rf amplifier with op amp
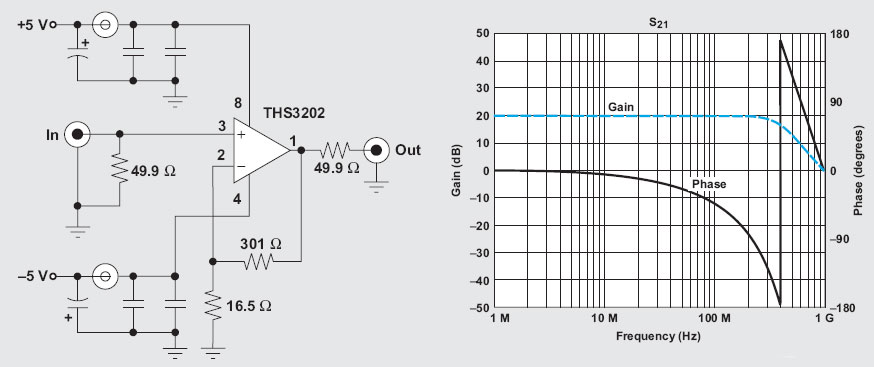
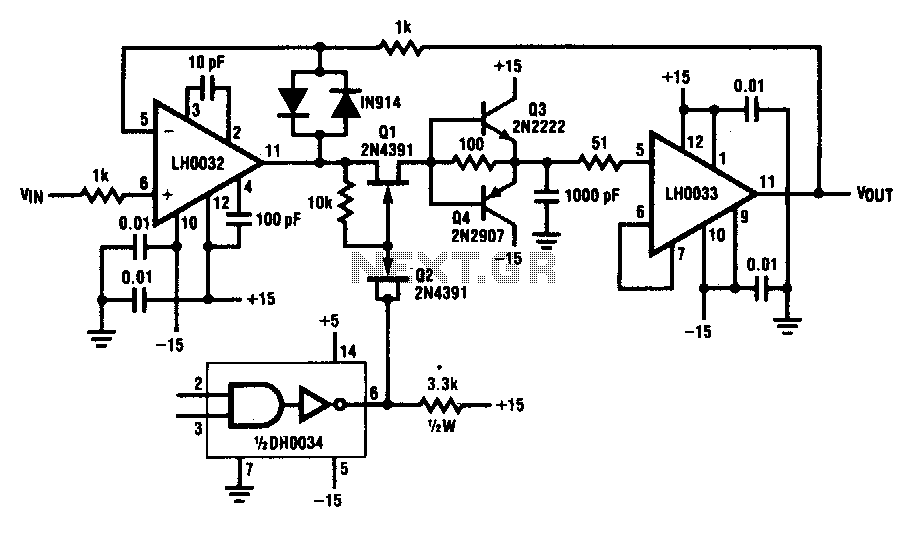
The operational amplifier (op-amp) has a significant history, particularly with the 741/301 series, which has been popular for approximately 20 years due to its ease of calculation (gain calculation), affordability, and simplicity of construction. The versatility of op-amps allows for various implementations, including attempts to build an "op-amp based computer." While op-amps can be used in many applications, they are generally not suitable for RF applications. However, advancements in semiconductor technology have led to the development of op-amps capable of operating at frequencies up to GHz. An article by Bruce Carter from Texas Instruments discusses the application of the THS3202 op-amp in RF circuits. This circuit provides a flat gain of 20 dB in the frequency range up to 200 MHz. The input and output impedance are determined by a 49.9 Ohm resistor. The voltage gain is set by resistors of 301 Ohm and 5.16 Ohm. The gain can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor values for feedback. The circuit achieves a total gain of 40 dB (2 x 20 dB). Additionally, a 332 Ohm resistor is used at the point-B0 SFELA10M7GA00 ceramic filter to determine the termination impedance.
The operational amplifier (op-amp) serves as a fundamental building block in analog electronic circuits. The 741 and 301 series of op-amps have become staples in the field due to their reliability and ease of use. The basic configuration of an op-amp allows for various gain settings through feedback resistors, making them adaptable for numerous applications.
In RF applications, the THS3202 op-amp exemplifies modern advancements, offering high-frequency performance that extends into the GHz range. This capability is essential for applications requiring fast signal processing and high fidelity. The circuit configuration described utilizes a flat gain of 20 dB, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity across a broad frequency spectrum up to 200 MHz.
