Temperature Controller For PC PCB
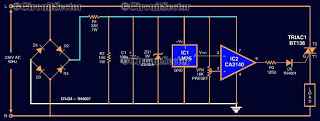
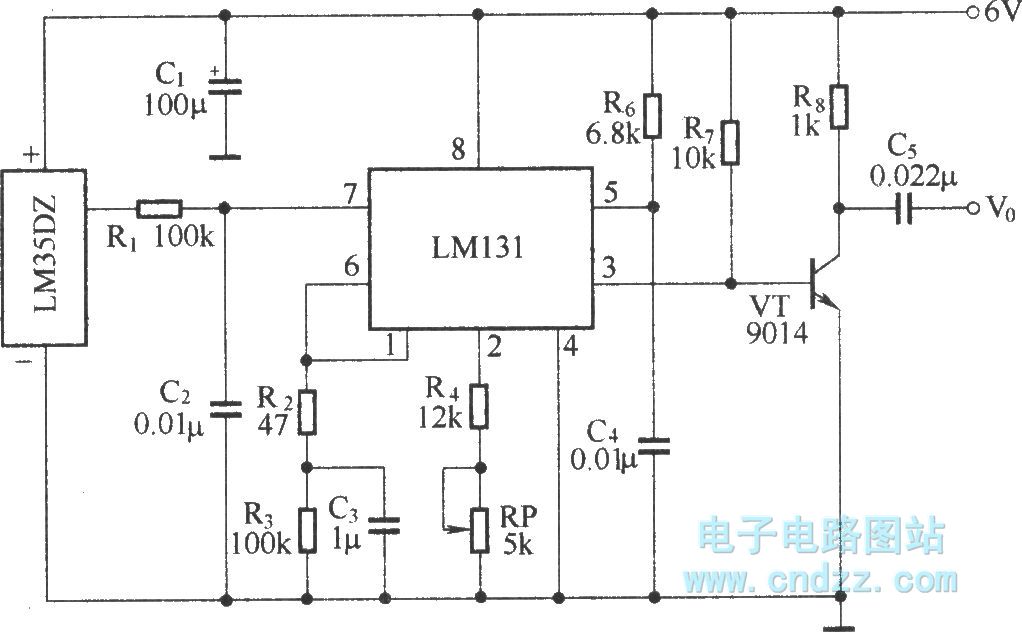
Computers often experience overheating due to prolonged use or high ambient temperatures, making temperature controllers essential. Accurate temperature measurement is necessary to ensure that the computer operates within a safe temperature range. A circuit diagram for a simple temperature controller for personal computers (PC) is presented, utilizing the LM35 temperature sensor and CA3140 comparator. This circuit automatically shuts off the PC when the temperature exceeds a specific optimum threshold, preventing overheating of integrated circuits (ICs) that may not dissipate heat effectively. The cutoff temperature is set at 55 degrees Celsius, which can be adjusted using a VR1 potentiometer that modifies the comparator's reference voltage. Resistors R1, R2, and ZD1 (9V, 0.5W) are employed to stabilize the output of the rectifier. Under normal temperature conditions, the comparator generates an error voltage that activates a triac supplying power to the PC. If the PC temperature surpasses the threshold, the comparator output goes low, deactivating the triac and shutting down the PC.
The temperature controller circuit is designed to maintain optimal operating conditions for personal computers by monitoring and regulating internal temperatures. The LM35 temperature sensor provides a precise voltage output proportional to the temperature, allowing for accurate monitoring. The CA3140 comparator compares the output voltage from the LM35 with a reference voltage set by the VR1 potentiometer. This adjustable reference allows for customization of the cutoff temperature according to user requirements.
When the temperature remains below the set threshold, the comparator outputs a high signal, keeping the triac in the conducting state, which allows current to flow to the PC. This ensures that the computer remains operational during normal conditions. However, once the temperature exceeds 55 degrees Celsius, the comparator's output drops to a low state, which turns off the triac. This action interrupts the power supply to the PC, effectively shutting it down and preventing potential damage from overheating.
