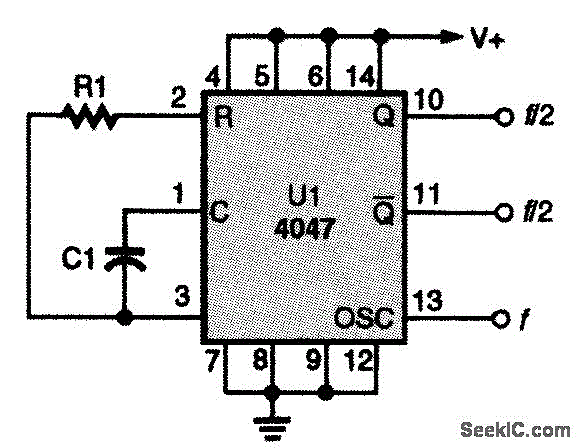
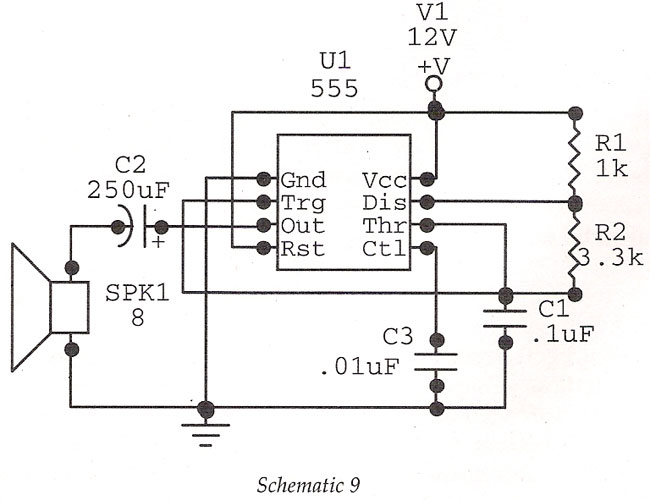
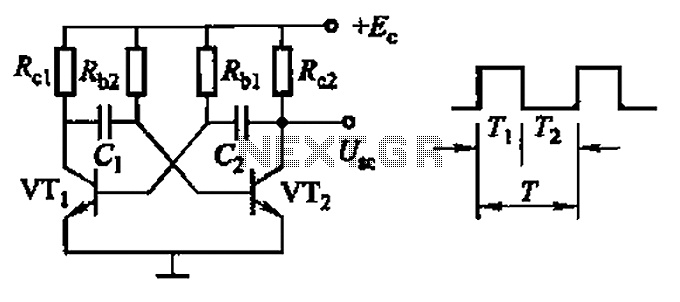
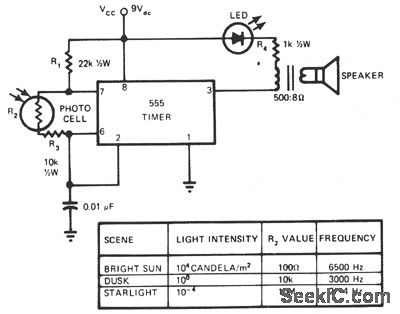
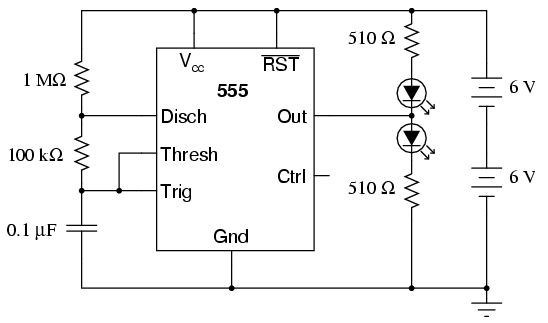
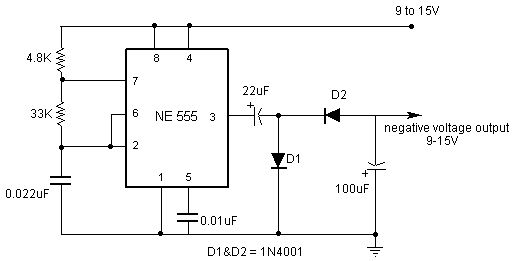
Pierce oscillator
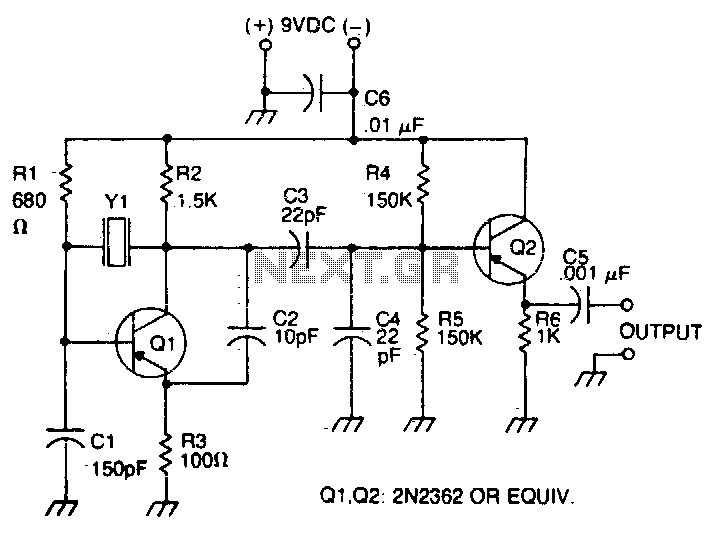
The oscillator transistor is Q1, and the crystal is placed between the collector and base. Feedback is improved by the use of the collector-emitter capacitor C2. Transistor Q2 is used as an output buffer.
The circuit described features an oscillator configuration utilizing a transistor (Q1) in conjunction with a crystal for frequency stabilization. The crystal is strategically positioned between the collector and base of Q1, which facilitates the generation of oscillations at a precise frequency determined by the characteristics of the crystal. This setup is typical in oscillator circuits where stability and accuracy are paramount.
To enhance feedback within the circuit, a capacitor (C2) is connected across the collector-emitter junction of Q1. This capacitor plays a critical role in shaping the feedback loop, ensuring that the oscillations are sustained and stable. The inclusion of C2 allows for better control over the phase shift and gain, contributing to improved performance of the oscillator.
Additionally, transistor Q2 serves as an output buffer. This component is essential for isolating the oscillator stage from subsequent circuitry, thereby preventing loading effects that could dampen the oscillations. The output buffer allows for a stronger drive capability, enabling the oscillator to interface effectively with other components or stages of the circuit without compromising the integrity of the oscillation signal.
