rf remote control encoder and decoder
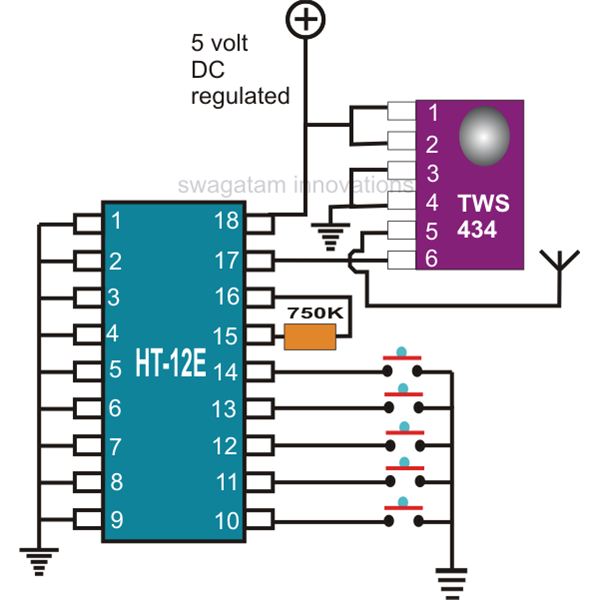
This document explains two RF 433kHz remote control chips specifically designed for remote control applications. The IC TWS-434, along with its encoder chip HT-12E from Holtek, forms a high-quality transmitter circuit, while the chip RWS-434, paired with the decoder IC HT-12D, operates as the receiver module. Both modules can exchange 4 bits of discrete data to control four external loads independently. With the easy accessibility of accurate remote control chips, creating universal remote control modules can be accomplished in just a few hours. This discussion focuses on compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules utilizing the chips HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, and RWS-434. The development of a high-end professional remote control system at home has become straightforward. The introduction of micro remote control encoder and decoder chips has made RF remote control creation a matter of minutes. The applications of remote controls made from these chips are numerous, with one of the best applications being car security systems. The TWS-434 and RWS-434 RF remote control chips complement each other, with the former serving as the transmitter and the latter as the receiver. The TWS-434 is a compact 4-bit transmitter module capable of transmitting four types of coded signals discretely, while the RWS-434 receives these signals and generates four discrete decoded signals at its outputs. However, both primarily function as wireless sender and receiver units, necessitating the integration of external encoders and decoders for their operation. The HOLTEK encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with TWS-434 and RWS-434, respectively, to achieve the desired universal remote control operating parameters. The TWS-434 IC features six pinouts: pins 1 and 2 are positive inputs, pins 3 and 4 are grounded, pin 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, and pin 5 serves as the antenna for radiating the transmitted signals. The RWS-434's antenna receives data transmitted by the TWS-434 and sends it to the HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data. The processed data is then output from pins 10, 11, 12, and 13, which can be further directed to an output driving circuit to activate the connected devices.
The TWS-434 and RWS-434 modules operate at a frequency of 433MHz, which is commonly used for remote control applications due to its favorable propagation characteristics. The TWS-434 transmitter module is designed to be compact, making it suitable for integration into various devices requiring remote control functionality. The transmitter's output power is sufficient to ensure reliable communication over reasonable distances, typically up to 100 meters in open areas, depending on environmental factors.
The HT-12E encoder chip is designed to work seamlessly with the TWS-434, facilitating the encoding of the data to be transmitted. It allows for a simple setup with a few external components, such as resistors and capacitors, to configure the address and data lines. The ability to connect up to 4 external devices makes this combination ideal for various applications, from home automation to industrial control systems.
On the receiving end, the RWS-434 module, paired with the HT-12D decoder, effectively captures the transmitted signals and decodes them into usable outputs. The HT-12D also supports multiple addresses, enabling multiple transmitters to communicate with a single receiver while avoiding interference. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where multiple remote controls are utilized within the same vicinity.
The integration of these components allows for the creation of a versatile remote control system that can be tailored to specific user needs, whether for controlling lights, motors, or security systems. The straightforward design and implementation process, combined with the reliability of the RF communication, make these modules a popular choice among hobbyists and professionals alike.Here we explain a couple RF 433kHz remote control chips especially designed for the purpose. The IC TWS-434 along with its encoder chip HOLTEK`s HT-12E form ahigh class transmitter circuit, whereas the chip RWS-434 through its complementing decoder IC HT-12D operates as the receiver module. Both of the above modules are able to exchange 4-bits of discrete data for control four external loads separately. With the easy availability of accurate remote control chips, making your own universal remote control modules is today just a matter of few hours. We discuss a couple of compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules here using the chips: HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, RWS-434 Making a hi-end professional remote control system at home is a child`s play now.
