Three-tone electronic doorbell 1
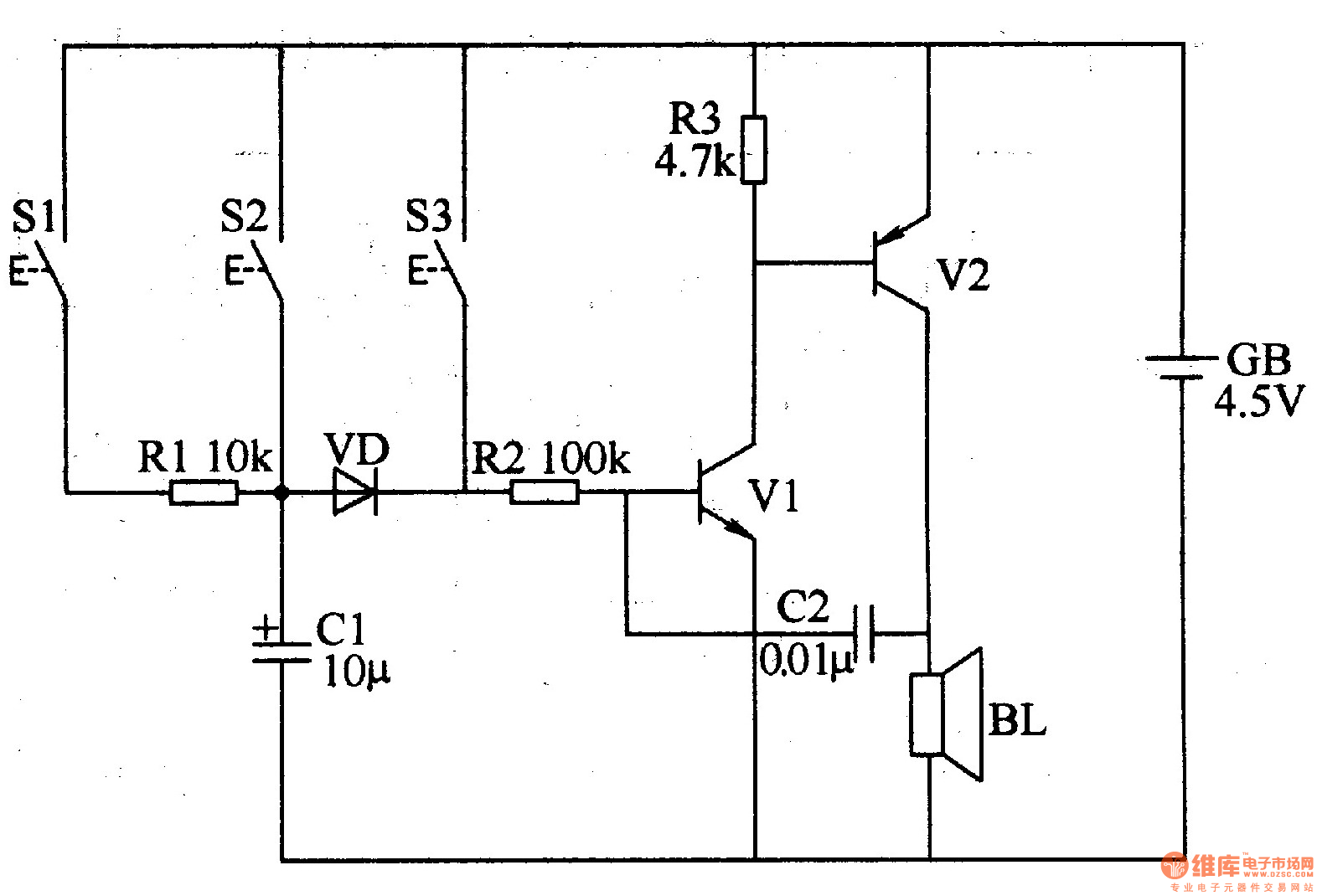
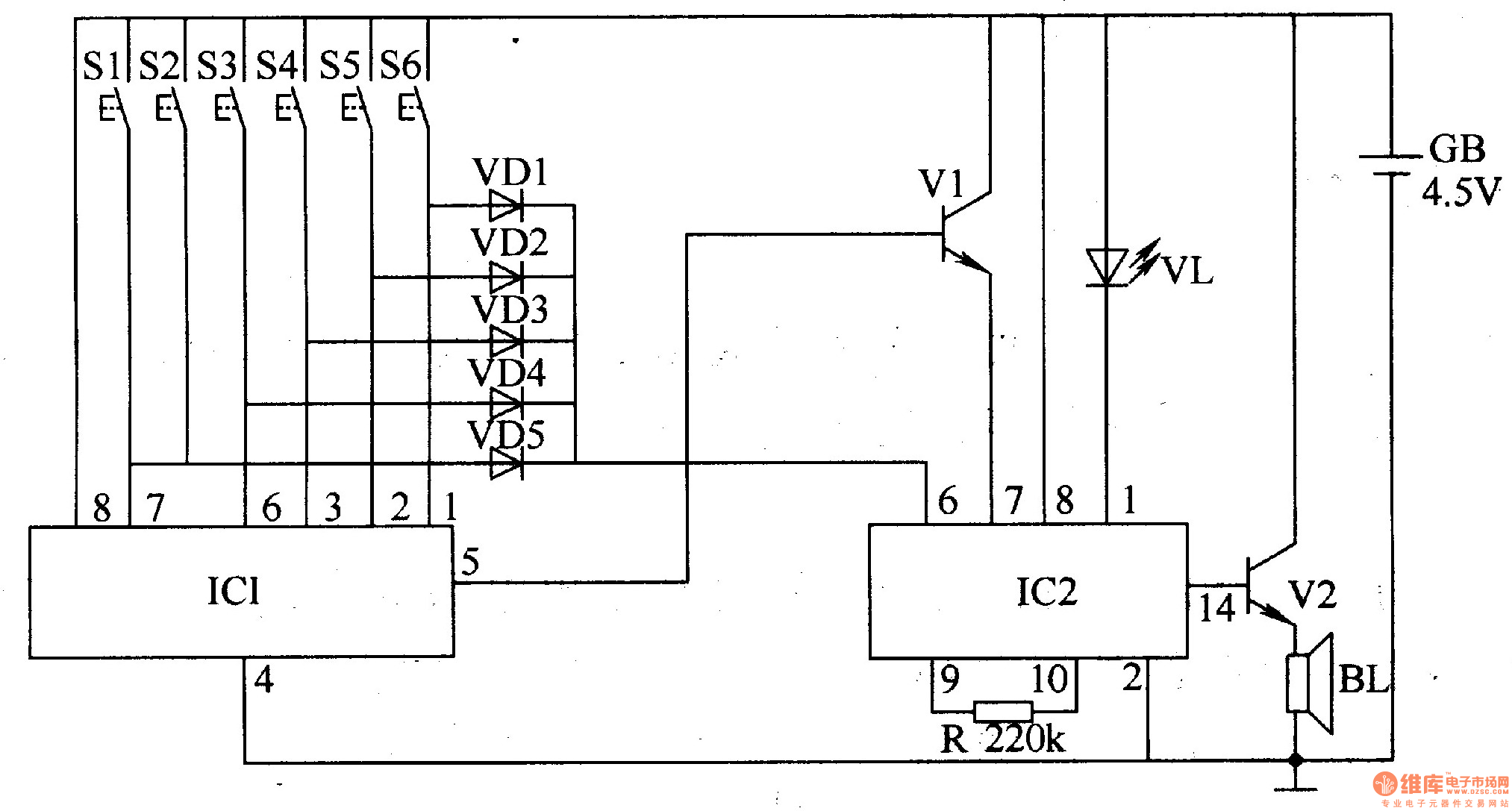
The three-tone electronic doorbell circuit includes buttons S1-S3, transistors V1 and V2, a speaker BL, resistors R1-R3, capacitors C1 and C2, a diode VD, and a battery GB, as illustrated in Figure 3-109. Resistors R1-R3 are 1/4W carbon film or metal film types. Capacitor C1 is an electrolytic capacitor rated for 16V, while C2 can be a monolithic or polyester capacitor. The diode VD may be a 2AP9 germanium diode or a 1N4148 silicon switching diode. Transistor V1 can be a 3DG6 or S9013 silicon NPN type, and transistor V2 can be a 3AX31 germanium PNP type.
