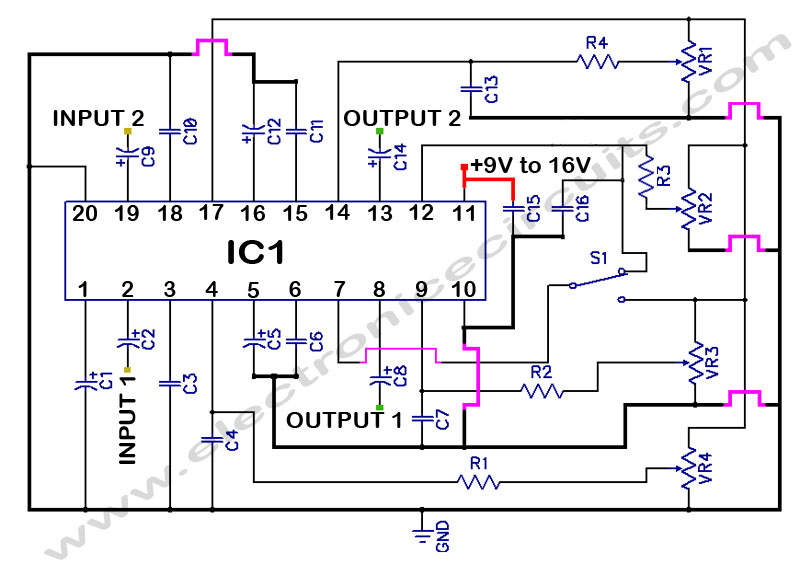
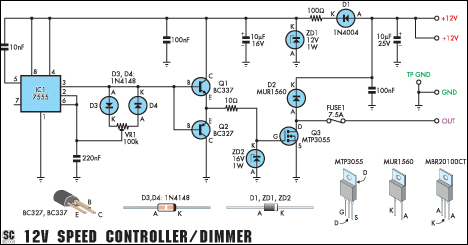
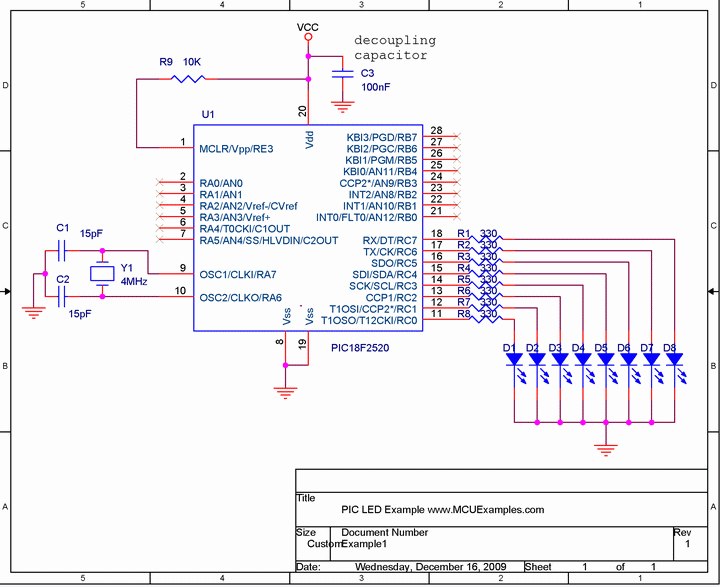
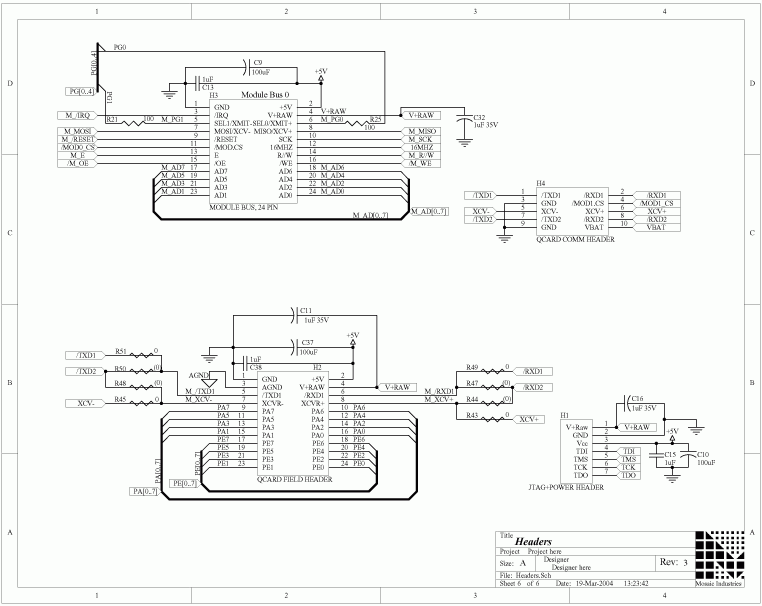
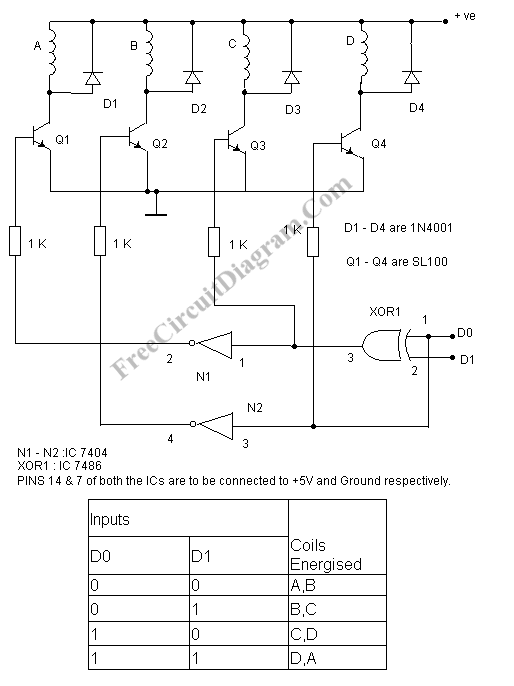
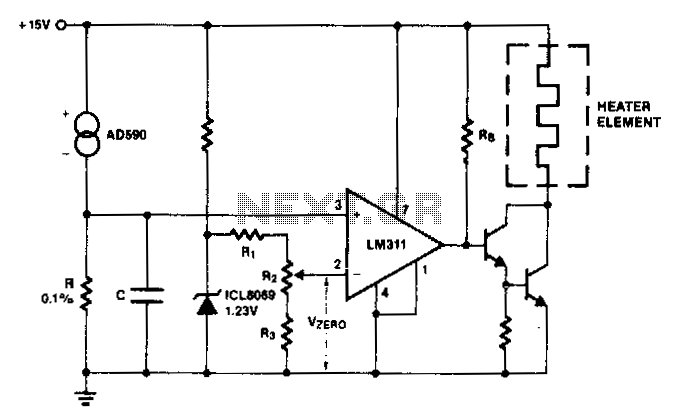
Temperature Controller with U217B
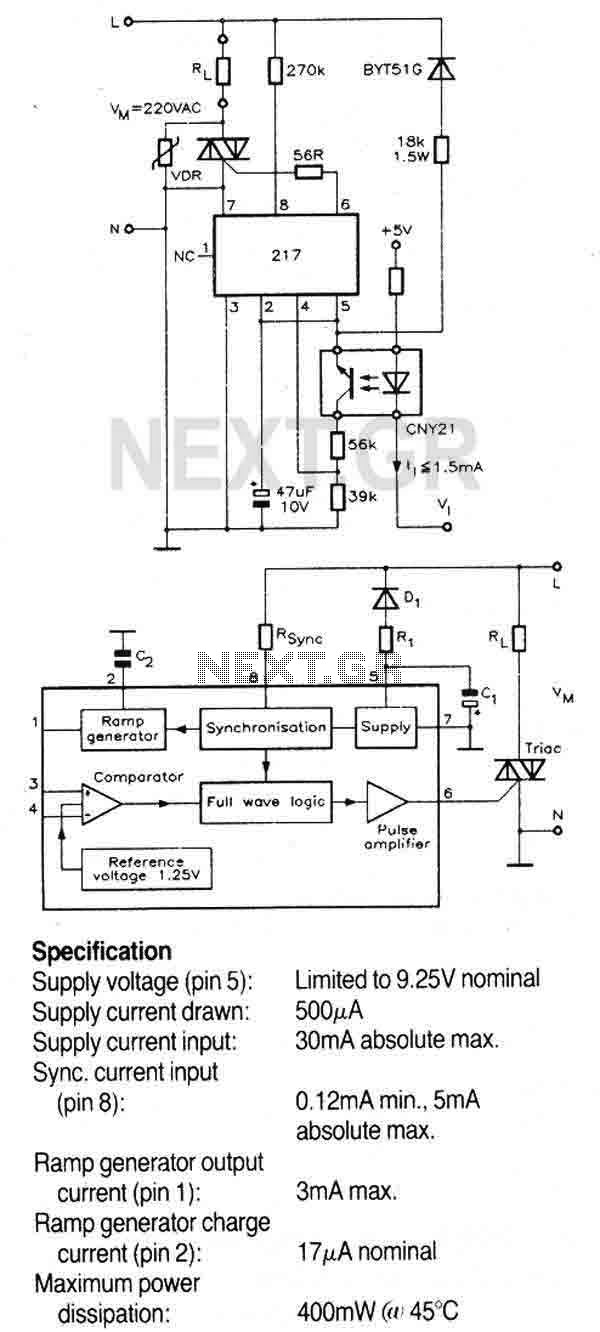
A triac controller for switching resistive loads directly from the mains supply using the zero crossing technique. The device is powered directly from the mains via a diode and dropper resistor, and the IC has its own regulator to limit its supply to 9.25V. To ensure that no switching occurs outside of the zero crossing point, full wave logic is employed to guarantee that complete mains cycles only are switched to the load. More: A ramp a freely selectable ramp duration (as determined by a timing capacitor), together with the full-wave logic block, synchronised to the AC supply at pin 8 via a dropper resistor (RSync). The ramp generator not only provides symmetrical trigger pulse.