The input and output impedance are crucial in RF designs, as they affect how the circuit interacts with other components. The 49.9 Ohm resistor serves to match the impedance, minimizing reflections and maximizing power transfer. The gain setting, determined by the resistors of 301 Ohm and 5.16 Ohm, allows for precise control over the amplification factor, which can be essential in maintaining signal quality.
The total gain of 40 dB achieved by the circuit is noteworthy, as it illustrates the potential for significant amplification in RF applications. The feedback mechanism is vital for stability and performance, and the selection of resistor values directly influences the op-amp's behavior. Furthermore, the inclusion of a 332 Ohm resistor at the ceramic filter point ensures that the termination impedance is correctly set, further enhancing the circuit's performance in handling high-frequency signals.
Overall, the evolution of op-amps like the THS3202 demonstrates the ongoing advancements in semiconductor technology and their implications for modern electronic design, particularly in high-frequency applications.Op-Amp`s right, not wrong title. I know the op amp is approximately 20 years ago, at age 741/301 series, an easy calculation (gain calculation), affordability, and simplicity of construction makes a very interesting op-amp. So many of the implementation of the op-amp, and even had time to try to build the "op-amp based computer".
Almost all can be built with op-amp, except for RF. But that first, reversing the progress of semiconductor technology this condition, a few years back the manufacturers have managed to build an op-amp with a working frequency up to GHz. An article from Texas Instrument by Bruce Carter describes the application of op-amp (THS3202) on the rf circuit.
Above circuit provides flat gain of 20dB in the range up to 200MHz. Terminasi input and output impedance is determined by the resistor 49. 9Ohm. Strengthening the voltage is determined by resistor 301 Ohm / 5. 16 Ohm. Choice of reinforcement could be done as to determine the op-amp gain. The circuit above provides 40dB gain (2 x 20dB). Consider the provision of value as a determinant of the gain resistor (feedback). Note also the termination impedance at the point-B0 SFELA10M7GA00 ceramic filter a 332 Ohm resistor is applied there. 🔗 External reference
The operational amplifier (op-amp) serves as a fundamental building block in analog electronic circuits. The 741 and 301 series of op-amps have become staples in the field due to their reliability and ease of use. The basic configuration of an op-amp allows for various gain settings through feedback resistors, making them adaptable for numerous applications.
In RF applications, the THS3202 op-amp exemplifies modern advancements, offering high-frequency performance that extends into the GHz range. This capability is essential for applications requiring fast signal processing and high fidelity. The circuit configuration described utilizes a flat gain of 20 dB, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity across a broad frequency spectrum up to 200 MHz.
The input and output impedance are crucial in RF designs, as they affect how the circuit interacts with other components. The 49.9 Ohm resistor serves to match the impedance, minimizing reflections and maximizing power transfer. The gain setting, determined by the resistors of 301 Ohm and 5.16 Ohm, allows for precise control over the amplification factor, which can be essential in maintaining signal quality.
The total gain of 40 dB achieved by the circuit is noteworthy, as it illustrates the potential for significant amplification in RF applications. The feedback mechanism is vital for stability and performance, and the selection of resistor values directly influences the op-amp's behavior. Furthermore, the inclusion of a 332 Ohm resistor at the ceramic filter point ensures that the termination impedance is correctly set, further enhancing the circuit's performance in handling high-frequency signals.
Overall, the evolution of op-amps like the THS3202 demonstrates the ongoing advancements in semiconductor technology and their implications for modern electronic design, particularly in high-frequency applications.Op-Amp`s right, not wrong title. I know the op amp is approximately 20 years ago, at age 741/301 series, an easy calculation (gain calculation), affordability, and simplicity of construction makes a very interesting op-amp. So many of the implementation of the op-amp, and even had time to try to build the "op-amp based computer".
Almost all can be built with op-amp, except for RF. But that first, reversing the progress of semiconductor technology this condition, a few years back the manufacturers have managed to build an op-amp with a working frequency up to GHz. An article from Texas Instrument by Bruce Carter describes the application of op-amp (THS3202) on the rf circuit.
Above circuit provides flat gain of 20dB in the range up to 200MHz. Terminasi input and output impedance is determined by the resistor 49. 9Ohm. Strengthening the voltage is determined by resistor 301 Ohm / 5. 16 Ohm. Choice of reinforcement could be done as to determine the op-amp gain. The circuit above provides 40dB gain (2 x 20dB). Consider the provision of value as a determinant of the gain resistor (feedback). Note also the termination impedance at the point-B0 SFELA10M7GA00 ceramic filter a 332 Ohm resistor is applied there. 🔗 External reference