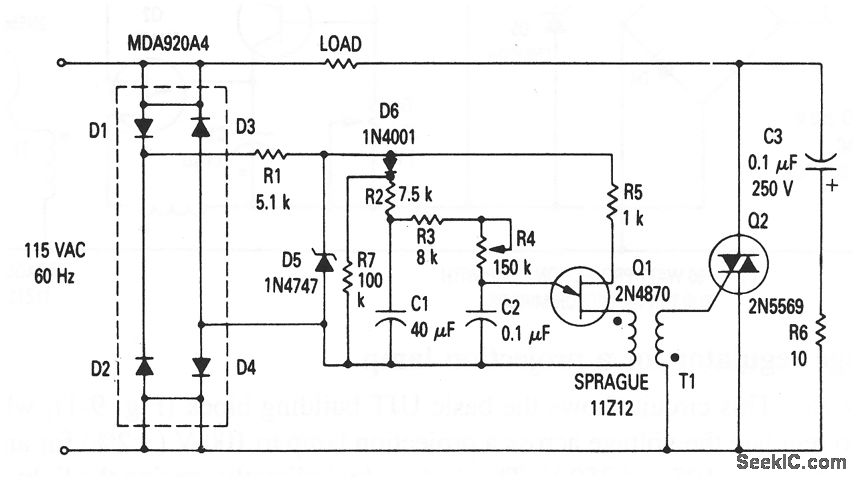
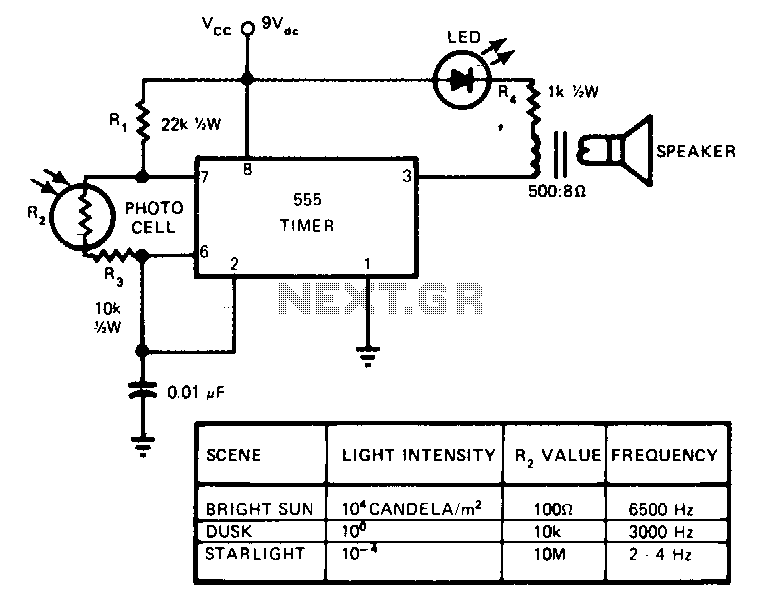
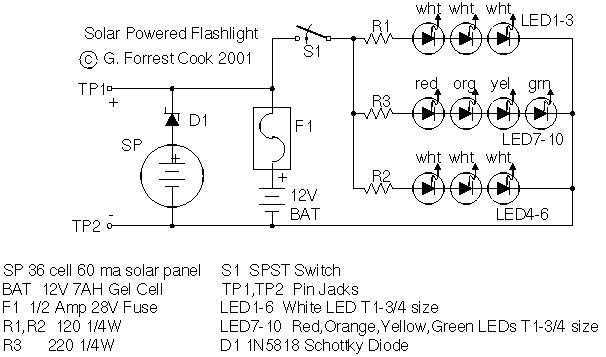
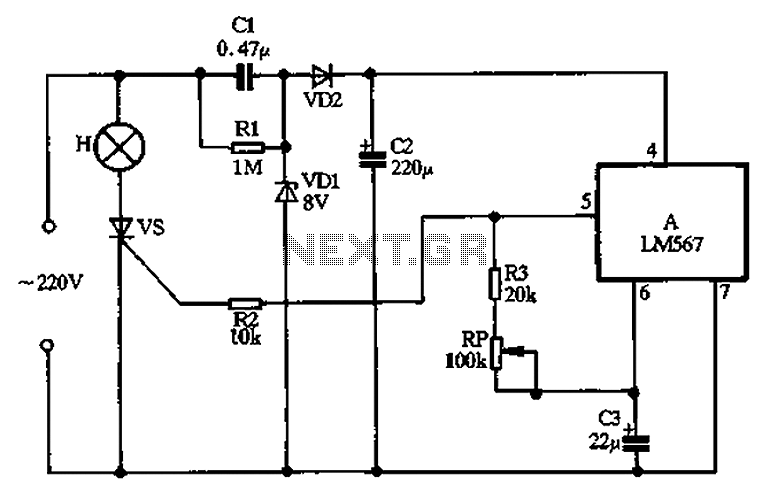
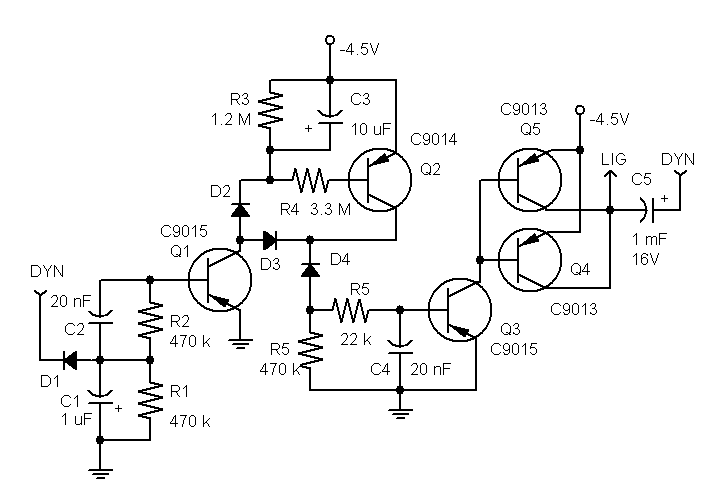
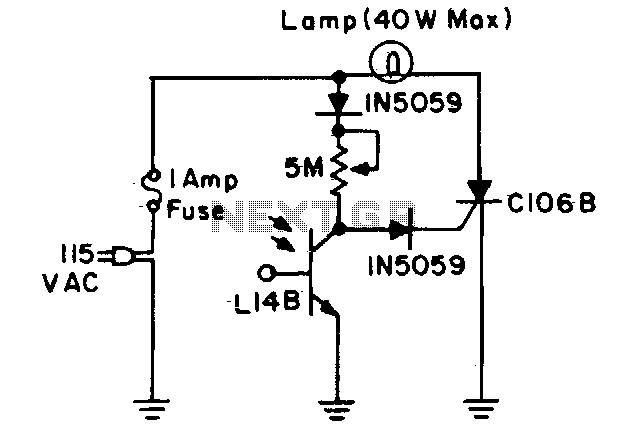
Sound-modulated light source
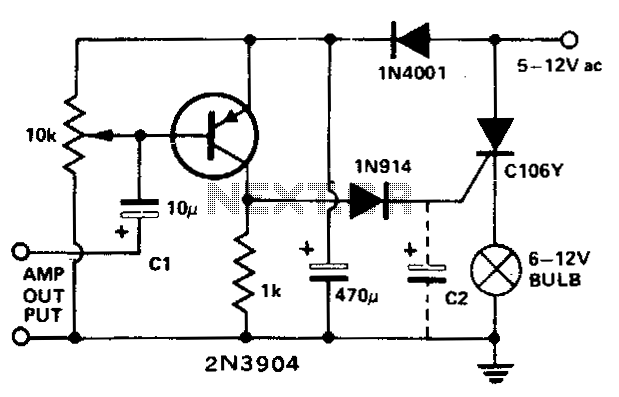
This circuit modulates a light beam using audio signals from an amplifier's output. By adjusting the 10 K potentiometer to a value slightly less than the Vbe of the transistor, the circuit operates as a peak detector. This configuration drives the gate of a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR), controlling the brightness of a connected bulb in accordance with the varying sound levels. The capacitor C2 can be omitted to achieve a faster response time.
The described circuit utilizes a transistor configured as a peak detector to modulate light intensity based on audio input. The 10 K potentiometer allows for fine-tuning the voltage bias at the base of the transistor, ensuring that it operates within the desired threshold for detecting peaks in the audio signal. When the audio signal exceeds this threshold, the transistor conducts, enabling current to flow through the gate of the SCR.
The SCR acts as a switch that controls the power delivered to the bulb. As the audio signal fluctuates, the SCR turns on and off, leading to variations in the bulb's brightness corresponding to the amplitude of the sound. This modulation creates a visual representation of the audio signal, providing an engaging effect.
In applications where a quicker response is required, the capacitor C2 can be removed. This alteration reduces the circuit's time constant, allowing the SCR to react more swiftly to changes in the audio signal. However, it is essential to consider that eliminating C2 may lead to a less stable operation under certain conditions, potentially resulting in flickering of the bulb.