This triac controller circuit is designed to effectively manage resistive loads, utilizing a zero-crossing detection method to minimize electrical noise and reduce the risk of arcing in the switching device. The circuit is powered directly from the AC mains, with the input voltage being rectified by a diode. The dropper resistor serves to limit the current flowing into the circuit, ensuring safe operation.
The integrated circuit (IC) within the controller features an internal voltage regulator that stabilizes the supply voltage to 9.25V, which is critical for maintaining consistent performance of the control logic and timing functions. The zero-crossing technique is implemented to prevent the triac from switching on or off at any point other than the zero voltage crossing of the AC waveform, thus reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improving the longevity of the connected load.
A timing capacitor is employed to determine the duration of the ramp signal, which is crucial for controlling the phase angle at which the triac is triggered. The ramp generator produces a symmetrical pulse that is synchronized with the AC supply voltage, ensuring that the timing of the triac activation is precisely coordinated with the mains frequency. The synchronization is achieved through a dedicated pin (pin 8) connected to the AC waveform via the dropper resistor (RSync), allowing the full-wave logic block to operate effectively.
The full-wave logic block plays a vital role in the circuit, ensuring that the triac is only activated during the appropriate half-cycles of the AC waveform. This functionality not only enhances the efficiency of the load control but also contributes to the overall safety and reliability of the system. With these design considerations, the triac controller provides a robust solution for switching resistive loads in various applications, from household appliances to industrial equipment.A triac controller for switching resistive loads directly from the mains supply using the zero crossing technique. The device is powered directly from the mains via a diode and dropper resistor, and the IC has its own regulator to limit its supply to 9.25V.
To ensure that no switching occurs outside of the zero crossing point, full wave logic is employed to guarantee that complete mains cycles only are switched to the load. A ramp a freely selectable ramp duration (as determined by a timing capacitor),together with the full-wave logic block, synchronised to the AC supply at pin 8 via a dropper resistor (RSync). The ramp generator not only provides symmetrical trigger pulse c 🔗 External reference
This triac controller circuit is designed to effectively manage resistive loads, utilizing a zero-crossing detection method to minimize electrical noise and reduce the risk of arcing in the switching device. The circuit is powered directly from the AC mains, with the input voltage being rectified by a diode. The dropper resistor serves to limit the current flowing into the circuit, ensuring safe operation.
The integrated circuit (IC) within the controller features an internal voltage regulator that stabilizes the supply voltage to 9.25V, which is critical for maintaining consistent performance of the control logic and timing functions. The zero-crossing technique is implemented to prevent the triac from switching on or off at any point other than the zero voltage crossing of the AC waveform, thus reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improving the longevity of the connected load.
A timing capacitor is employed to determine the duration of the ramp signal, which is crucial for controlling the phase angle at which the triac is triggered. The ramp generator produces a symmetrical pulse that is synchronized with the AC supply voltage, ensuring that the timing of the triac activation is precisely coordinated with the mains frequency. The synchronization is achieved through a dedicated pin (pin 8) connected to the AC waveform via the dropper resistor (RSync), allowing the full-wave logic block to operate effectively.
The full-wave logic block plays a vital role in the circuit, ensuring that the triac is only activated during the appropriate half-cycles of the AC waveform. This functionality not only enhances the efficiency of the load control but also contributes to the overall safety and reliability of the system. With these design considerations, the triac controller provides a robust solution for switching resistive loads in various applications, from household appliances to industrial equipment.A triac controller for switching resistive loads directly from the mains supply using the zero crossing technique. The device is powered directly from the mains via a diode and dropper resistor, and the IC has its own regulator to limit its supply to 9.25V.
To ensure that no switching occurs outside of the zero crossing point, full wave logic is employed to guarantee that complete mains cycles only are switched to the load. A ramp a freely selectable ramp duration (as determined by a timing capacitor),together with the full-wave logic block, synchronised to the AC supply at pin 8 via a dropper resistor (RSync). The ramp generator not only provides symmetrical trigger pulse c 🔗 External reference