The three-tone electronic doorbell circuit is designed to produce distinct sound tones based on the button pressed. The circuit utilizes three buttons (S1, S2, S3) that, when activated, trigger different sound outputs through the speaker (BL). Each button corresponds to a specific tone, achieved by altering the circuit's configuration through the transistors (V1 and V2).
Transistor V1, which can be either a 3DG6 or S9013 silicon NPN type, is responsible for amplifying the signal generated when a button is pressed. Similarly, transistor V2, which can be a 3AX31 germanium PNP type, helps to manage the power supply to the speaker, ensuring that the sound output is both loud and clear.
The resistors (R1-R3) are critical for controlling current flow within the circuit, and their specifications as 1/4W carbon film or metal film types ensure reliability and stability during operation. Capacitor C1, rated for 16V, is an electrolytic capacitor that provides necessary filtering and stabilization, while C2, which can be a monolithic or polyester capacitor, aids in the timing and tone generation aspects of the circuit.
The diode (VD), which can be a 2AP9 germanium diode or a 1N4148 silicon switching diode, serves as a protective component, allowing current to flow in one direction and preventing potential damage to the circuit from reverse polarity.
Overall, this circuit is a practical application of basic electronic components, providing an engaging and functional doorbell solution with customizable sound options. Proper selection and integration of these components are essential for achieving the desired performance and longevity of the doorbell system.The three-tone electronic doorbell circuit consists of buttons Sl-S3, transistors Vl, V2, speaker BL, resistors Rl-R3, capacitors Cl, C2, diode VD and battery GB, and it is shown in Figure 3-109. Rl-R3 use the 1/4W carbon film resistors or metal film resistors. Cl uses the electrolytic capacitor with voltage in 16V; C2 uses the monolithic capacito rs or polyester capacitors. VD uses the 2AP9 germanium ordinary diode or 1N4148 silicon switching diode. Vl uses the 3DG6 or S9013 silicon NPN transistor; V2 uses the 3AX31 germanium PNP transistor. 🔗 External reference
The three-tone electronic doorbell circuit is designed to produce distinct sound tones based on the button pressed. The circuit utilizes three buttons (S1, S2, S3) that, when activated, trigger different sound outputs through the speaker (BL). Each button corresponds to a specific tone, achieved by altering the circuit's configuration through the transistors (V1 and V2).
Transistor V1, which can be either a 3DG6 or S9013 silicon NPN type, is responsible for amplifying the signal generated when a button is pressed. Similarly, transistor V2, which can be a 3AX31 germanium PNP type, helps to manage the power supply to the speaker, ensuring that the sound output is both loud and clear.
The resistors (R1-R3) are critical for controlling current flow within the circuit, and their specifications as 1/4W carbon film or metal film types ensure reliability and stability during operation. Capacitor C1, rated for 16V, is an electrolytic capacitor that provides necessary filtering and stabilization, while C2, which can be a monolithic or polyester capacitor, aids in the timing and tone generation aspects of the circuit.
The diode (VD), which can be a 2AP9 germanium diode or a 1N4148 silicon switching diode, serves as a protective component, allowing current to flow in one direction and preventing potential damage to the circuit from reverse polarity.
Overall, this circuit is a practical application of basic electronic components, providing an engaging and functional doorbell solution with customizable sound options. Proper selection and integration of these components are essential for achieving the desired performance and longevity of the doorbell system.The three-tone electronic doorbell circuit consists of buttons Sl-S3, transistors Vl, V2, speaker BL, resistors Rl-R3, capacitors Cl, C2, diode VD and battery GB, and it is shown in Figure 3-109. Rl-R3 use the 1/4W carbon film resistors or metal film resistors. Cl uses the electrolytic capacitor with voltage in 16V; C2 uses the monolithic capacito rs or polyester capacitors. VD uses the 2AP9 germanium ordinary diode or 1N4148 silicon switching diode. Vl uses the 3DG6 or S9013 silicon NPN transistor; V2 uses the 3AX31 germanium PNP transistor. 🔗 External reference