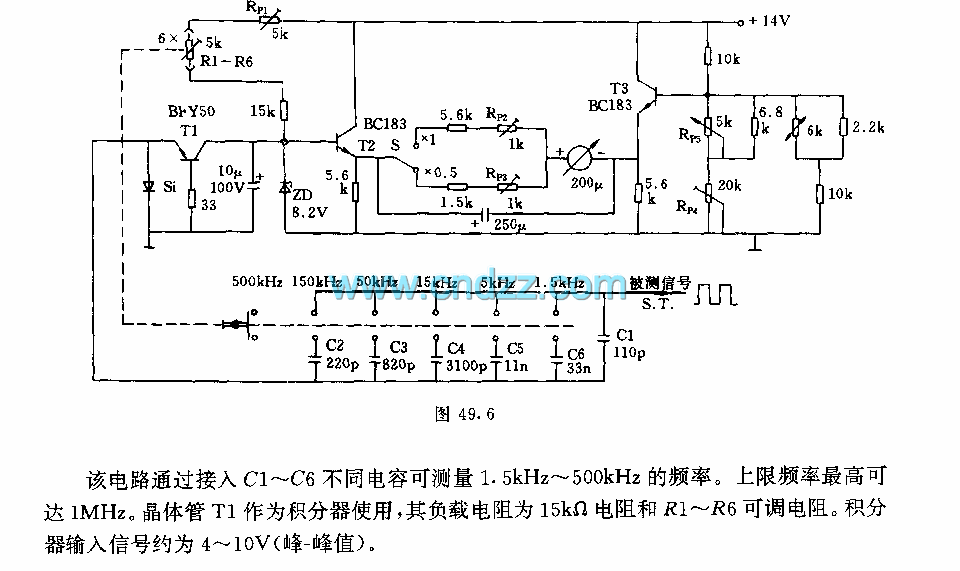
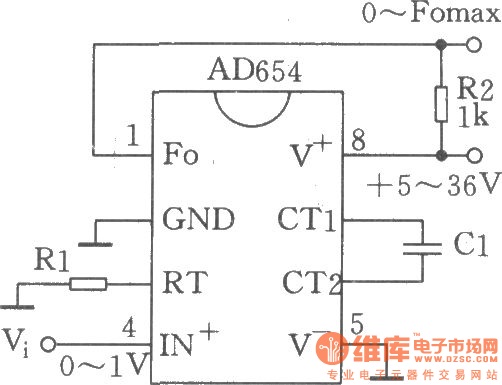
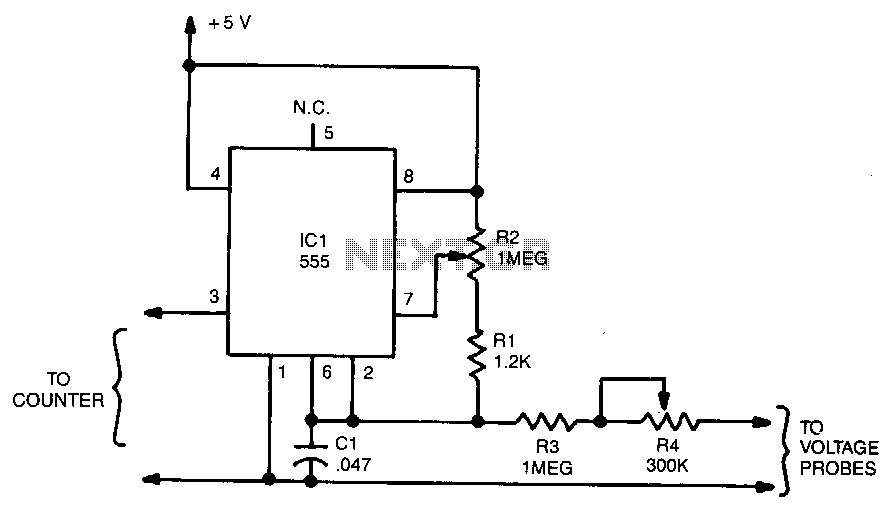
RF-Radio Frequency 6
This circuit is designed to attenuate signal frequency, with a customizable range from 1 to 40 dB. For UHF band usage, it should be enclosed within a shielded frame, and capacitors C1 to C3 should be appropriately selected. The connection lines should be kept as short as possible, and a low-capacitance, high-speed diode is recommended. The potentiometer can be installed separately if desired, along with resistor R3 and a Zener diode. Ignition noise pulses from the engine can interfere with radio communication equipment in vehicles, leading to various issues. This circuit enhances the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N ratio) by connecting between the output of the detector circuit and the audio input, which can be high impedance or in the impedance range of the audio section. An Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuit is also integrated, simplifying the compression of audio signals in radio receivers. It is particularly suited for shortwave radio receivers in areas with weak signals. The master volume control should be adjusted to achieve the desired signal intensity while tuning the receiver. The circuit is designed to assist installers and maintainers of video systems and features a video sync separator (IC1) followed by a LED and buzzer driver (IC2, Q1, and Q2). When connected to a video cable, the device indicates video presence with a flashing LED at approximately 10Hz. If no video is detected, the LED will flash briefly every few seconds. An optional buzzer can provide an audible indication, useful for tracing cabling faults or identifying the correct cable among many. The buzzer can also indicate video faults, triggering an alarm when no video signal is detected. IC1 is based on the LM1881 video sync separator circuit, with a switch (S1) to toggle 75-ohm termination in or out. The composite sync output at pin 1 remains low without video input and pulses high upon detecting composite sync. The frequency control is managed by the NE566 IC oscillator, which operates as a phase-locked loop demodulator. The output at pin 7 connects to an op-amp (IC 741) configured as a voltage follower, allowing the driver IC (NE566) to function effectively. The voltage at pin 6 of the op-amp is fed into pin 5 of the NE566 to control its frequency at leg 3. The frequency multiplication is determined by resistors R1, C1, R2, and C2 for circuit stability. The values of R1 and C1 must be selected to suit the operating frequency. Additionally, this