Overall, this configuration exemplifies a common approach in electronic oscillator design, where stability, feedback control, and output buffering are critical considerations for successful operation.The oscillator transistor is Ql, and the crystal is placed between the collector and base. Feedback is improved by the use of the collector-emitter capacitor C2 Transistor Q2 is used as an output buffer. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described features an oscillator configuration utilizing a transistor (Q1) in conjunction with a crystal for frequency stabilization. The crystal is strategically positioned between the collector and base of Q1, which facilitates the generation of oscillations at a precise frequency determined by the characteristics of the crystal. This setup is typical in oscillator circuits where stability and accuracy are paramount.
To enhance feedback within the circuit, a capacitor (C2) is connected across the collector-emitter junction of Q1. This capacitor plays a critical role in shaping the feedback loop, ensuring that the oscillations are sustained and stable. The inclusion of C2 allows for better control over the phase shift and gain, contributing to improved performance of the oscillator.
Additionally, transistor Q2 serves as an output buffer. This component is essential for isolating the oscillator stage from subsequent circuitry, thereby preventing loading effects that could dampen the oscillations. The output buffer allows for a stronger drive capability, enabling the oscillator to interface effectively with other components or stages of the circuit without compromising the integrity of the oscillation signal.
Overall, this configuration exemplifies a common approach in electronic oscillator design, where stability, feedback control, and output buffering are critical considerations for successful operation.The oscillator transistor is Ql, and the crystal is placed between the collector and base. Feedback is improved by the use of the collector-emitter capacitor C2 Transistor Q2 is used as an output buffer. 🔗 External reference