The resistors R1 and R2 serve to stabilize the output voltage from the rectifier circuit, ensuring reliable operation of the temperature controller. The ZD1 component, a zener diode rated at 9V and 0.5W, provides additional voltage regulation, maintaining consistent performance across varying input conditions.
This temperature control circuit is particularly beneficial for high-performance PCs that generate significant heat during operation, as it helps to prolong the lifespan of critical components by preventing thermal stress. By integrating this simple yet effective temperature controller, users can safeguard their systems from the adverse effects of overheating, ensuring stable and reliable performance.Our computer may often heated up due to long use or the hot climate, temperature controllers are necessary. You need to do a temperature measurement to ensure that the computer is work within the allowed range.
To reduce pc temperature, here is circuit diagram of a simple temperature controller for your personal computer (PC) based on a temperatur e sensor LM35 and a comparator CA3140. The circuit turns off the PC when the temperature of the computer increases beyond a particular, optimum temperature value. This avoids overheating of some integrated chips (IC) that may not be able to dissipate heat fast enough.
For this pc temperature controller, the cut off temperature is assumed to be 55 degree Celsius. The circuit contains a temperature sensor LM35 and comparator. ( The threshold value of 55 can be adjusted using VR1 potentiometer actually varies the comparator reference voltage). The R1, R2 and ZD1(9V, 0. 5W) used for stabilizing the output of the rectifier. In normal temperature, the comparator produces an error voltage which triggers the triac that give supply to PC (load).
Whenever the PC temperature go beyond the threshold value, the comparator output become low, causes to shut down the triac hence the PC. 🔗 External reference
The temperature controller circuit is designed to maintain optimal operating conditions for personal computers by monitoring and regulating internal temperatures. The LM35 temperature sensor provides a precise voltage output proportional to the temperature, allowing for accurate monitoring. The CA3140 comparator compares the output voltage from the LM35 with a reference voltage set by the VR1 potentiometer. This adjustable reference allows for customization of the cutoff temperature according to user requirements.
When the temperature remains below the set threshold, the comparator outputs a high signal, keeping the triac in the conducting state, which allows current to flow to the PC. This ensures that the computer remains operational during normal conditions. However, once the temperature exceeds 55 degrees Celsius, the comparator's output drops to a low state, which turns off the triac. This action interrupts the power supply to the PC, effectively shutting it down and preventing potential damage from overheating.
The resistors R1 and R2 serve to stabilize the output voltage from the rectifier circuit, ensuring reliable operation of the temperature controller. The ZD1 component, a zener diode rated at 9V and 0.5W, provides additional voltage regulation, maintaining consistent performance across varying input conditions.
This temperature control circuit is particularly beneficial for high-performance PCs that generate significant heat during operation, as it helps to prolong the lifespan of critical components by preventing thermal stress. By integrating this simple yet effective temperature controller, users can safeguard their systems from the adverse effects of overheating, ensuring stable and reliable performance.Our computer may often heated up due to long use or the hot climate, temperature controllers are necessary. You need to do a temperature measurement to ensure that the computer is work within the allowed range.
To reduce pc temperature, here is circuit diagram of a simple temperature controller for your personal computer (PC) based on a temperatur e sensor LM35 and a comparator CA3140. The circuit turns off the PC when the temperature of the computer increases beyond a particular, optimum temperature value. This avoids overheating of some integrated chips (IC) that may not be able to dissipate heat fast enough.
For this pc temperature controller, the cut off temperature is assumed to be 55 degree Celsius. The circuit contains a temperature sensor LM35 and comparator. ( The threshold value of 55 can be adjusted using VR1 potentiometer actually varies the comparator reference voltage). The R1, R2 and ZD1(9V, 0. 5W) used for stabilizing the output of the rectifier. In normal temperature, the comparator produces an error voltage which triggers the triac that give supply to PC (load).
Whenever the PC temperature go beyond the threshold value, the comparator output become low, causes to shut down the triac hence the PC. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713