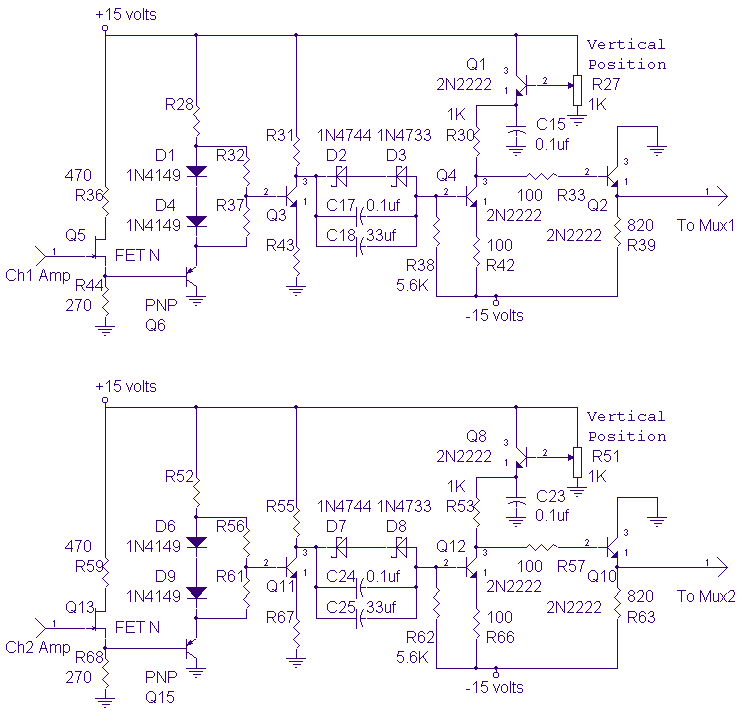
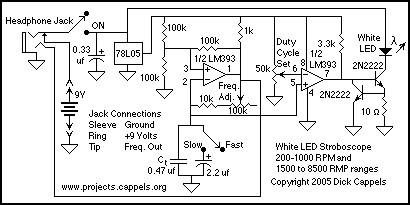
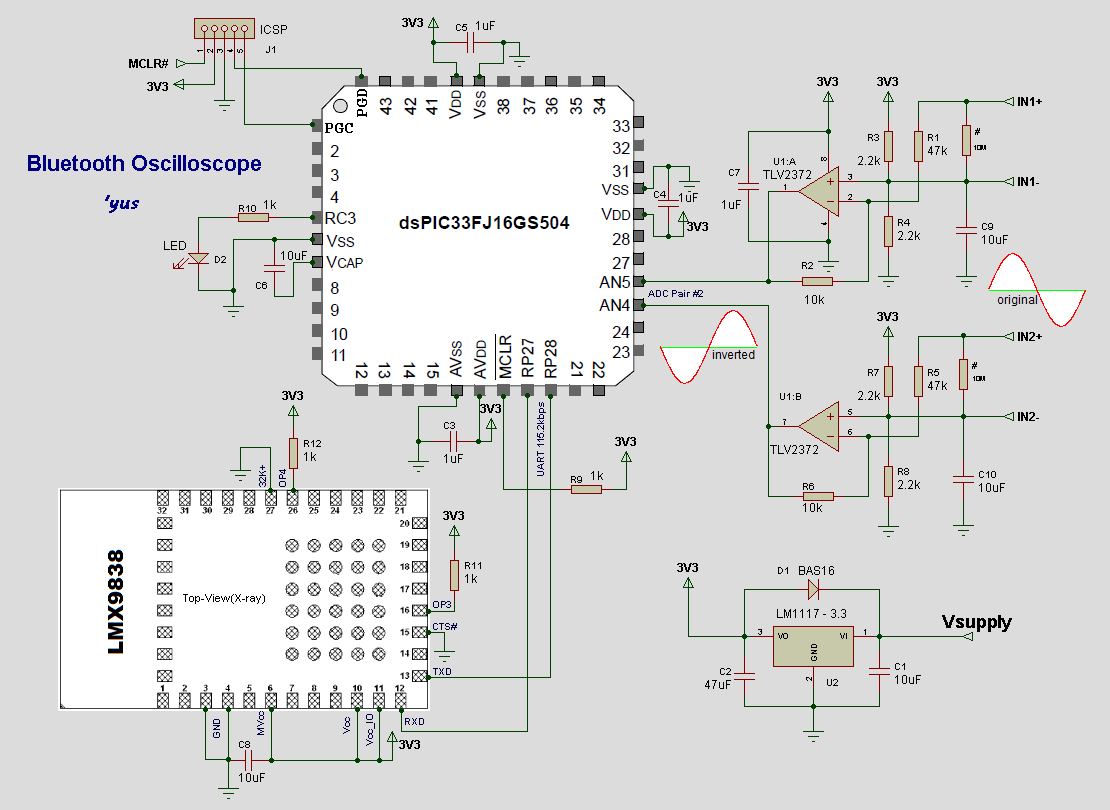
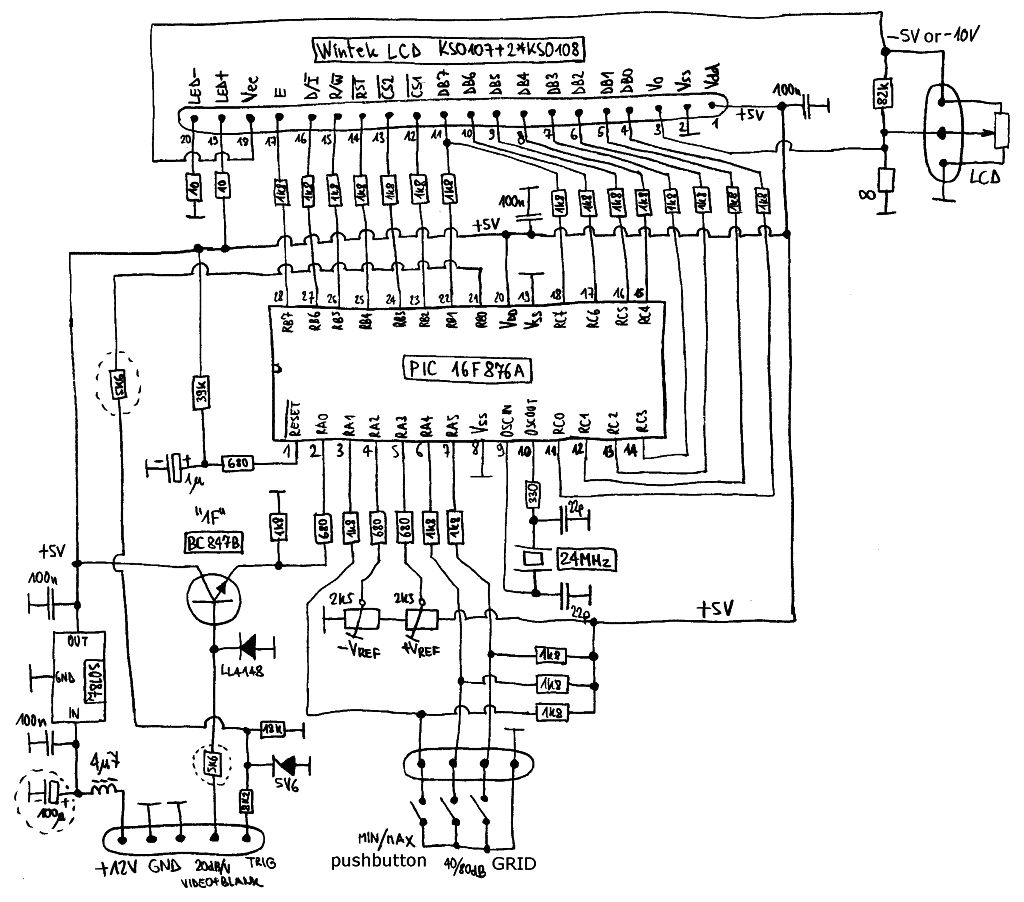
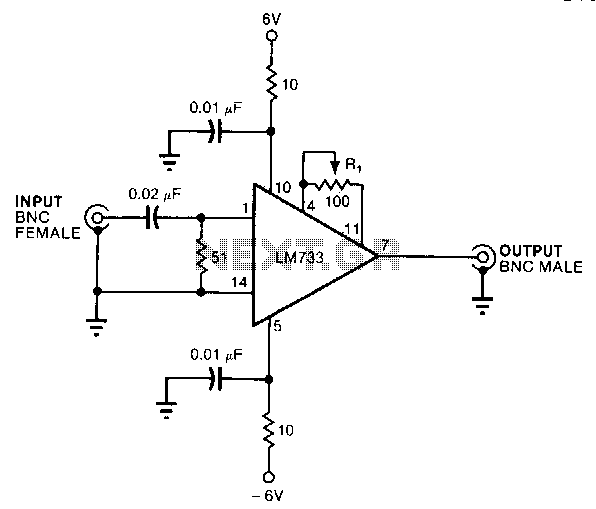
Scope calibrator
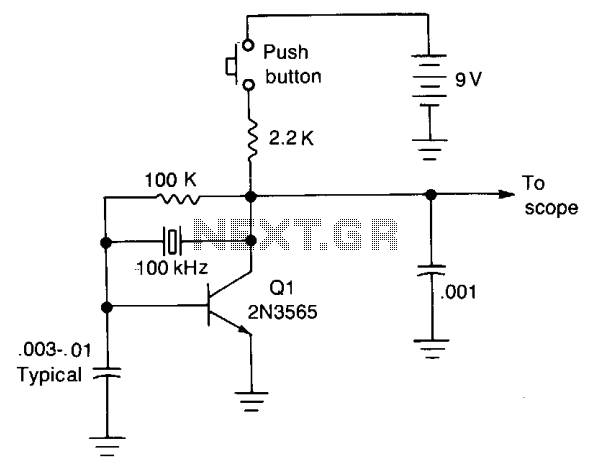
The calibrator operates at a precise frequency of 100 kHz, serving as a reference for calibrating the variable time base oscillator of general-purpose oscilloscopes. For instance, if the oscilloscope is configured such that one cycle of the signal occupies exactly 10 graticule divisions, each division corresponds to 1 MHz or 1 microsecond. Conversely, if the oscilloscope is adjusted to display 10 cycles across 10 graticule divisions (1 cycle per division), each division then represents 100 kHz or 10 microseconds.
