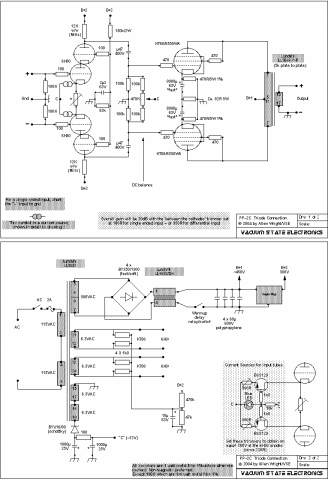
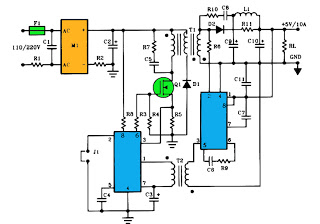
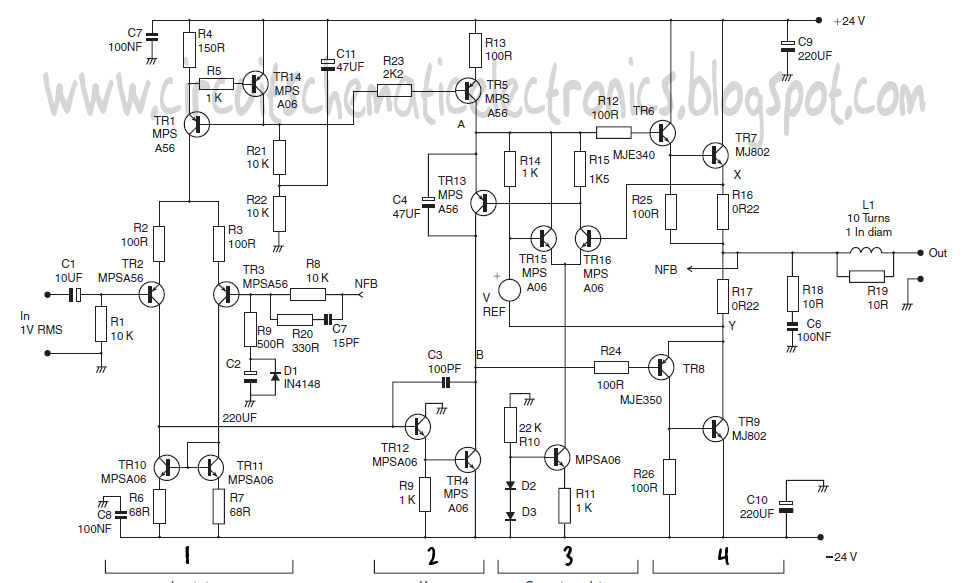
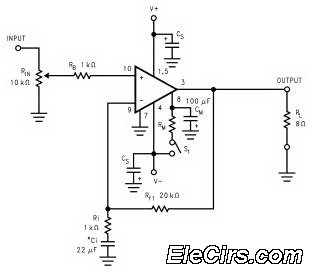
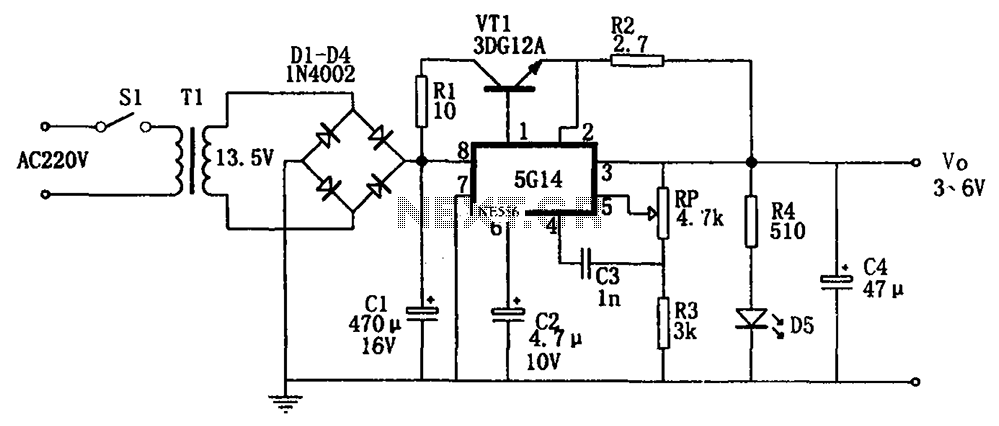
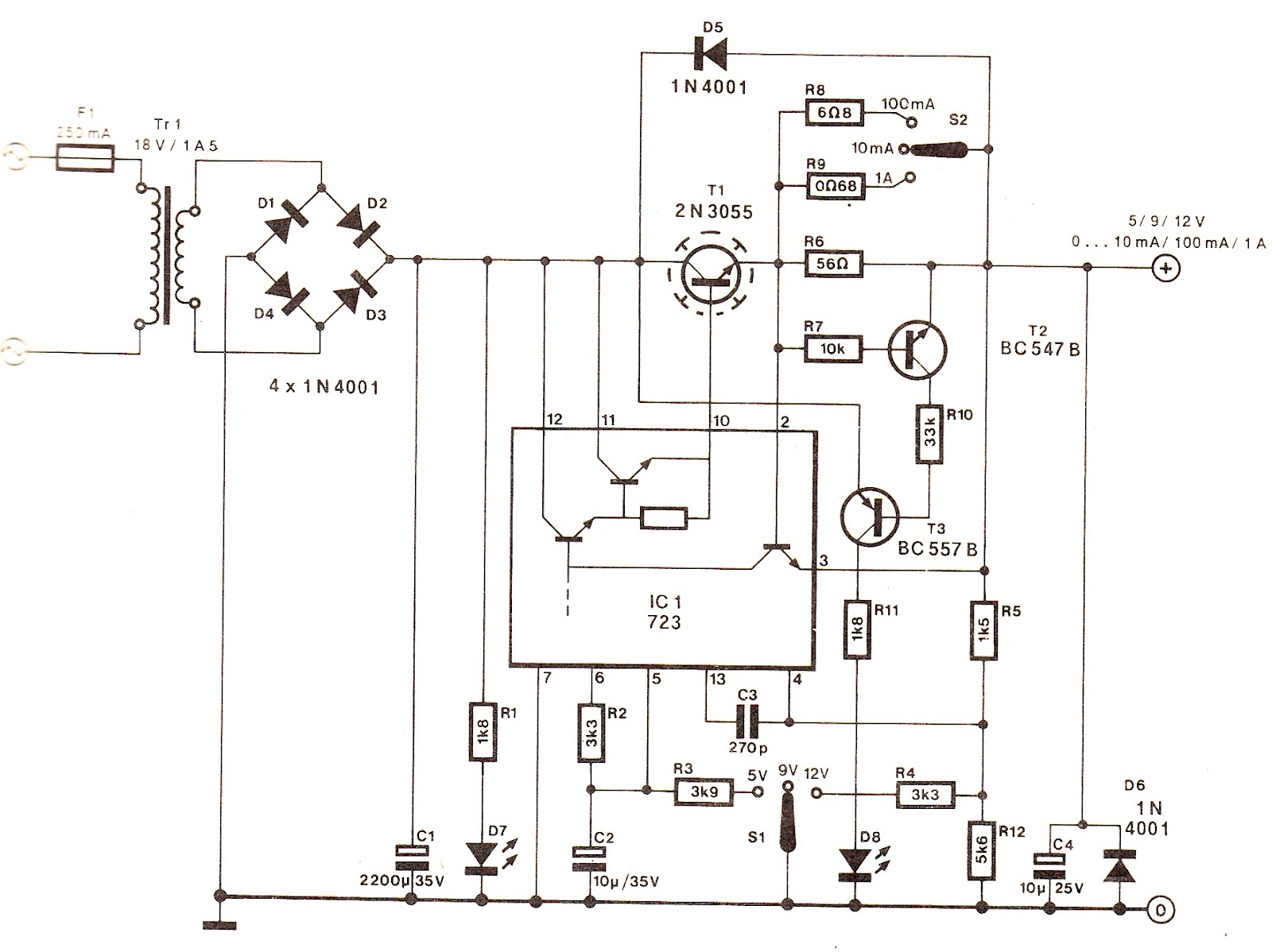
Triple Power Supply
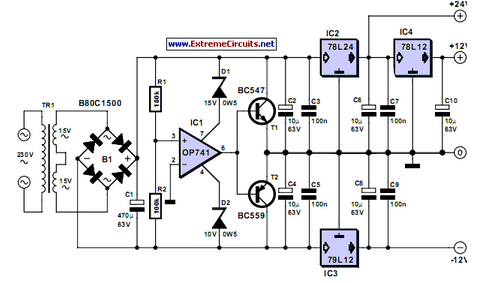
Inexpensive miniature transformers typically offer one or two secondary voltages, which are adequate for producing a set of positive and negative supply voltages.
