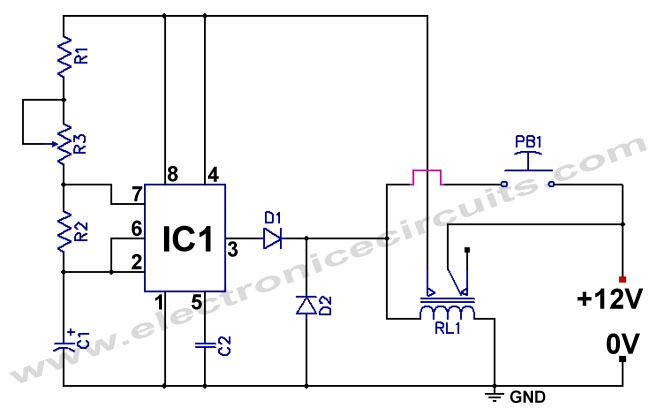
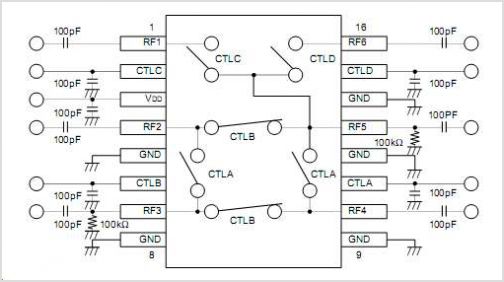
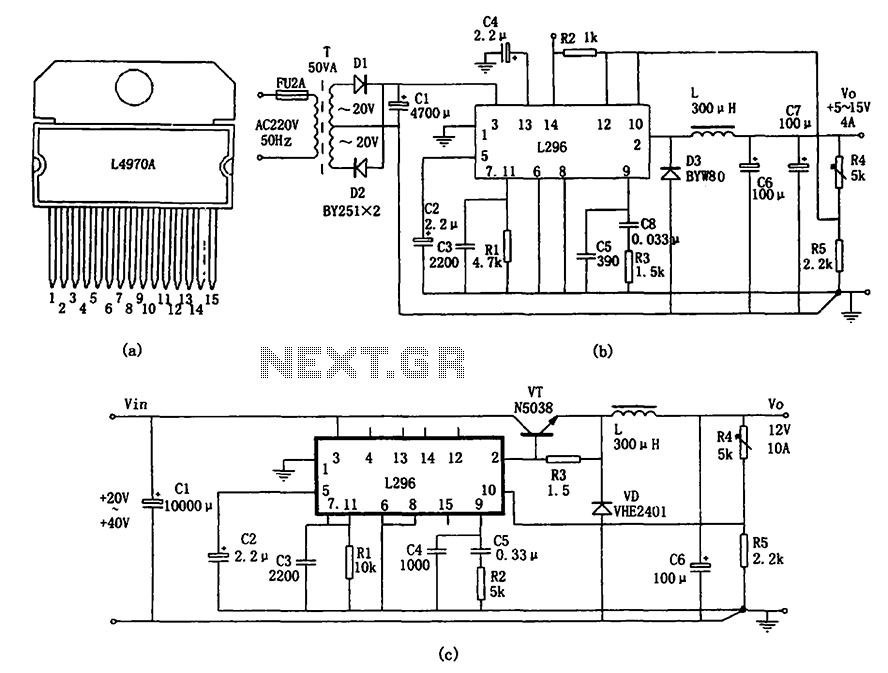
Touch Switch Monostable/Timer with 555 IC
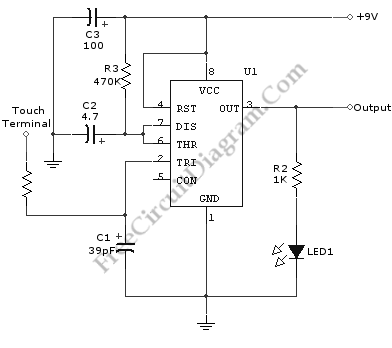
A schematic diagram of a touch switch circuit is presented. This circuit comprises a timer, a one-shot multivibrator, and a touch terminal. The timer utilized in this circuit is a 555 timer, which is connected to the one-shot multivibrator. The touch terminal serves as the trigger for this circuit. The output can be employed to drive a power transistor, CMOS circuitry, hexFET transistor, or optocoupler. According to the schematic diagram, the circuit has a timed ON period of 4 seconds. The values of C2 and R3 determine the ON time; increasing the values of C2 or R3 will extend the ON time, whereas decreasing these values will shorten the ON time.