The 100 kHz calibrator is an essential tool in the calibration and testing of oscilloscopes, ensuring accurate time measurements and frequency representations. The output signal generated by the calibrator is typically a sine wave or square wave, depending on the design specifications, and is characterized by a stable amplitude and low distortion. This stability is crucial for precise measurements in various applications, including electronics design, troubleshooting, and educational purposes.
In practical applications, the calibrator can be connected to the oscilloscope via a BNC connector, which is standard in many laboratory environments. The oscilloscope's time base settings must be adjusted to ensure that the displayed waveform accurately reflects the frequency of the calibrator. This involves setting the horizontal scale of the oscilloscope to achieve the desired number of cycles per division, which facilitates a clear visual representation of the signal.
Furthermore, the calibrator may feature additional outputs or adjustable parameters to accommodate different testing scenarios. For example, some models allow the user to switch between different frequencies or waveform types, providing versatility in calibration tasks. The design may also include indicators or digital displays to provide real-time feedback on the output frequency and amplitude, enhancing usability and precision in calibration processes.
Overall, the 100 kHz calibrator plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of oscilloscopes, contributing to the overall quality of electronic measurements and testing. Proper use of this tool can significantly improve the performance of electronic equipment and facilitate effective troubleshooting and design validation.The calibrator operates on exactly 100 kHz providing a reference for calibrating the variable time base oscillator of general purpose scopes. For example, if the scope is set so that one cycle of the signal fills exactly 10 graticule divisions then each division represents 1 MHz, or 1 microsecond.
If the scope is adjusted for 10 cycles on 10 graticule divisions. (1 cycle per division) then each division represents 100 kHz or 10 microseconds.
The 100 kHz calibrator is an essential tool in the calibration and testing of oscilloscopes, ensuring accurate time measurements and frequency representations. The output signal generated by the calibrator is typically a sine wave or square wave, depending on the design specifications, and is characterized by a stable amplitude and low distortion. This stability is crucial for precise measurements in various applications, including electronics design, troubleshooting, and educational purposes.
In practical applications, the calibrator can be connected to the oscilloscope via a BNC connector, which is standard in many laboratory environments. The oscilloscope's time base settings must be adjusted to ensure that the displayed waveform accurately reflects the frequency of the calibrator. This involves setting the horizontal scale of the oscilloscope to achieve the desired number of cycles per division, which facilitates a clear visual representation of the signal.
Furthermore, the calibrator may feature additional outputs or adjustable parameters to accommodate different testing scenarios. For example, some models allow the user to switch between different frequencies or waveform types, providing versatility in calibration tasks. The design may also include indicators or digital displays to provide real-time feedback on the output frequency and amplitude, enhancing usability and precision in calibration processes.
Overall, the 100 kHz calibrator plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of oscilloscopes, contributing to the overall quality of electronic measurements and testing. Proper use of this tool can significantly improve the performance of electronic equipment and facilitate effective troubleshooting and design validation.The calibrator operates on exactly 100 kHz providing a reference for calibrating the variable time base oscillator of general purpose scopes. For example, if the scope is set so that one cycle of the signal fills exactly 10 graticule divisions then each division represents 1 MHz, or 1 microsecond.
If the scope is adjusted for 10 cycles on 10 graticule divisions. (1 cycle per division) then each division represents 100 kHz or 10 microseconds.