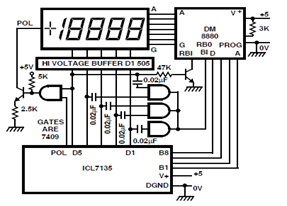
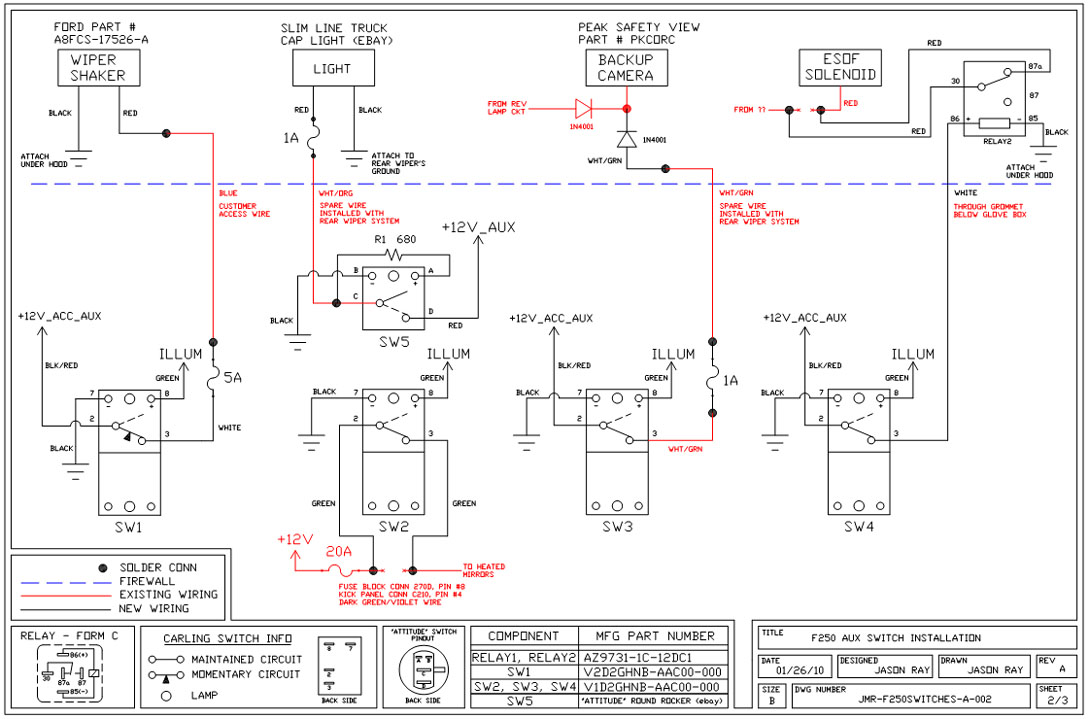
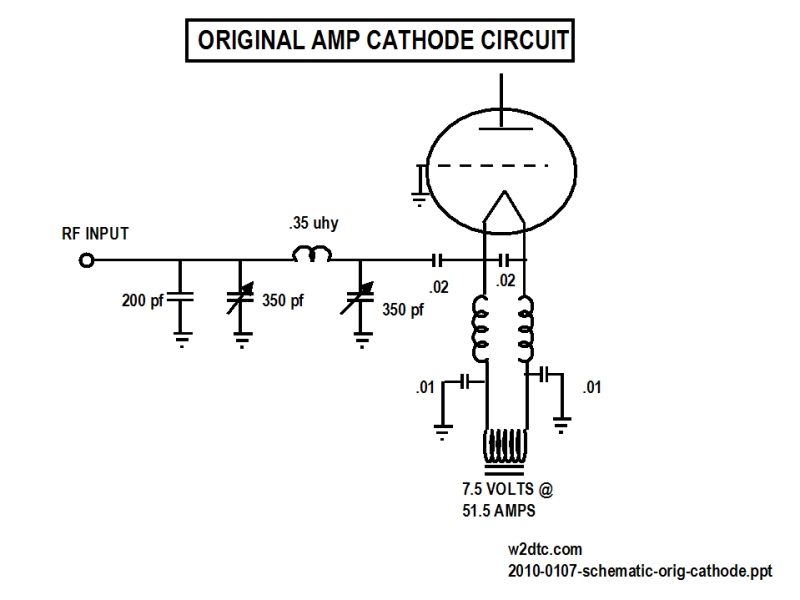
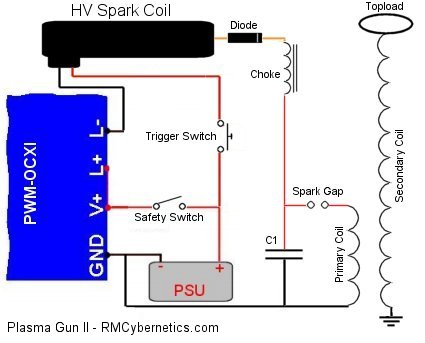
Plasma propulsion Lifter EM Antigravity
The interior of a sphere maintains a constant potential of zero volts, allowing it to continuously receive charge from the coil-pack.