Miniature transformers are compact devices commonly utilized in various electronic applications, particularly in power supply circuits. These transformers are designed to convert alternating current (AC) voltage from the primary side to one or two lower voltages on the secondary side. The ability to provide both positive and negative voltage outputs makes these transformers particularly valuable in applications such as operational amplifier circuits, analog signal processing, and other electronic systems requiring dual supply voltages.
The construction of miniature transformers usually involves a core made from magnetic materials, which enhances the efficiency of magnetic coupling between the primary and secondary windings. The number of turns in each winding determines the voltage transformation ratio, which is critical for achieving the desired output voltages. It is essential to select a transformer with appropriate ratings for current and voltage to ensure reliable operation and prevent overheating.
In practical applications, these transformers are often used in conjunction with rectifiers and voltage regulators to produce stable DC voltages from the AC output. The rectification process typically involves using diodes to convert AC to pulsating DC, followed by filtering capacitors to smooth the output. The resulting DC voltage can then be further regulated to meet specific voltage requirements.
Miniature transformers are widely available and cost-effective, making them an ideal choice for hobbyists and professionals alike when designing compact electronic circuits that require dual power supplies. Their versatility and ease of integration into various designs contribute to their popularity in the electronics industry.Inexpensive miniature transformers normally provide one or two secondary voltages, which is sufficient for generating a set of positive and negative suppl.. 🔗 External reference
Miniature transformers are compact devices commonly utilized in various electronic applications, particularly in power supply circuits. These transformers are designed to convert alternating current (AC) voltage from the primary side to one or two lower voltages on the secondary side. The ability to provide both positive and negative voltage outputs makes these transformers particularly valuable in applications such as operational amplifier circuits, analog signal processing, and other electronic systems requiring dual supply voltages.
The construction of miniature transformers usually involves a core made from magnetic materials, which enhances the efficiency of magnetic coupling between the primary and secondary windings. The number of turns in each winding determines the voltage transformation ratio, which is critical for achieving the desired output voltages. It is essential to select a transformer with appropriate ratings for current and voltage to ensure reliable operation and prevent overheating.
In practical applications, these transformers are often used in conjunction with rectifiers and voltage regulators to produce stable DC voltages from the AC output. The rectification process typically involves using diodes to convert AC to pulsating DC, followed by filtering capacitors to smooth the output. The resulting DC voltage can then be further regulated to meet specific voltage requirements.
Miniature transformers are widely available and cost-effective, making them an ideal choice for hobbyists and professionals alike when designing compact electronic circuits that require dual power supplies. Their versatility and ease of integration into various designs contribute to their popularity in the electronics industry.Inexpensive miniature transformers normally provide one or two secondary voltages, which is sufficient for generating a set of positive and negative suppl.. 🔗 External reference