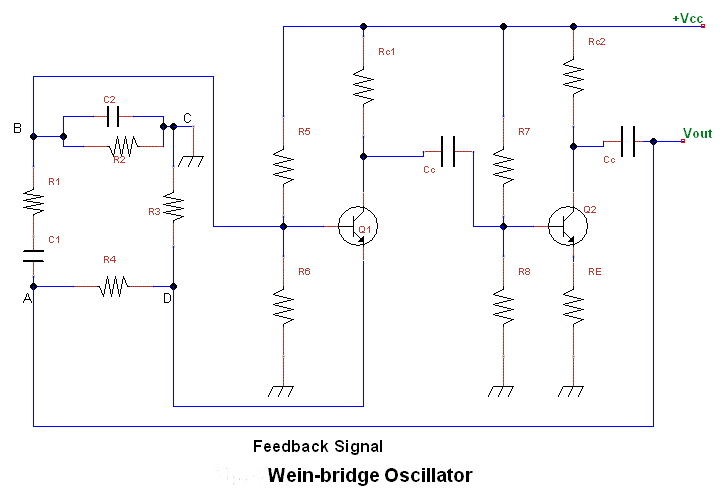
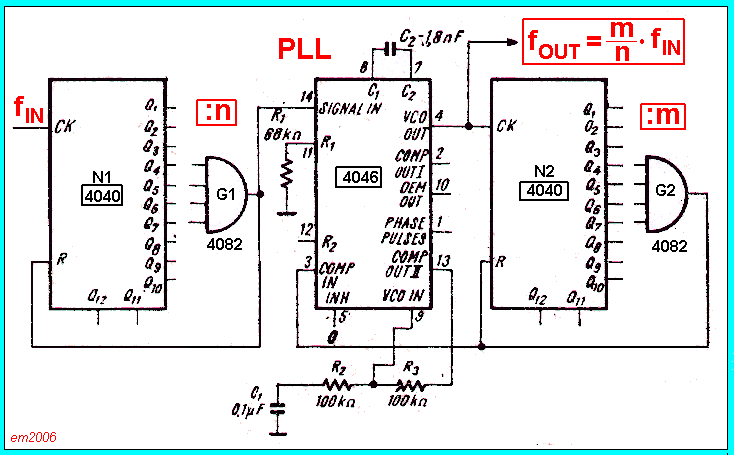
The Quartz crystal oscillator circuit
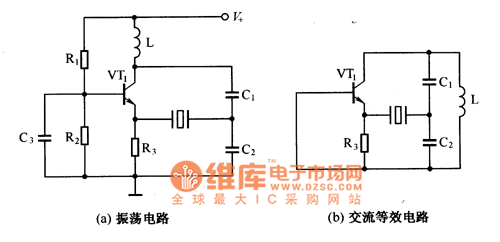
The oscillator that consists of a quartz crystal can be classified into two types: the parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and the series resonant type crystal oscillator. The parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and its AC equivalent circuit are illustrated in figure 1. In this circuit, the quartz crystal is represented as an inductance LD.
The parallel resonant crystal oscillator operates based on the principles of resonance, where the quartz crystal exhibits a frequency at which it can oscillate efficiently. This type of oscillator typically includes components such as capacitors and resistors in addition to the quartz crystal, forming an LC circuit. The parallel resonant circuit is characterized by its ability to maintain a stable oscillation frequency, which is primarily determined by the characteristics of the quartz crystal.
In the AC equivalent circuit, the quartz crystal can be modeled as a series combination of an inductance (LD), a series resistance (RS), and a parallel capacitance (CP). The inductance represents the mechanical vibrations of the crystal, while the series resistance accounts for energy losses due to the internal friction of the crystal material. The parallel capacitance reflects the capacitance between the electrodes of the crystal.
When analyzing the behavior of the parallel resonant crystal oscillator, it is essential to consider the quality factor (Q) of the circuit, which indicates the sharpness of the resonance peak. A higher Q factor implies a narrower bandwidth and better frequency stability. The oscillator can be utilized in various applications, including clock generation in digital circuits, RF signal generation, and frequency stabilization in communication systems.
The series resonant type crystal oscillator, in contrast, operates differently, where the crystal is connected in series with the load. This configuration is typically used in situations where a lower output impedance is required. The series resonant oscillator also relies on the quartz crystal's properties but exhibits distinct characteristics in terms of output signal and frequency stability.
Overall, crystal oscillators are critical components in modern electronic systems, providing precise frequency references essential for the operation of various devices.The oscillator that is composed of the quartz crystal can be divided into two kinds: the parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and the series resonant type crystal oscillator. The parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and the AC equivalent circuit of it are as shown in figure 1, if the quartz crystal is equivalent to the inductance LD, this circuit i..
🔗 External reference
The parallel resonant crystal oscillator operates based on the principles of resonance, where the quartz crystal exhibits a frequency at which it can oscillate efficiently. This type of oscillator typically includes components such as capacitors and resistors in addition to the quartz crystal, forming an LC circuit. The parallel resonant circuit is characterized by its ability to maintain a stable oscillation frequency, which is primarily determined by the characteristics of the quartz crystal.
In the AC equivalent circuit, the quartz crystal can be modeled as a series combination of an inductance (LD), a series resistance (RS), and a parallel capacitance (CP). The inductance represents the mechanical vibrations of the crystal, while the series resistance accounts for energy losses due to the internal friction of the crystal material. The parallel capacitance reflects the capacitance between the electrodes of the crystal.
When analyzing the behavior of the parallel resonant crystal oscillator, it is essential to consider the quality factor (Q) of the circuit, which indicates the sharpness of the resonance peak. A higher Q factor implies a narrower bandwidth and better frequency stability. The oscillator can be utilized in various applications, including clock generation in digital circuits, RF signal generation, and frequency stabilization in communication systems.
The series resonant type crystal oscillator, in contrast, operates differently, where the crystal is connected in series with the load. This configuration is typically used in situations where a lower output impedance is required. The series resonant oscillator also relies on the quartz crystal's properties but exhibits distinct characteristics in terms of output signal and frequency stability.
Overall, crystal oscillators are critical components in modern electronic systems, providing precise frequency references essential for the operation of various devices.The oscillator that is composed of the quartz crystal can be divided into two kinds: the parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and the series resonant type crystal oscillator. The parallel resonant type crystal oscillator and the AC equivalent circuit of it are as shown in figure 1, if the quartz crystal is equivalent to the inductance LD, this circuit i..
🔗 External reference