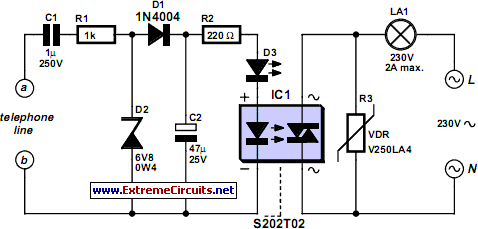
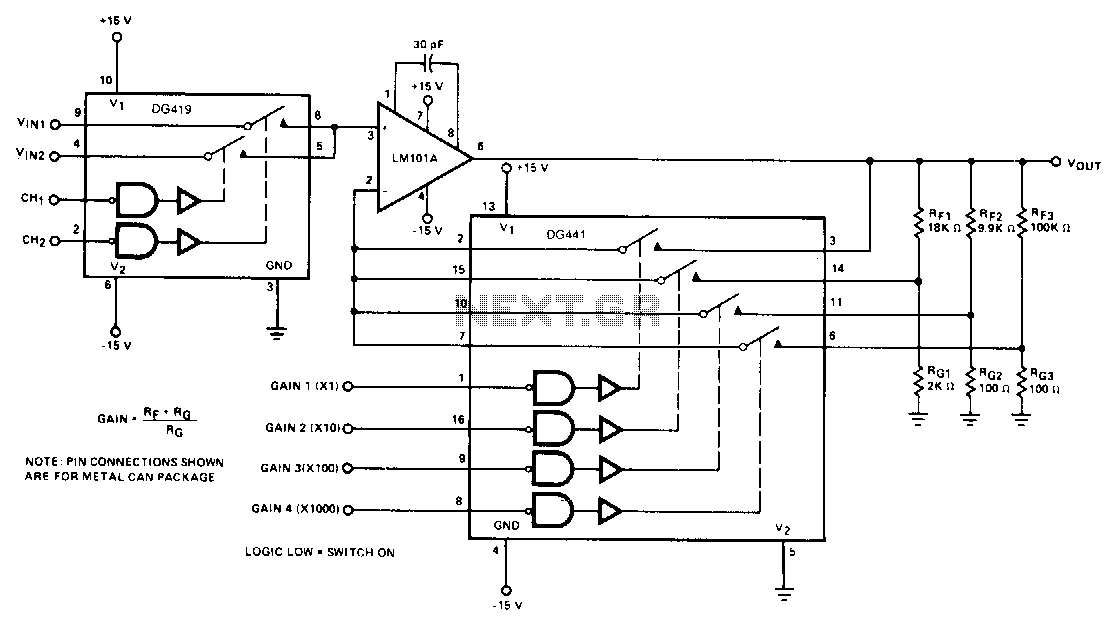
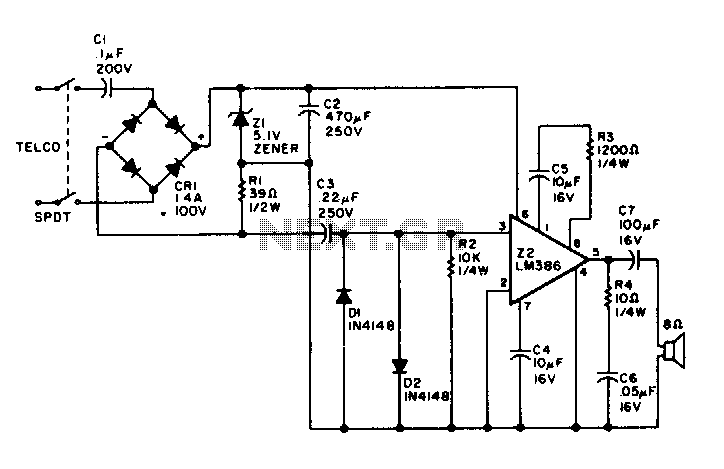
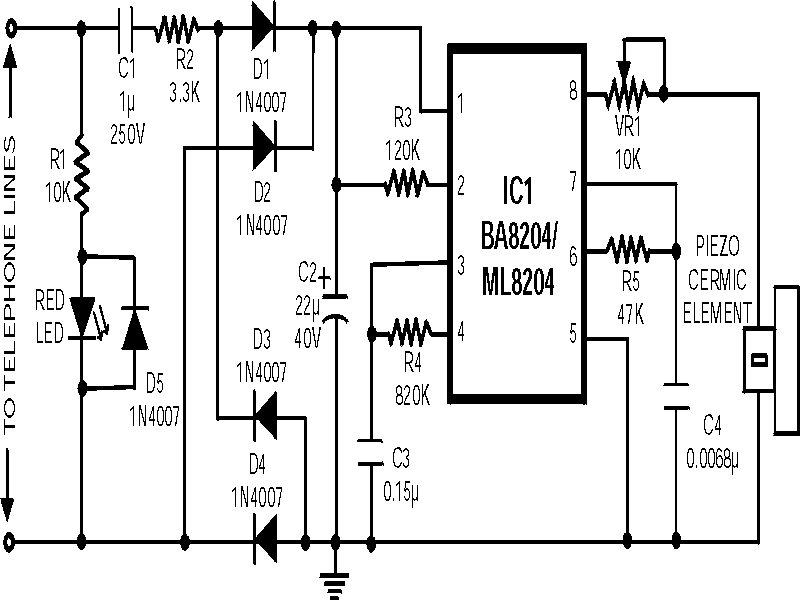
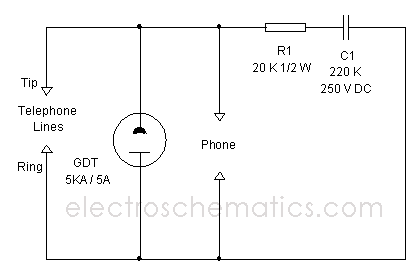
Programmable multi-tone telephone ringer
