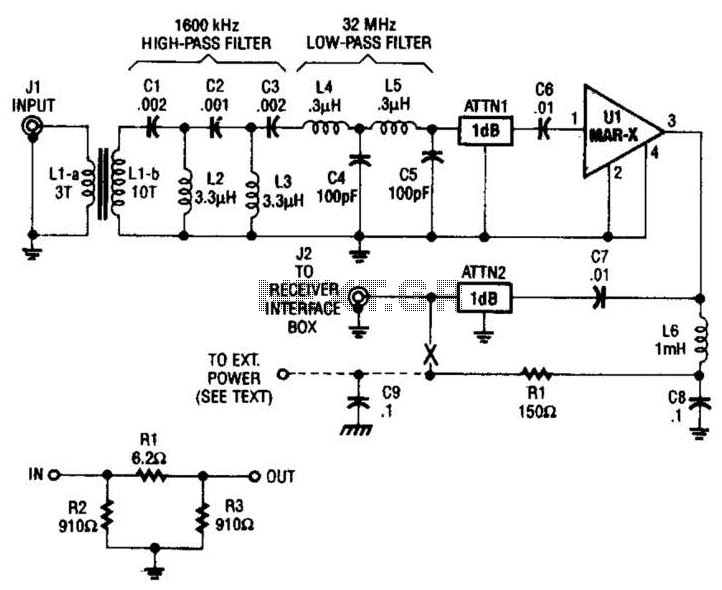
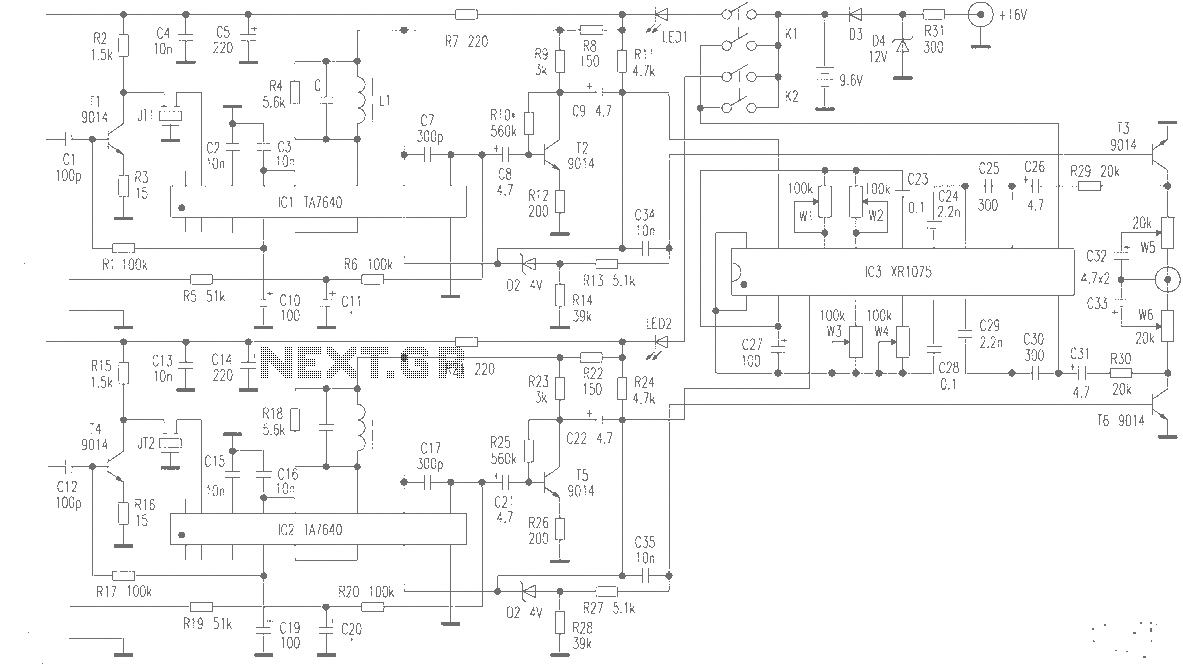
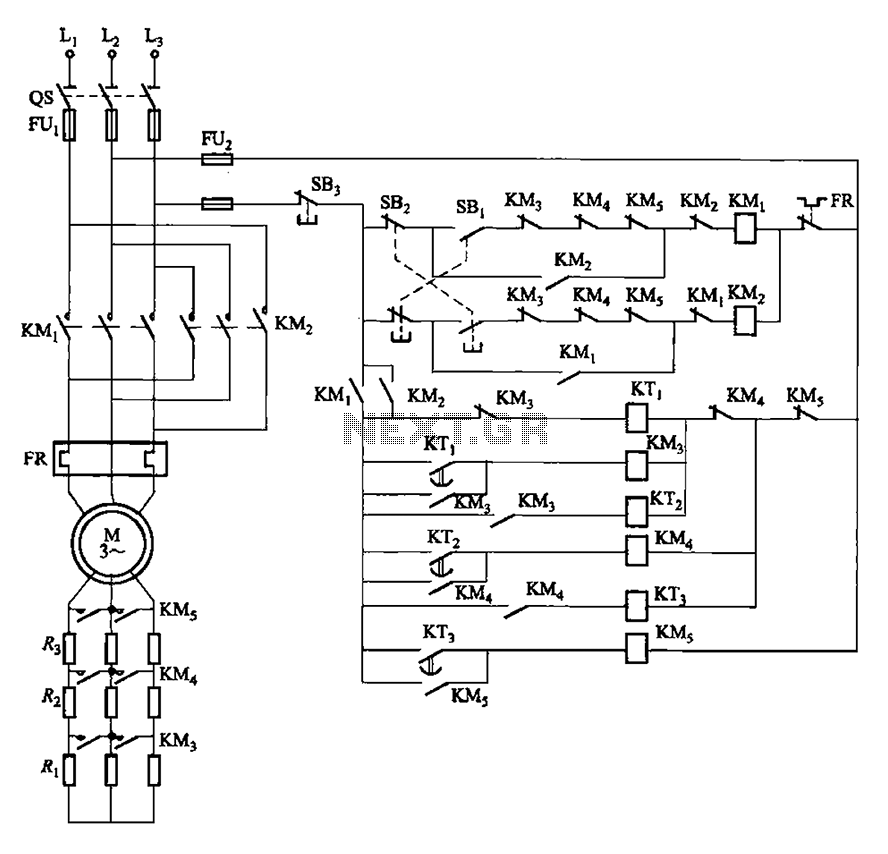
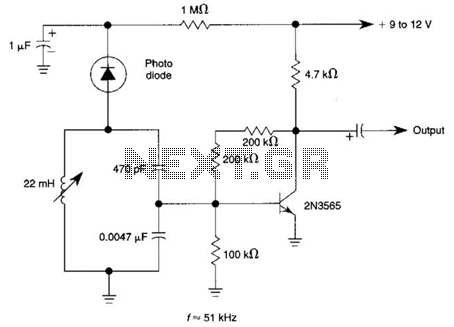
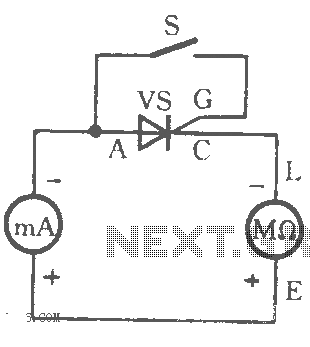
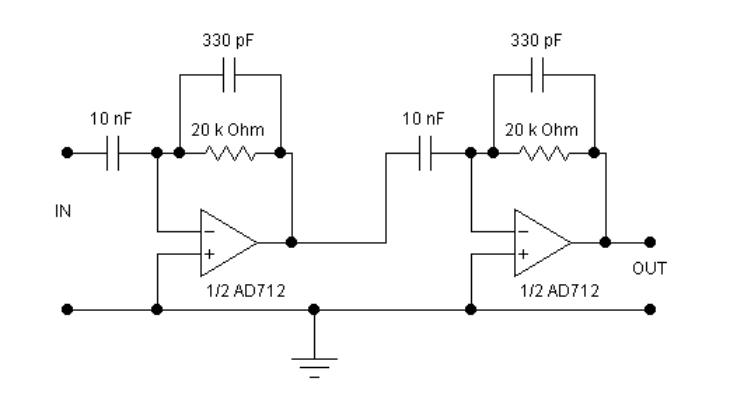
Simple Field Strength Meter I Circuit
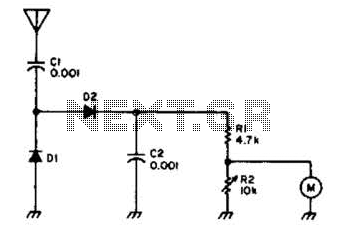
Useful for checking transmitters and antennas, this circuit utilizes a voltage-doubling detector consisting of diodes D1 and D2, which can be HP 5082-2800 hot carrier types or alternatives such as 1N34 or IN82. The circuit incorporates a 100-mA meter movement.
This circuit is designed to facilitate the testing of transmitters and antennas by employing a voltage-doubling mechanism. The primary components, diodes D1 and D2, play a crucial role in the detection process. The HP 5082-2800 diodes are known for their efficiency in high-frequency applications due to their hot carrier characteristics. Alternatively, the circuit can utilize standard silicon diodes such as the 1N34 or IN82, which are readily available and offer sufficient performance for most transmitter testing applications.