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for visualizing audio signals through light modulation, combining basic electronic components to achieve a dynamic interaction between sound and light.This circuit modulates a light beam with voice or music from the output of an amplifier. If the 10 K pot is adjusted to slightly less than the Vbe of the transistor, the circuit forms a peak detector This drives the gate of the SCR, lighting the bulb whose brightness will vary as the sound level varies. C2 may be removed for a faster response. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a transistor configured as a peak detector to modulate light intensity based on audio input. The 10 K potentiometer allows for fine-tuning the voltage bias at the base of the transistor, ensuring that it operates within the desired threshold for detecting peaks in the audio signal. When the audio signal exceeds this threshold, the transistor conducts, enabling current to flow through the gate of the SCR.
The SCR acts as a switch that controls the power delivered to the bulb. As the audio signal fluctuates, the SCR turns on and off, leading to variations in the bulb's brightness corresponding to the amplitude of the sound. This modulation creates a visual representation of the audio signal, providing an engaging effect.
In applications where a quicker response is required, the capacitor C2 can be removed. This alteration reduces the circuit's time constant, allowing the SCR to react more swiftly to changes in the audio signal. However, it is essential to consider that eliminating C2 may lead to a less stable operation under certain conditions, potentially resulting in flickering of the bulb.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective method for visualizing audio signals through light modulation, combining basic electronic components to achieve a dynamic interaction between sound and light.This circuit modulates a light beam with voice or music from the output of an amplifier. If the 10 K pot is adjusted to slightly less than the Vbe of the transistor, the circuit forms a peak detector This drives the gate of the SCR, lighting the bulb whose brightness will vary as the sound level varies. C2 may be removed for a faster response. 🔗 External reference