With the advent of micro remote control encoder and decoders chips, making a RF remote control is today a matter of a few hours or rather minutes. Applications of remote controls made from these chips are countless; you may use it for controlling practically any electrical gadget that you can think of, the best application being for car security systems.
A couple of RF remote control chips, the TWS-434 and the RWS-434 both complement each other, the first one being the transmitter and the later one the receiver. The chip TWS-434 is basically a tiny 4-bit transmitter module, which is able to transmit 4 types of coded signals discretely, whereas the RWS-434 exactly compliments these signals by receiving them and generating 4 discrete decoded signals at its outputs.
However both the above primarily functions just as wireless sender and receiver and therefore require external encoders and decoders to be integrated for the said operations. A couple of HOLTEK`s encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with TWS-434 and RWS-434 respectively to produce the desired ideal universal remote control operating parameters.
The IC TWS-434 has in all 6 pin outs, 1 and 2 are the positive inputs, 3 and 4 are to be grounded, 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, pin 5 being the antenna for radiating the received signals. Here, the chip RWS-434, s antenna receive the data transmitted by the above transmitter module and sends it to the IC HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data which ultimately is decoded and produced at the respective outputs for driving the connected loads.
Pin 14 receives the information received by RSW-434 and after decoding the processed data is obtained from the pins 10, 11, 12, 13 respectively, which is further fed to the output driving circuit for activating the connected gadgets. 🔗 External reference
The TWS-434 and RWS-434 modules operate at a frequency of 433MHz, which is commonly used for remote control applications due to its favorable propagation characteristics. The TWS-434 transmitter module is designed to be compact, making it suitable for integration into various devices requiring remote control functionality. The transmitter's output power is sufficient to ensure reliable communication over reasonable distances, typically up to 100 meters in open areas, depending on environmental factors.
The HT-12E encoder chip is designed to work seamlessly with the TWS-434, facilitating the encoding of the data to be transmitted. It allows for a simple setup with a few external components, such as resistors and capacitors, to configure the address and data lines. The ability to connect up to 4 external devices makes this combination ideal for various applications, from home automation to industrial control systems.
On the receiving end, the RWS-434 module, paired with the HT-12D decoder, effectively captures the transmitted signals and decodes them into usable outputs. The HT-12D also supports multiple addresses, enabling multiple transmitters to communicate with a single receiver while avoiding interference. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications where multiple remote controls are utilized within the same vicinity.
The integration of these components allows for the creation of a versatile remote control system that can be tailored to specific user needs, whether for controlling lights, motors, or security systems. The straightforward design and implementation process, combined with the reliability of the RF communication, make these modules a popular choice among hobbyists and professionals alike.Here we explain a couple RF 433kHz remote control chips especially designed for the purpose. The IC TWS-434 along with its encoder chip HOLTEK`s HT-12E form ahigh class transmitter circuit, whereas the chip RWS-434 through its complementing decoder IC HT-12D operates as the receiver module. Both of the above modules are able to exchange 4-bits of discrete data for control four external loads separately. With the easy availability of accurate remote control chips, making your own universal remote control modules is today just a matter of few hours. We discuss a couple of compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules here using the chips: HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, RWS-434 Making a hi-end professional remote control system at home is a child`s play now.
With the advent of micro remote control encoder and decoders chips, making a RF remote control is today a matter of a few hours or rather minutes. Applications of remote controls made from these chips are countless; you may use it for controlling practically any electrical gadget that you can think of, the best application being for car security systems.
A couple of RF remote control chips, the TWS-434 and the RWS-434 both complement each other, the first one being the transmitter and the later one the receiver. The chip TWS-434 is basically a tiny 4-bit transmitter module, which is able to transmit 4 types of coded signals discretely, whereas the RWS-434 exactly compliments these signals by receiving them and generating 4 discrete decoded signals at its outputs.
However both the above primarily functions just as wireless sender and receiver and therefore require external encoders and decoders to be integrated for the said operations. A couple of HOLTEK`s encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with TWS-434 and RWS-434 respectively to produce the desired ideal universal remote control operating parameters.
The IC TWS-434 has in all 6 pin outs, 1 and 2 are the positive inputs, 3 and 4 are to be grounded, 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, pin 5 being the antenna for radiating the received signals. Here, the chip RWS-434, s antenna receive the data transmitted by the above transmitter module and sends it to the IC HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data which ultimately is decoded and produced at the respective outputs for driving the connected loads.
Pin 14 receives the information received by RSW-434 and after decoding the processed data is obtained from the pins 10, 11, 12, 13 respectively, which is further fed to the output driving circuit for activating the connected gadgets. 🔗 External reference