The voltage-doubling configuration allows the circuit to effectively increase the voltage output from the antenna or transmitter, making it easier to measure the signal strength with the integrated 100-mA meter movement. This meter is calibrated to provide accurate readings of the voltage levels, which correspond to the power output of the transmitter or the efficiency of the antenna.
In practical applications, the circuit can be connected directly to the output of a transmitter or the feed point of an antenna. The readings obtained from the meter can assist engineers in diagnosing performance issues, optimizing antenna placement, or verifying transmitter output levels. The design emphasizes simplicity and reliability, making it a valuable tool for both amateur radio operators and professional technicians in the field of electronics. Useful for checking transmitters and antennas, this circuit uses a voltage-doubling detector D1 and D2 (HP 5082-2800 hot carrier types). D1 and D2 can also be type 1N34 or IN82. is a 100-mA meter movement. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to facilitate the testing of transmitters and antennas by employing a voltage-doubling mechanism. The primary components, diodes D1 and D2, play a crucial role in the detection process. The HP 5082-2800 diodes are known for their efficiency in high-frequency applications due to their hot carrier characteristics. Alternatively, the circuit can utilize standard silicon diodes such as the 1N34 or IN82, which are readily available and offer sufficient performance for most transmitter testing applications.
The voltage-doubling configuration allows the circuit to effectively increase the voltage output from the antenna or transmitter, making it easier to measure the signal strength with the integrated 100-mA meter movement. This meter is calibrated to provide accurate readings of the voltage levels, which correspond to the power output of the transmitter or the efficiency of the antenna.
In practical applications, the circuit can be connected directly to the output of a transmitter or the feed point of an antenna. The readings obtained from the meter can assist engineers in diagnosing performance issues, optimizing antenna placement, or verifying transmitter output levels. The design emphasizes simplicity and reliability, making it a valuable tool for both amateur radio operators and professional technicians in the field of electronics. Useful for checking transmitters and antennas, this circuit uses a voltage-doubling detector D1 and D2 (HP 5082-2800 hot carrier types). D1 and D2 can also be type 1N34 or IN82. is a 100-mA meter movement. 🔗 External reference