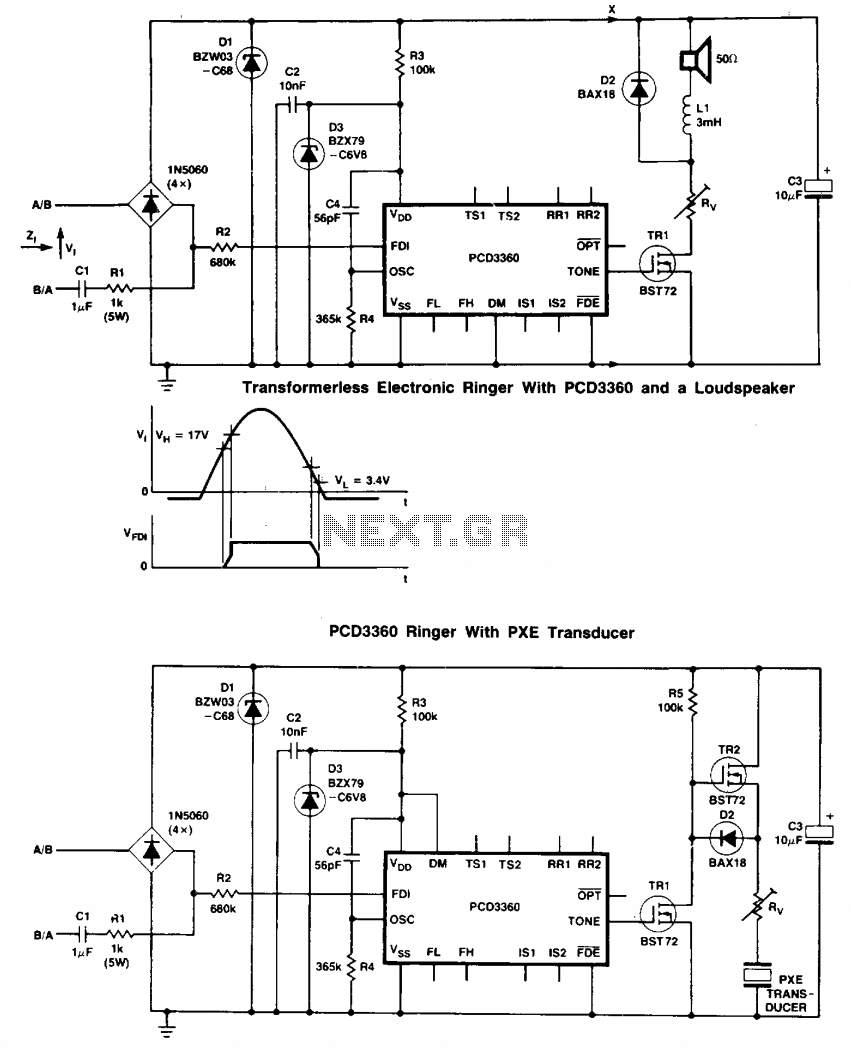
Two BST72 transistors provide an output voltage swing almost equal to the voltage at C3. Pins IS1 and IS2 are inoperative because DM = HIGH. Volume control is possible using resistor Rv.
