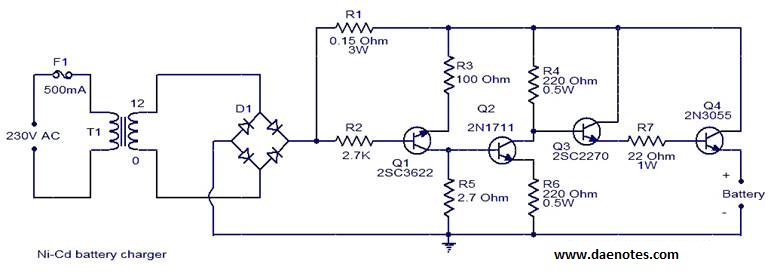
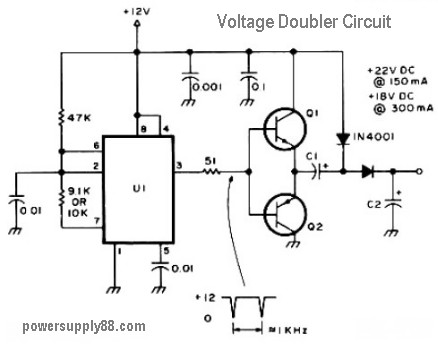
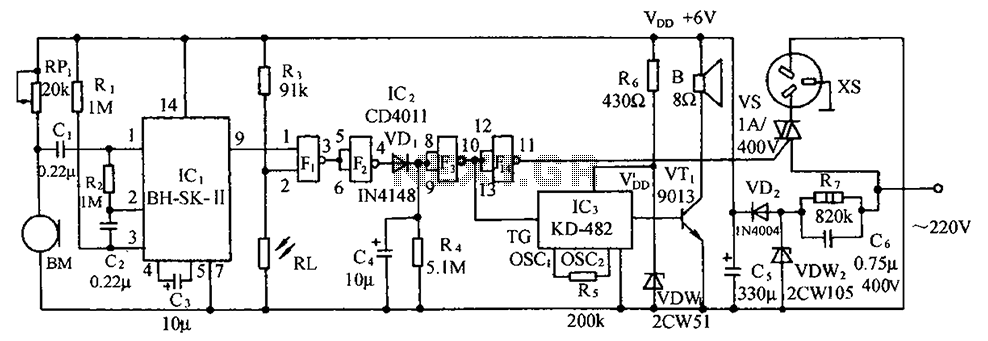
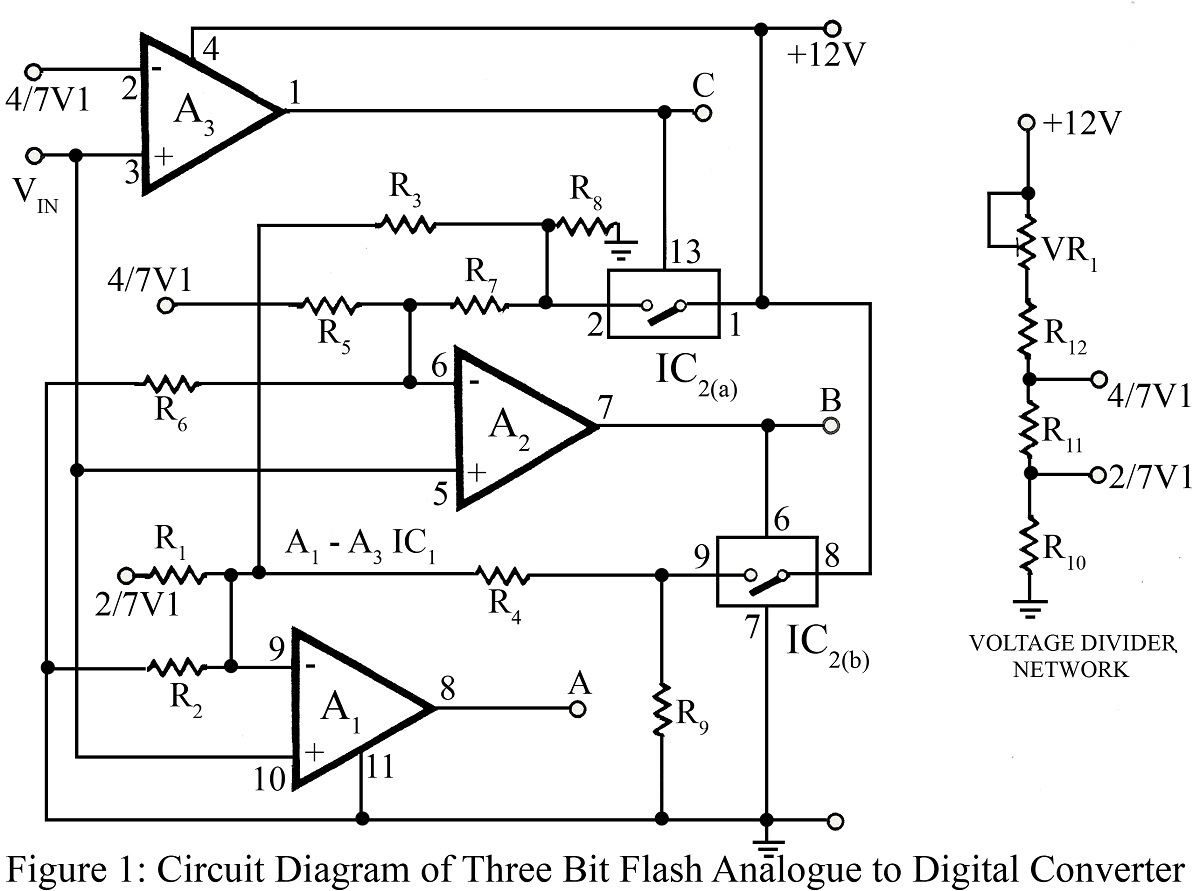
Simple Cellphone Battery Charger Circuit
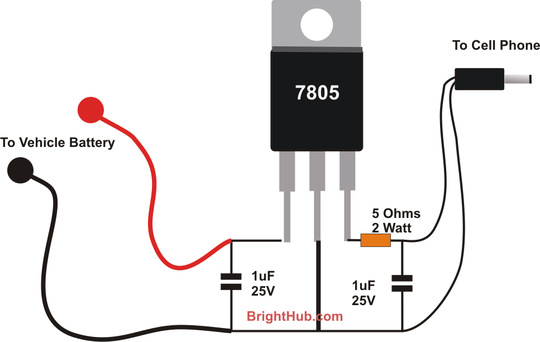
With the advent of modern integrated circuits (ICs), sophisticated circuits today are no longer required to be complex and lengthy. The chips themselves contain most of the intricate circuitry built-in and can independently perform the desired functions. For instance, consider the contemporary battery-operated cell phone charger circuit, which is designed for the specific application of charging a cell phone battery. This circuit can be constructed using only a few passive components along with a single active component (the IC 7805). Building the circuit as illustrated in the schematic is straightforward, and successfully completing it will yield satisfactory results. The input voltage (maximum 35 volts) can be supplied from any automobile lead-acid or sealed maintenance-free (SMF) battery. Upon connection, a regulated 5-volt output is achieved at the respective terminal of the IC through a current-limiting resistor. The output should be connected to the appropriate charging pin commonly found in most AC-operated cell phone chargers.
The battery-operated cell phone charger circuit leverages the voltage regulation capabilities of the IC 7805, which is a popular linear voltage regulator. This IC is capable of providing a stable output voltage of 5 volts, which is essential for charging most modern cell phones. The design requires minimal additional components, typically comprising a few resistors and capacitors that help stabilize the output and filter any noise from the input voltage source.
The input voltage to the circuit is sourced from a lead-acid or SMF battery, which can deliver a maximum of 35 volts. This high input voltage is reduced to a safe and usable level by the 7805 regulator. The current-limiting resistor is a crucial component in this setup, as it protects the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage the IC or the device being charged.
In practical applications, the output from the IC is connected to the charging pin of the cell phone, ensuring compatibility with the device's charging requirements. It is important to ensure that the connections are secure and that the polarity is correct to prevent damage to the cell phone.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the efficiency and simplicity that modern integrated circuits bring to electronic design, allowing for effective solutions to everyday problems such as charging mobile devices. The straightforward nature of the design makes it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike, emphasizing the significant advancements in circuit design facilitated by integrated technology.With the advent of modern ICs, sophisticated circuits today no longer have to be complex and lengthy. The chips themselves carry most of the complex circuitry built-in and single handedly perform the desired function.
