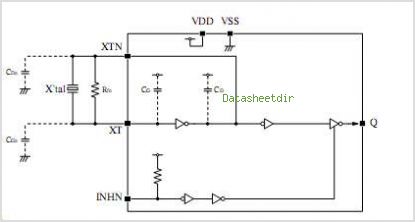
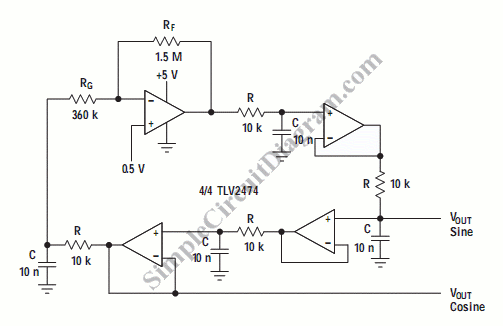
Quadrature Oscillator
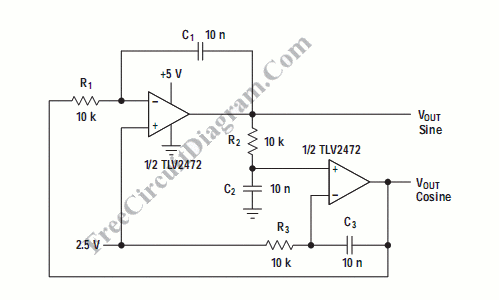
A quadrature oscillator generates two sine-wave signals, with one signal shifted 90 degrees from the other. The output that leads the other is referred to as cosine.
A quadrature oscillator is an essential electronic circuit used to produce two sinusoidal waveforms that are phase-shifted by 90 degrees (or π/2 radians). This phase relationship is crucial in various applications, such as in communication systems, signal processing, and in the generation of quadrature signals for modulation techniques.
The circuit typically consists of an active device, such as an operational amplifier or a transistor, configured to generate the sine waves. The oscillator can be implemented using several methods, including Wien bridge oscillators, phase-shift oscillators, or using digital techniques such as Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS).
In a classic analog implementation, the quadrature oscillator may utilize two integrators in a feedback loop. The first integrator generates a sine wave, while the second integrator, which is connected to the output of the first, produces a cosine wave due to the 90-degree phase shift inherent in the integration process. The feedback network is designed to ensure that the oscillation frequency is stable and can be adjusted using external components like resistors or capacitors.
For practical applications, the output signals can be used in various configurations, such as in the creation of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signals, where the two sine waves represent orthogonal carriers. The ability to produce two phase-shifted signals makes quadrature oscillators invaluable in modern communication systems, where precise timing and phase relationships are critical for signal integrity and performance.
In summary, the quadrature oscillator is a versatile circuit that provides two synchronized signals essential for a wide range of electronic applications. Its design can vary based on the specific requirements of the application, but the fundamental principle of generating phase-shifted sine waves remains consistent.Quadrature oscillator generate two sine-wave signal, but one signal is shifted 90 degree from the other signal. One output that lead the other called cosine. 🔗 External reference
A quadrature oscillator is an essential electronic circuit used to produce two sinusoidal waveforms that are phase-shifted by 90 degrees (or π/2 radians). This phase relationship is crucial in various applications, such as in communication systems, signal processing, and in the generation of quadrature signals for modulation techniques.
The circuit typically consists of an active device, such as an operational amplifier or a transistor, configured to generate the sine waves. The oscillator can be implemented using several methods, including Wien bridge oscillators, phase-shift oscillators, or using digital techniques such as Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS).
In a classic analog implementation, the quadrature oscillator may utilize two integrators in a feedback loop. The first integrator generates a sine wave, while the second integrator, which is connected to the output of the first, produces a cosine wave due to the 90-degree phase shift inherent in the integration process. The feedback network is designed to ensure that the oscillation frequency is stable and can be adjusted using external components like resistors or capacitors.
For practical applications, the output signals can be used in various configurations, such as in the creation of quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signals, where the two sine waves represent orthogonal carriers. The ability to produce two phase-shifted signals makes quadrature oscillators invaluable in modern communication systems, where precise timing and phase relationships are critical for signal integrity and performance.
In summary, the quadrature oscillator is a versatile circuit that provides two synchronized signals essential for a wide range of electronic applications. Its design can vary based on the specific requirements of the application, but the fundamental principle of generating phase-shifted sine waves remains consistent.Quadrature oscillator generate two sine-wave signal, but one signal is shifted 90 degree from the other signal. One output that lead the other called cosine. 🔗 External reference