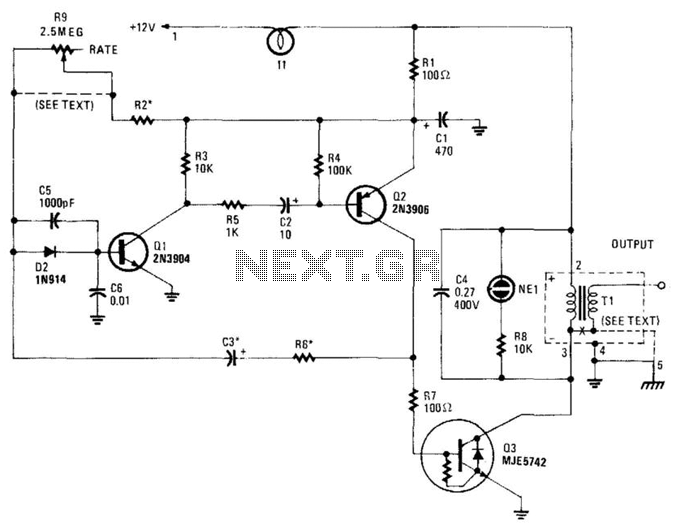
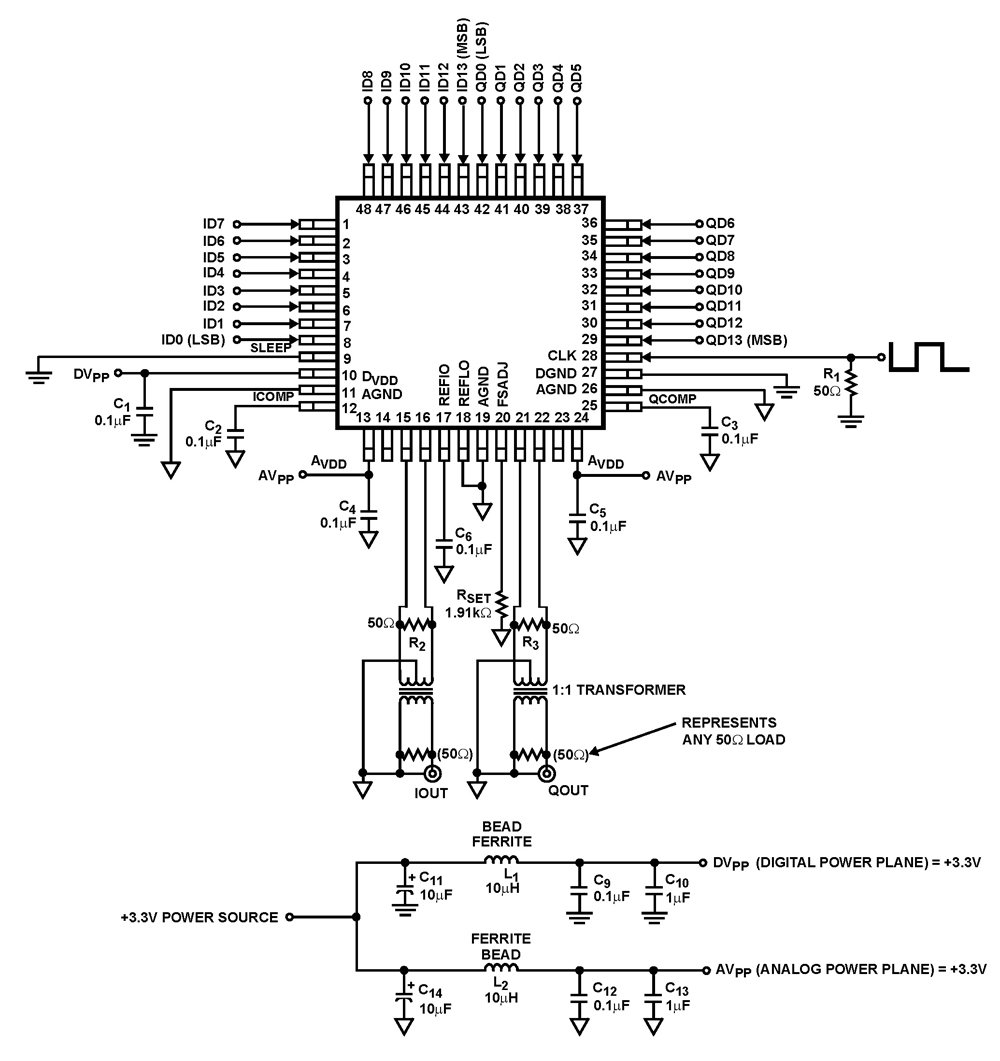
Tube Amplifier Isolates High Voltages
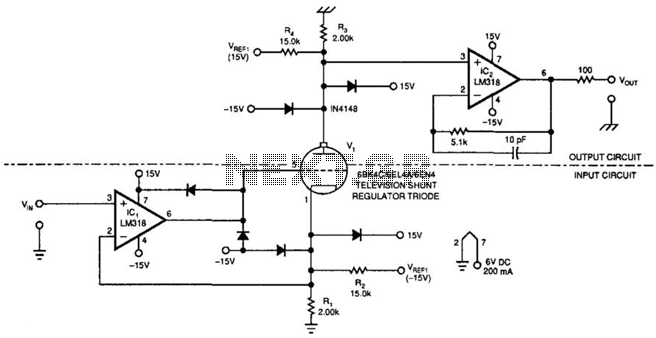
This amplifier can transfer DC to 5 MHz signals across a potential difference of 25,000 V. It can be utilized in CRT displays and high-voltage applications. It is important to note that the tube must be shielded due to X-ray generation. Typically, a sheet metal thickness of about 0.1 inches would be used for this purpose.
The described amplifier is designed for high-frequency signal amplification, capable of handling a wide range of frequencies from direct current (DC) up to 5 megahertz (MHz). This capability makes it suitable for various applications, including cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, where precise signal transmission is critical for image clarity and performance. The amplifier's ability to operate at a high potential difference of 25,000 volts indicates its robustness in high-voltage environments, which is essential for certain industrial and scientific applications.
In terms of safety, the mention of X-ray generation necessitates the implementation of adequate shielding measures to protect users and surrounding equipment from harmful radiation. A shielding solution typically involves the use of a 0.1-inch thick sheet metal enclosure, which effectively absorbs and contains the X-rays produced during operation. The choice of material for the shielding should consider factors such as electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and mechanical strength to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Overall, the amplifier's design must incorporate not only the electrical specifications but also the necessary safety features to mitigate the risks associated with high-voltage operation and radiation emission. Proper installation and maintenance protocols should also be established to ensure optimal performance and safety during operation. This amplifier can transfer dc-to 5-MHz signals across a potential difference of 25 000 V. This circu it can be used in CRT displays, high-voltage applications, etc. Notice that the tube must be shielded because the tube will generate X-rays. Typically, about 0.1 "-thick sheet metal would be used. 🔗 External reference
The described amplifier is designed for high-frequency signal amplification, capable of handling a wide range of frequencies from direct current (DC) up to 5 megahertz (MHz). This capability makes it suitable for various applications, including cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, where precise signal transmission is critical for image clarity and performance. The amplifier's ability to operate at a high potential difference of 25,000 volts indicates its robustness in high-voltage environments, which is essential for certain industrial and scientific applications.
In terms of safety, the mention of X-ray generation necessitates the implementation of adequate shielding measures to protect users and surrounding equipment from harmful radiation. A shielding solution typically involves the use of a 0.1-inch thick sheet metal enclosure, which effectively absorbs and contains the X-rays produced during operation. The choice of material for the shielding should consider factors such as electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and mechanical strength to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Overall, the amplifier's design must incorporate not only the electrical specifications but also the necessary safety features to mitigate the risks associated with high-voltage operation and radiation emission. Proper installation and maintenance protocols should also be established to ensure optimal performance and safety during operation. This amplifier can transfer dc-to 5-MHz signals across a potential difference of 25 000 V. This circu it can be used in CRT displays, high-voltage applications, etc. Notice that the tube must be shielded because the tube will generate X-rays. Typically, about 0.1 "-thick sheet metal would be used. 🔗 External reference