description includes a direct-coupled radio circuit ideal for receiving nearby stations, utilizing transistor Q1 as a diode detector and initial audio amplifier. The detection occurs across the emitter-base junction, functioning as a diode, with base-emitter capacitance providing radio filtering. Resistor R1 is adjusted to minimize distortion while maintaining consistent volume. Transistors Q2 and Q3 serve as additional audio amplifiers. Furthermore, a simple AM transmitter circuit is described, capable of transmitting audio within a backyard. This circuit adheres to FCC regulations by limiting power output while providing sufficient amplitude modulation in the medium wave band for personal use. The circuit consists of two primary components: an audio amplifier and a radio frequency oscillator built around transistor Q1.This circuit can be designed to attenuate signal frequency. Customizable from 1 to 40 dB. If you want to use the band uhf, should be fitted within the frame shield, and C1 to C3 type feeds true. The line should be as short as possible, and the diode should be a kind of low capacity on high speed.
The potentiometer can be installed separately, if des ired, as well as R3 and Zener diode Interference from ignition noise pulse of the engine, it can cause various problems associated with radio communication equipment installed in the car. This circuit improves signal to noise ratio (S / N-ratio) was better, To connected between the output of the detector circuit with the audio input (if high impedance) or region of the impedance between the high dance audio section.
The automatic Gian control circuit also AGC with audio signal is simplest for compress to signal in the Radio receiver. It is ideal for short wave radio receiver used in areas with weak signals. You should adjust the master volume control dress until the desired signal intensity. While tuning the receiver to the station light, then gradually tuned to the power station and adjust the AGC pot until the pressure in the hearing as needed This circuit was designed as an aid to installers and maintainers of video systems.
It is basically a video sync separator (IC1) followed by a LED and buzzer driver (IC2, Q1 & Q2). In use, the device is connected to a video cable and if there is video present, the LED will flash at about 10Hz. If there is no video, the LED flashes briefly every couple of seconds. A buzzer can also be switched in to provide an audible indication. The buzzer is particularly useful when tracing cabling faults or trying to find a correct cable amongst many, where it is difficult to keep an eye on the LED.
