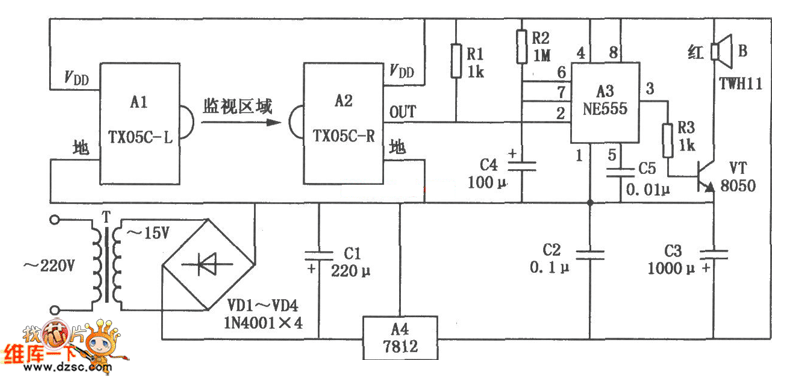
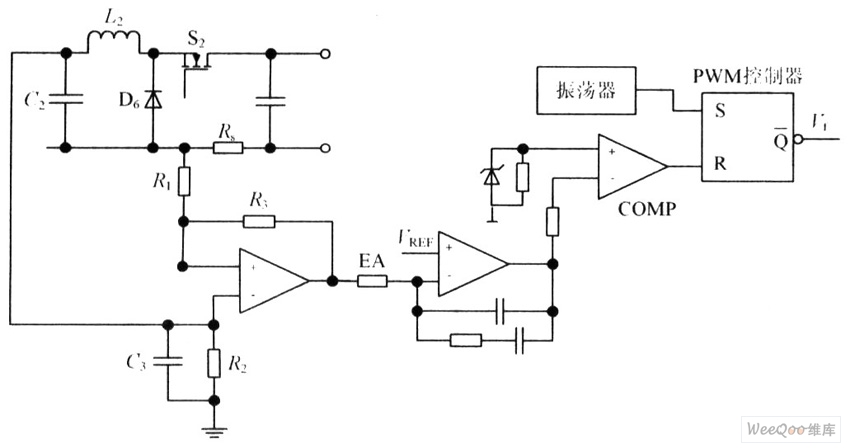
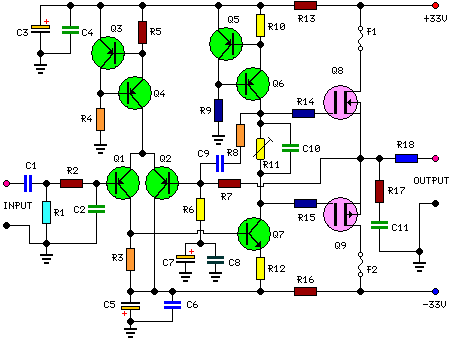
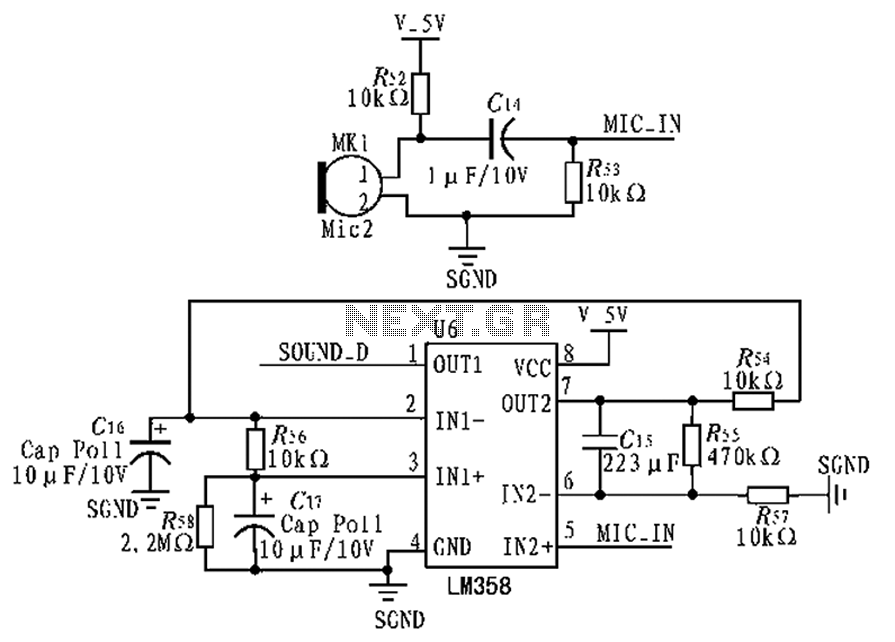
Telephone Intercom Circuit
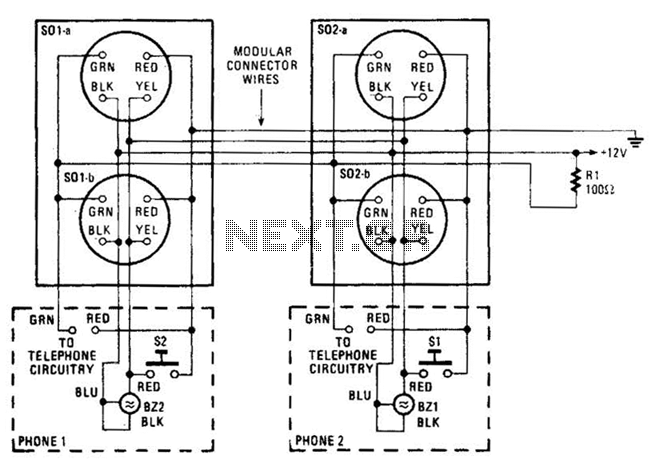
An intercom utilizing dual-modular wall jacks is depicted in this circuit. If the wires are accessible in the home telephone cable, this system can be installed with minimal difficulty.
The intercom system described employs dual-modular wall jacks, which are standard connectors commonly used in telecommunications. The use of these jacks allows for easy connectivity and installation, particularly in residential settings where existing telephone wiring can be repurposed.
The circuit typically consists of two main components: the intercom units and the dual-modular wall jacks. Each intercom unit is equipped with a microphone and a speaker, enabling two-way communication. The dual-modular wall jacks serve as the interface points where the intercom units connect to the existing telephone wiring.
To install the system, the existing telephone cables, which usually contain multiple pairs of wires, can be utilized. The intercom units are connected to the appropriate pairs of wires at each wall jack. This setup not only simplifies the installation process but also minimizes the need for additional wiring, making it a cost-effective solution for home communication.
The intercom system can be powered through the existing telephone line, eliminating the need for separate power supplies. This feature enhances the convenience of the installation, as it reduces the complexity and potential points of failure in the system.
In summary, the intercom using dual-modular wall jacks is a practical solution for home communication, leveraging existing infrastructure to provide a straightforward installation process. The design ensures that users can easily communicate across different rooms without the need for extensive modifications to their home wiring. An intercom using dual-modular wall jacks is shown in this circuit. If the wires are available in the home telephone cable, this system can be installed with little trouble. 🔗 External reference
The intercom system described employs dual-modular wall jacks, which are standard connectors commonly used in telecommunications. The use of these jacks allows for easy connectivity and installation, particularly in residential settings where existing telephone wiring can be repurposed.
The circuit typically consists of two main components: the intercom units and the dual-modular wall jacks. Each intercom unit is equipped with a microphone and a speaker, enabling two-way communication. The dual-modular wall jacks serve as the interface points where the intercom units connect to the existing telephone wiring.
To install the system, the existing telephone cables, which usually contain multiple pairs of wires, can be utilized. The intercom units are connected to the appropriate pairs of wires at each wall jack. This setup not only simplifies the installation process but also minimizes the need for additional wiring, making it a cost-effective solution for home communication.
The intercom system can be powered through the existing telephone line, eliminating the need for separate power supplies. This feature enhances the convenience of the installation, as it reduces the complexity and potential points of failure in the system.
In summary, the intercom using dual-modular wall jacks is a practical solution for home communication, leveraging existing infrastructure to provide a straightforward installation process. The design ensures that users can easily communicate across different rooms without the need for extensive modifications to their home wiring. An intercom using dual-modular wall jacks is shown in this circuit. If the wires are available in the home telephone cable, this system can be installed with little trouble. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713