Take for example the present battery operated cell phone charger circuit, which is intended for a relatively application of chargin g a cell phone battery yet can be simply built using just a couple of passive parts along with a single active part (the IC 7805). Yes indeed, if you build the circuit which is shown, exactly as per the guidelines of the schematic, completing and getting rewarded through its service won`t be difficult at all.
The input (max 35 volts) from any automobile lead acid or SMF battery is applied to the input of the circuit, instantly a regulated 5 volt output is obtained at the respective terminal of the IC via the current limiter resistor. The output must be terminated through an appropriate charging pin as used in most of the AC operated cell phone chargers.
🔗 External reference
The battery-operated cell phone charger circuit leverages the voltage regulation capabilities of the IC 7805, which is a popular linear voltage regulator. This IC is capable of providing a stable output voltage of 5 volts, which is essential for charging most modern cell phones. The design requires minimal additional components, typically comprising a few resistors and capacitors that help stabilize the output and filter any noise from the input voltage source.
The input voltage to the circuit is sourced from a lead-acid or SMF battery, which can deliver a maximum of 35 volts. This high input voltage is reduced to a safe and usable level by the 7805 regulator. The current-limiting resistor is a crucial component in this setup, as it protects the circuit from excessive current that could potentially damage the IC or the device being charged.
In practical applications, the output from the IC is connected to the charging pin of the cell phone, ensuring compatibility with the device's charging requirements. It is important to ensure that the connections are secure and that the polarity is correct to prevent damage to the cell phone.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the efficiency and simplicity that modern integrated circuits bring to electronic design, allowing for effective solutions to everyday problems such as charging mobile devices. The straightforward nature of the design makes it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike, emphasizing the significant advancements in circuit design facilitated by integrated technology.With the advent of modern ICs, sophisticated circuits today no longer have to be complex and lengthy. The chips themselves carry most of the complex circuitry built-in and single handedly perform the desired function.
Take for example the present battery operated cell phone charger circuit, which is intended for a relatively application of chargin g a cell phone battery yet can be simply built using just a couple of passive parts along with a single active part (the IC 7805). Yes indeed, if you build the circuit which is shown, exactly as per the guidelines of the schematic, completing and getting rewarded through its service won`t be difficult at all.
The input (max 35 volts) from any automobile lead acid or SMF battery is applied to the input of the circuit, instantly a regulated 5 volt output is obtained at the respective terminal of the IC via the current limiter resistor. The output must be terminated through an appropriate charging pin as used in most of the AC operated cell phone chargers.
🔗 External reference