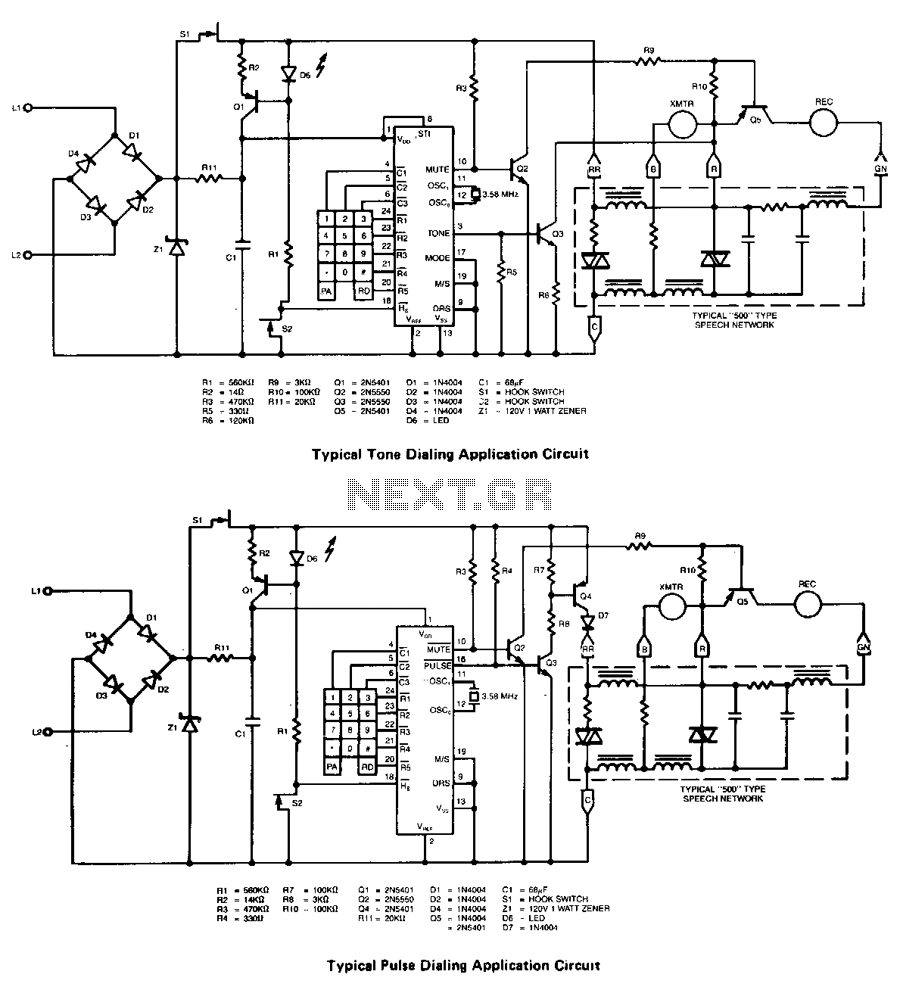
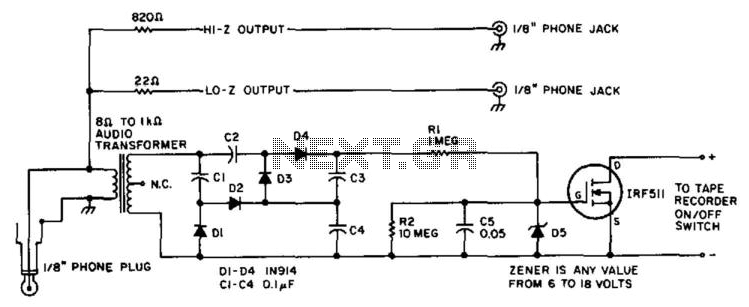
Telephone-line powered repertory dialer

A repertory dialer phone contains a library of phone numbers that can be entered and dialed, allowing access to up to fifteen frequently used numbers. It also includes the capability to store the last dialed number or an additional telephone number in standard CMOS RAM for automatic dialing.
The repertory dialer phone circuit primarily consists of a microcontroller, a memory module, a keypad, and a dialing mechanism. The microcontroller is responsible for managing user inputs via the keypad, controlling the dialing process, and interfacing with the memory module. The memory module, typically implemented using CMOS RAM, stores up to fifteen phone numbers, as well as the last dialed number. This allows for quick access and retrieval of frequently used contacts.
The keypad is designed to allow users to input phone numbers easily and select which number to dial. Each key corresponds to a specific function, such as storing a new number, dialing a number, or accessing the last dialed number. The dialing mechanism can be either a traditional rotary dial or a more modern DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) system, which generates the necessary tones for dialing.
When a user wishes to store a phone number, the microcontroller receives the input from the keypad and writes the number into the CMOS RAM. This process ensures that the number is saved even when the phone is powered off, thanks to the non-volatile nature of CMOS technology. To dial a number, the user simply selects it from the stored list, and the microcontroller sends the appropriate signals to the dialing mechanism, allowing the phone to connect to the desired line automatically.
In summary, the design of the repertory dialer phone integrates various electronic components to facilitate efficient phone number storage and dialing, enhancing user convenience and functionality in everyday communication.Repertory dialer phone has a library of phone numbers to be keyed in and dialed out fifteen frequently used numbers (plus the last directly or a telephone number to be stored in number dialed) stored in a standard CMOS the RAM and dialed automatically. 🔗 External reference
The repertory dialer phone circuit primarily consists of a microcontroller, a memory module, a keypad, and a dialing mechanism. The microcontroller is responsible for managing user inputs via the keypad, controlling the dialing process, and interfacing with the memory module. The memory module, typically implemented using CMOS RAM, stores up to fifteen phone numbers, as well as the last dialed number. This allows for quick access and retrieval of frequently used contacts.
The keypad is designed to allow users to input phone numbers easily and select which number to dial. Each key corresponds to a specific function, such as storing a new number, dialing a number, or accessing the last dialed number. The dialing mechanism can be either a traditional rotary dial or a more modern DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) system, which generates the necessary tones for dialing.
When a user wishes to store a phone number, the microcontroller receives the input from the keypad and writes the number into the CMOS RAM. This process ensures that the number is saved even when the phone is powered off, thanks to the non-volatile nature of CMOS technology. To dial a number, the user simply selects it from the stored list, and the microcontroller sends the appropriate signals to the dialing mechanism, allowing the phone to connect to the desired line automatically.
In summary, the design of the repertory dialer phone integrates various electronic components to facilitate efficient phone number storage and dialing, enhancing user convenience and functionality in everyday communication.Repertory dialer phone has a library of phone numbers to be keyed in and dialed out fifteen frequently used numbers (plus the last directly or a telephone number to be stored in number dialed) stored in a standard CMOS the RAM and dialed automatically. 🔗 External reference