The circuit utilizes two BST72 transistors configured to amplify signals, resulting in an output voltage swing that closely matches the voltage at capacitor C3. This configuration is advantageous for applications requiring precise voltage regulation or signal amplification.
In this setup, the transistors serve as the primary amplification elements, with their collector-emitter paths connected in such a way that enhances the output voltage. The choice of the BST72 transistors is critical due to their favorable characteristics, such as high gain and fast switching capabilities, which contribute to the overall performance of the circuit.
Pins IS1 and IS2 are noted to be inoperative when the DM signal is HIGH. This indicates that the circuit has a built-in mechanism for disabling certain functions or components based on the state of the DM signal, which can be used to manage power consumption or signal routing within the circuit. The design may include additional logic to ensure that these pins are only activated under specific conditions, thereby optimizing the circuit's operation.
Volume control is facilitated by the inclusion of resistor Rv. This resistor allows for adjustable attenuation of the output signal, providing a means to control the volume in audio applications or to modulate signal strength in other contexts. The value of Rv can be selected based on the desired range of volume control, and it may be part of a potentiometer arrangement for variable adjustment.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines transistor amplification, signal management, and user-adjustable volume control, making it suitable for various electronic applications where signal integrity and user interaction are essential.Two BST72 transistors provide an output voltage swing almost equal to the voltage at C3. Pins IS1 and IS2 are inoperative because DM = HIGH. Volume control is possible using resistor Rv. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes two BST72 transistors configured to amplify signals, resulting in an output voltage swing that closely matches the voltage at capacitor C3. This configuration is advantageous for applications requiring precise voltage regulation or signal amplification.
In this setup, the transistors serve as the primary amplification elements, with their collector-emitter paths connected in such a way that enhances the output voltage. The choice of the BST72 transistors is critical due to their favorable characteristics, such as high gain and fast switching capabilities, which contribute to the overall performance of the circuit.
Pins IS1 and IS2 are noted to be inoperative when the DM signal is HIGH. This indicates that the circuit has a built-in mechanism for disabling certain functions or components based on the state of the DM signal, which can be used to manage power consumption or signal routing within the circuit. The design may include additional logic to ensure that these pins are only activated under specific conditions, thereby optimizing the circuit's operation.
Volume control is facilitated by the inclusion of resistor Rv. This resistor allows for adjustable attenuation of the output signal, providing a means to control the volume in audio applications or to modulate signal strength in other contexts. The value of Rv can be selected based on the desired range of volume control, and it may be part of a potentiometer arrangement for variable adjustment.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines transistor amplification, signal management, and user-adjustable volume control, making it suitable for various electronic applications where signal integrity and user interaction are essential.Two BST72 transistors provide an output voltage swing almost equal to the voltage at C3. Pins IS1 and IS2 are inoperative because DM = HIGH. Volume control is possible using resistor Rv. 🔗 External reference