Another use for the buzzer option is to provide a video fault indication. For example, it could be inserted in bridging mode, with switch S1 in high impedance mode (position 2) across a video line and set to alarm when there is no video present. If someone pulls out a cable or the video source is powered off, the alarm would sound. IC1 is a standard LM1881 video sync separator circuit and 75 termination can be switched in or out with switch S1a.
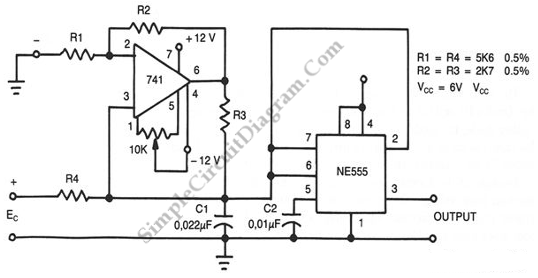
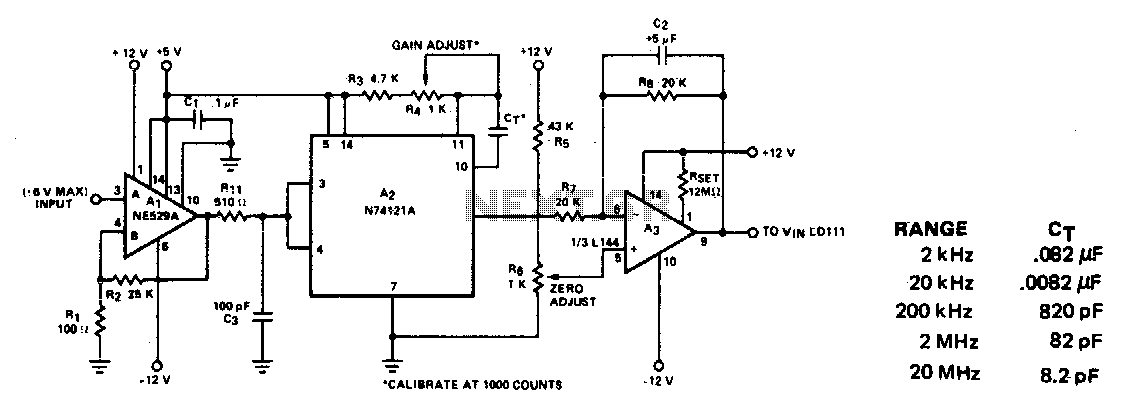
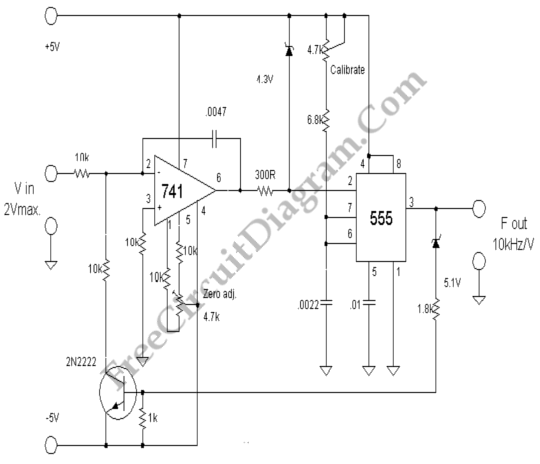
The other pole of the switch, S1b, turns on the power. The composite sync output at pin 1 is low with no video input and it pulses high when composite sync is detected It changes frequency as the incoming voltage, Frequency control. That, from the IC Oscillator NE566. IC phase locked loop circuit is in the nature of Demodulator. The output at Pin 7 and is connected to the IC op amp 741. Which is connected in a manner of Voltage-follower circuit. to the driver IC 566 to work. The voltage passing through the pin 6 of IC op amp, will be entered into a 5-pin of the IC 566. To control the frequency of leg 3 of the IC NE566. the multiplication of frequency equal to R1, C1, R2, C2. For the operation of the circuit stability. Therefore the value of R1 and C1 should be chosen to suit the frequency. Here is the circuit of an excellent direct coupled radio ideal for listening to near by stations. The circuit uses Q1 as a diode detector and first audio amplifier. The detection is across the first emitter base junction which operates as a diode. The base emitter capacitance provides the radio filtering. The resistor R1 is adjusted to obtain the least distortion with consistent volume. Transistors Q2 and Q3 also serve as audio amplifiers Here is the circuit diagram of a simple AM transmitter circuit that can transmit your audios to your backyard.
