between stages and to the load; and a heat sink for thermal management, as power amplifiers generate significant heat during operation.
In the context of jamming, this amplifier would be used to disrupt communication signals within the specified frequency range. The design would need to incorporate features that allow for stable operation under varying load conditions and the ability to handle high-frequency signals without distortion.
The input stage may include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) to boost the incoming signal before it is processed by the main amplification stage. Following amplification, a filtering stage is often employed to suppress unwanted harmonics and ensure that the output signal remains within the desired frequency band.
Power supply considerations are also critical, requiring a stable DC supply that can handle the current demands of the amplifier. Additionally, protection circuits may be included to prevent damage from over-voltage or over-current conditions, ensuring reliable long-term operation.
Overall, the design of an RF power amplifier for jamming applications involves a careful balance of performance, efficiency, and reliability, suitable for the intended operational environment.RF Power Amplifier 1 Watt. Jams Cellular Downlink Band: 800-950 MHz. 🔗 External reference
The RF power amplifier described is designed to operate within the cellular downlink frequency range of 800 to 950 MHz, delivering an output power of 1 Watt. Such amplifiers are crucial in communication systems, particularly for enhancing signal strength in various applications, including jamming scenarios.
The amplifier typically consists of several key components: a transistor, which serves as the active device for signal amplification; biasing circuits to set the operating point of the transistor; impedance matching networks to ensure efficient power transfer between stages and to the load; and a heat sink for thermal management, as power amplifiers generate significant heat during operation.
In the context of jamming, this amplifier would be used to disrupt communication signals within the specified frequency range. The design would need to incorporate features that allow for stable operation under varying load conditions and the ability to handle high-frequency signals without distortion.
The input stage may include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) to boost the incoming signal before it is processed by the main amplification stage. Following amplification, a filtering stage is often employed to suppress unwanted harmonics and ensure that the output signal remains within the desired frequency band.
Power supply considerations are also critical, requiring a stable DC supply that can handle the current demands of the amplifier. Additionally, protection circuits may be included to prevent damage from over-voltage or over-current conditions, ensuring reliable long-term operation.
Overall, the design of an RF power amplifier for jamming applications involves a careful balance of performance, efficiency, and reliability, suitable for the intended operational environment.RF Power Amplifier 1 Watt. Jams Cellular Downlink Band: 800-950 MHz. 🔗 External reference