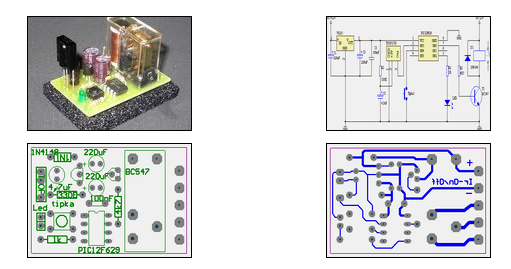
Remote Control Toy Car Schematic
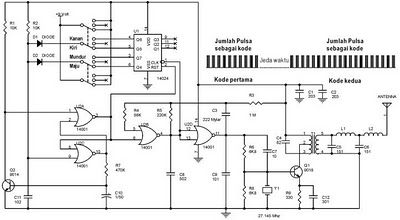
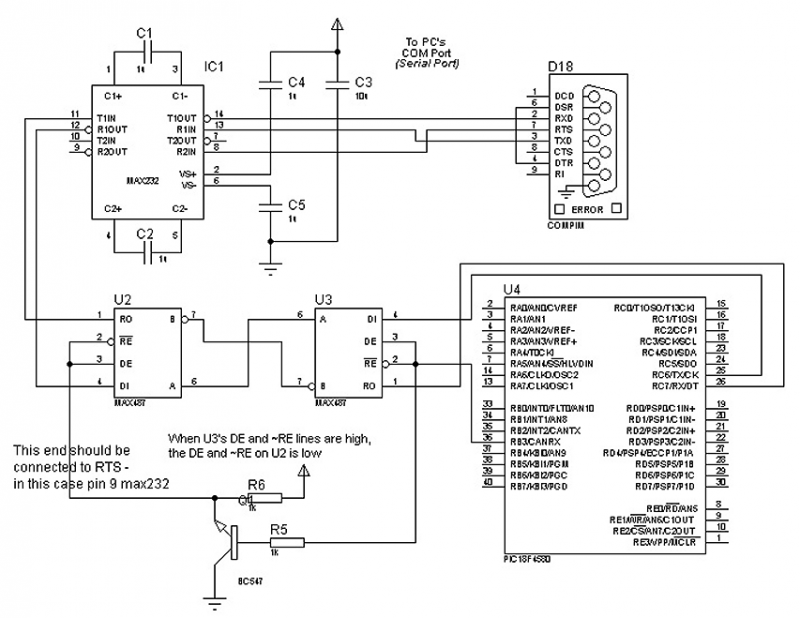
The following circuit illustrates a schematic diagram for a remote control toy car. Features: it does not interfere with the performance of the original design.
The remote control toy car circuit typically consists of several key components that enable wireless control and operation. The main elements include a transmitter, a receiver, a motor driver, and the toy car's DC motors.
The transmitter is generally equipped with a control interface, such as a joystick or buttons, which sends radio frequency (RF) signals to the receiver. The transmitter circuit may include a microcontroller that processes user inputs and modulates the RF signal for transmission.
The receiver, located within the toy car, is designed to decode the incoming RF signals. It usually incorporates a demodulator and a microcontroller that interprets the commands and controls the motor driver accordingly.
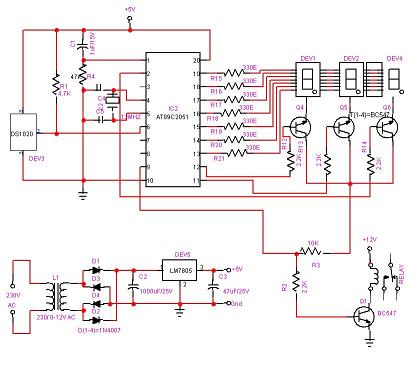
The motor driver is a crucial component that interfaces between the receiver and the DC motors. It amplifies the control signals from the receiver and provides the necessary current to drive the motors. Commonly, an H-bridge configuration is used, allowing for bidirectional control of the motors, which enables forward, reverse, and turning maneuvers.
The DC motors are responsible for propelling the toy car. They are typically equipped with gear systems to enhance torque and speed. Power for the entire circuit is usually supplied by a battery pack, which must be adequately rated to ensure sufficient operational time and performance.
Overall, the remote control toy car circuit is designed to be user-friendly, providing a seamless interface for operation while maintaining the integrity of the original toy's performance. The careful selection and integration of components are essential to ensure reliability and responsiveness in the toy car's movements.The following circuit shows about Remote Control Toy Car Schematic Circuit Diagram. Features: does not impose on the performance of the original .. 🔗 External reference
The remote control toy car circuit typically consists of several key components that enable wireless control and operation. The main elements include a transmitter, a receiver, a motor driver, and the toy car's DC motors.
The transmitter is generally equipped with a control interface, such as a joystick or buttons, which sends radio frequency (RF) signals to the receiver. The transmitter circuit may include a microcontroller that processes user inputs and modulates the RF signal for transmission.
The receiver, located within the toy car, is designed to decode the incoming RF signals. It usually incorporates a demodulator and a microcontroller that interprets the commands and controls the motor driver accordingly.
The motor driver is a crucial component that interfaces between the receiver and the DC motors. It amplifies the control signals from the receiver and provides the necessary current to drive the motors. Commonly, an H-bridge configuration is used, allowing for bidirectional control of the motors, which enables forward, reverse, and turning maneuvers.
The DC motors are responsible for propelling the toy car. They are typically equipped with gear systems to enhance torque and speed. Power for the entire circuit is usually supplied by a battery pack, which must be adequately rated to ensure sufficient operational time and performance.
Overall, the remote control toy car circuit is designed to be user-friendly, providing a seamless interface for operation while maintaining the integrity of the original toy's performance. The careful selection and integration of components are essential to ensure reliability and responsiveness in the toy car's movements.The following circuit shows about Remote Control Toy Car Schematic Circuit Diagram. Features: does not impose on the performance of the original .. 🔗 External reference