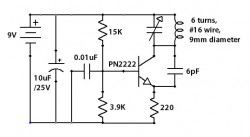
This circuit is designed with limited the power output to match the FCC regulations and still produces enough amplitude modulation of voice in the medium wave band to satisfy your personal needs. You will love this!. The circuit has two parts, an audio amplifier and a radio frequency oscillator. The oscillator is built around Q1 🔗 External reference
The potentiometer can be installed separately, if des ired, as well as R3 and Zener diode Interference from ignition noise pulse of the engine, it can cause various problems associated with radio communication equipment installed in the car. This circuit improves signal to noise ratio (S / N-ratio) was better, To connected between the output of the detector circuit with the audio input (if high impedance) or region of the impedance between the high dance audio section.
The automatic Gian control circuit also AGC with audio signal is simplest for compress to signal in the Radio receiver. It is ideal for short wave radio receiver used in areas with weak signals. You should adjust the master volume control dress until the desired signal intensity. While tuning the receiver to the station light, then gradually tuned to the power station and adjust the AGC pot until the pressure in the hearing as needed This circuit was designed as an aid to installers and maintainers of video systems.
It is basically a video sync separator (IC1) followed by a LED and buzzer driver (IC2, Q1 & Q2). In use, the device is connected to a video cable and if there is video present, the LED will flash at about 10Hz. If there is no video, the LED flashes briefly every couple of seconds. A buzzer can also be switched in to provide an audible indication. The buzzer is particularly useful when tracing cabling faults or trying to find a correct cable amongst many, where it is difficult to keep an eye on the LED.
Another use for the buzzer option is to provide a video fault indication. For example, it could be inserted in bridging mode, with switch S1 in high impedance mode (position 2) across a video line and set to alarm when there is no video present. If someone pulls out a cable or the video source is powered off, the alarm would sound. IC1 is a standard LM1881 video sync separator circuit and 75 termination can be switched in or out with switch S1a.
The other pole of the switch, S1b, turns on the power. The composite sync output at pin 1 is low with no video input and it pulses high when composite sync is detected It changes frequency as the incoming voltage, Frequency control. That, from the IC Oscillator NE566. IC phase locked loop circuit is in the nature of Demodulator. The output at Pin 7 and is connected to the IC op amp 741. Which is connected in a manner of Voltage-follower circuit. to the driver IC 566 to work. The voltage passing through the pin 6 of IC op amp, will be entered into a 5-pin of the IC 566. To control the frequency of leg 3 of the IC NE566. the multiplication of frequency equal to R1, C1, R2, C2. For the operation of the circuit stability. Therefore the value of R1 and C1 should be chosen to suit the frequency. Here is the circuit of an excellent direct coupled radio ideal for listening to near by stations. The circuit uses Q1 as a diode detector and first audio amplifier. The detection is across the first emitter base junction which operates as a diode. The base emitter capacitance provides the radio filtering. The resistor R1 is adjusted to obtain the least distortion with consistent volume. Transistors Q2 and Q3 also serve as audio amplifiers Here is the circuit diagram of a simple AM transmitter circuit that can transmit your audios to your backyard.
This circuit is designed with limited the power output to match the FCC regulations and still produces enough amplitude modulation of voice in the medium wave band to satisfy your personal needs. You will love this!. The circuit has two parts, an audio amplifier and a radio frequency oscillator. The oscillator is built around Q1 🔗 External reference