Pwm Motor-Drive Circuit Circuit
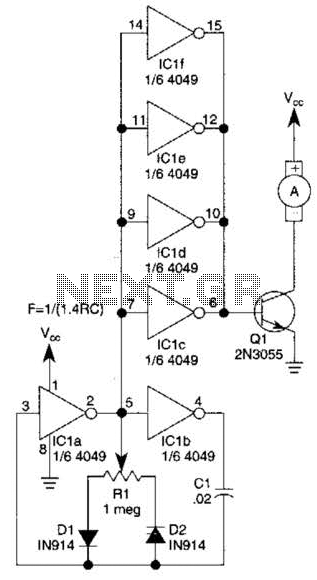
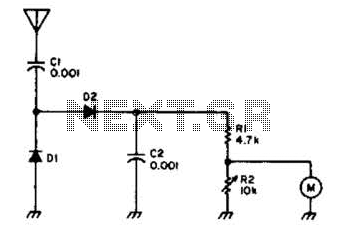
This circuit will drive a small DC motor over a wide range of speeds without stalling by controlling the duty cycle of the motor, rather than the supply voltage.
The described circuit utilizes pulse width modulation (PWM) to effectively control the speed of a small DC motor. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage applied to the motor can be adjusted, allowing for precise speed control without the need to alter the supply voltage. This method is advantageous as it minimizes power loss and heat generation compared to linear voltage regulation methods.
The circuit typically consists of a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller that generates the PWM signal. This signal is fed into a transistor or a MOSFET, which acts as a switch to control the flow of current to the motor. The duty cycle, defined as the ratio of the on-time to the total cycle time, can be adjusted programmatically or through a variable resistor, enabling a smooth transition between different speeds.
In addition to the motor, the circuit may include protective elements such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the switching components and capacitors for filtering the PWM signal to reduce electrical noise. Feedback mechanisms, such as tachometers or encoders, can also be integrated to provide real-time speed monitoring and closed-loop control, ensuring optimal performance and preventing stalling under varying load conditions.
Overall, this circuit design effectively balances efficiency and performance, making it suitable for applications requiring variable speed control of small DC motors in robotics, automation, and other electronic systems. This circuit will drive a small dc motor over a wide range of speeds without stalling by controlling the duty cycle of the motor, rather than the supply voltage. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes pulse width modulation (PWM) to effectively control the speed of a small DC motor. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage applied to the motor can be adjusted, allowing for precise speed control without the need to alter the supply voltage. This method is advantageous as it minimizes power loss and heat generation compared to linear voltage regulation methods.
The circuit typically consists of a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM controller that generates the PWM signal. This signal is fed into a transistor or a MOSFET, which acts as a switch to control the flow of current to the motor. The duty cycle, defined as the ratio of the on-time to the total cycle time, can be adjusted programmatically or through a variable resistor, enabling a smooth transition between different speeds.
In addition to the motor, the circuit may include protective elements such as diodes to prevent back EMF from damaging the switching components and capacitors for filtering the PWM signal to reduce electrical noise. Feedback mechanisms, such as tachometers or encoders, can also be integrated to provide real-time speed monitoring and closed-loop control, ensuring optimal performance and preventing stalling under varying load conditions.
Overall, this circuit design effectively balances efficiency and performance, making it suitable for applications requiring variable speed control of small DC motors in robotics, automation, and other electronic systems. This circuit will drive a small dc motor over a wide range of speeds without stalling by controlling the duty cycle of the motor, rather than the supply voltage. 🔗 External reference