The touch switch circuit operates by utilizing the 555 timer in monostable mode, where the timer generates a single pulse when triggered by the touch terminal. The touch terminal acts as a momentary switch that, when activated, sends a signal to the timer, initiating the timing sequence. The one-shot multivibrator, connected to the 555 timer, ensures that a single output pulse is generated for a predetermined duration, defined by the resistor (R3) and capacitor (C2) values.
The output of the circuit can be interfaced with various components such as power transistors, CMOS circuitry, hexFET transistors, or optocouplers, allowing for a wide range of applications, including LED control, relay activation, or other electronic device management. The selection of the output stage component depends on the required load current and voltage specifications.
The timing characteristics of the circuit are governed by the formula: T = 1.1 * R3 * C2, where T is the time duration for which the output remains high. By adjusting the resistance of R3 or the capacitance of C2, the ON time can be finely tuned to meet specific application requirements. Increasing either component will result in a longer ON time, providing flexibility in the design and functionality of the touch switch circuit. Conversely, reducing the values will decrease the ON time, allowing for quicker response times in applications where rapid switching is desirable.
Overall, this touch switch circuit exemplifies a versatile and efficient method for controlling electronic devices through a simple touch interface, leveraging the reliable performance of the 555 timer and the configurability of passive components.A schematic diagram of a touch switch circuit is shown below. This circuit consist of timer, one shoot multivibrator and touch terminal. As timer, this circuit uses 555 timer which is connected to one-shot multivibrator. The touch terminal is used to trigger this circuit. The output of this circuit can be used to drive a power transistor, CMOS ci rcuitry, hexFET transistor or optocoupler. Here is the schematic diagram of the touch switch circuit: Using the given values as shown in the schematic diagram, this circuit has timed ON period of 4 seconds. The value of C2 and R3 determines the ON time, increasing the value of C2 or R3 will increase the ON time.
The ON time is decreased if the value of C2 or R3 is decreased. 🔗 External reference
The touch switch circuit operates by utilizing the 555 timer in monostable mode, where the timer generates a single pulse when triggered by the touch terminal. The touch terminal acts as a momentary switch that, when activated, sends a signal to the timer, initiating the timing sequence. The one-shot multivibrator, connected to the 555 timer, ensures that a single output pulse is generated for a predetermined duration, defined by the resistor (R3) and capacitor (C2) values.
The output of the circuit can be interfaced with various components such as power transistors, CMOS circuitry, hexFET transistors, or optocouplers, allowing for a wide range of applications, including LED control, relay activation, or other electronic device management. The selection of the output stage component depends on the required load current and voltage specifications.
The timing characteristics of the circuit are governed by the formula: T = 1.1 * R3 * C2, where T is the time duration for which the output remains high. By adjusting the resistance of R3 or the capacitance of C2, the ON time can be finely tuned to meet specific application requirements. Increasing either component will result in a longer ON time, providing flexibility in the design and functionality of the touch switch circuit. Conversely, reducing the values will decrease the ON time, allowing for quicker response times in applications where rapid switching is desirable.
Overall, this touch switch circuit exemplifies a versatile and efficient method for controlling electronic devices through a simple touch interface, leveraging the reliable performance of the 555 timer and the configurability of passive components.A schematic diagram of a touch switch circuit is shown below. This circuit consist of timer, one shoot multivibrator and touch terminal. As timer, this circuit uses 555 timer which is connected to one-shot multivibrator. The touch terminal is used to trigger this circuit. The output of this circuit can be used to drive a power transistor, CMOS ci rcuitry, hexFET transistor or optocoupler. Here is the schematic diagram of the touch switch circuit: Using the given values as shown in the schematic diagram, this circuit has timed ON period of 4 seconds. The value of C2 and R3 determines the ON time, increasing the value of C2 or R3 will increase the ON time.
The ON time is decreased if the value of C2 or R3 is decreased. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713