The concept of a spherical conductor maintaining a zero-volt potential is rooted in electrostatics, particularly in the behavior of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium. When a conductive sphere is charged, the charge distributes itself uniformly across the surface of the sphere. This results in the electric field inside the sphere being zero, which is a fundamental property of conductors.
In practical applications, when a coil-pack is introduced to this system, it can induce a voltage that may lead to the transfer of charge to the sphere. The coil-pack, often used in ignition systems or electromagnetic devices, generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in nearby conductive materials, including the sphere.
As the sphere continues to receive charge from the coil-pack, it can lead to various outcomes depending on the circuit design and the components involved. For instance, if the sphere is connected to a load, the continuous charging can result in a steady voltage output, which can be harnessed for powering devices. Alternatively, if the sphere is not properly managed, it may lead to issues such as dielectric breakdown or excessive current draw, which can damage circuit components.
To effectively integrate this concept into an electronic schematic, it is essential to include components such as the coil-pack, the conductive sphere, and any necessary load or regulation circuitry. The schematic should illustrate the connections between the coil-pack and the sphere, showing how the induced charge can be utilized or stored. Additionally, incorporating safety features such as voltage clamps or current limiting resistors would be prudent to prevent potential damage from overcharging or excessive current flow.
Overall, the interaction between the coil-pack and the conductive sphere presents a unique opportunity for energy transfer and storage in electronic applications, warranting careful consideration in circuit design and implementation.Originally Posted by Harvey The inside of a sphere is always zero volts potential, so it will keep taking new charge indefinitely from the coil-pack 🔗 External reference
The concept of a spherical conductor maintaining a zero-volt potential is rooted in electrostatics, particularly in the behavior of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium. When a conductive sphere is charged, the charge distributes itself uniformly across the surface of the sphere. This results in the electric field inside the sphere being zero, which is a fundamental property of conductors.
In practical applications, when a coil-pack is introduced to this system, it can induce a voltage that may lead to the transfer of charge to the sphere. The coil-pack, often used in ignition systems or electromagnetic devices, generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. This changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in nearby conductive materials, including the sphere.
As the sphere continues to receive charge from the coil-pack, it can lead to various outcomes depending on the circuit design and the components involved. For instance, if the sphere is connected to a load, the continuous charging can result in a steady voltage output, which can be harnessed for powering devices. Alternatively, if the sphere is not properly managed, it may lead to issues such as dielectric breakdown or excessive current draw, which can damage circuit components.
To effectively integrate this concept into an electronic schematic, it is essential to include components such as the coil-pack, the conductive sphere, and any necessary load or regulation circuitry. The schematic should illustrate the connections between the coil-pack and the sphere, showing how the induced charge can be utilized or stored. Additionally, incorporating safety features such as voltage clamps or current limiting resistors would be prudent to prevent potential damage from overcharging or excessive current flow.
Overall, the interaction between the coil-pack and the conductive sphere presents a unique opportunity for energy transfer and storage in electronic applications, warranting careful consideration in circuit design and implementation.Originally Posted by Harvey The inside of a sphere is always zero volts potential, so it will keep taking new charge indefinitely from the coil-pack 🔗 External reference